tb62209f TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION, tb62209f Datasheet
tb62209f
Available stocks
Related parts for tb62209f
tb62209f Summary of contents
Page 1
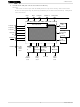
... TOSHIBA BiCD Processor IC Silicon Monolithic Preliminary Stepping Motor Driver IC Using PWM Chopper Type The TB62209F is a stepping motor driver driven by chopper micro-step pseudo sine wave. The TB62209F integrates a decoder for CLK input in micro steps as a system to facilitate driving a two-phase stepping motor using micro-step pseudo sine waves ...
Page 2
... Ccp B Pump Unit Ccp A MDT 1 MDT 2 4-bit DA (sine angle control) Output control R S COMP 1 (Mixed Decay control COMP 2 STANDBY Output (H-bridge) × 2 ENABLE Stepping Moter 2 TB62209F Chopper OSC CR OCS CR-CLK converter ISD TSD TSD V /V DDR protect M DD ...
Page 3
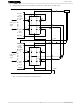
... Micro-step Phase × 2 bits current data × 1 bit B unit side × 4 bits B unit side B unit side Mixed DA circuit Decay circuit 3 TB62209F Decay × 2 bits A unit side Micro-step current data × 4 bits A unit side Phase × 1 bit A unit side Output control circuit ...
Page 4
... Chopping reference circuit Output stop signal (ALL OFF) <Use in Charge mode> COMP circuit NF 1 (set current (Note 1) reached signal) RNF R S COMP (set current circuit monitor signal) 2 (Note 2) <Use in FAST MODE> 4 TB62209F CR Mixed Decay timing circuit Output control circuit 2001-09-05 ...
Page 5
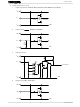
... Charge pump halt signal Internal Charge stop pump signal circuit select circuit Mixed Decay timing table clear signal LOGIC 5 TB62209F Chopping reference circuit Mixed Decay timing circuit Output circuit V M Power supply for upper drive output Output circuit V H Cop A Cop B ...
Page 6
... From output U2 control L1 circuit L2 L1 Output driver circuit Phase B Note: The diode on the dotted line is parasitic diode Output A L2 Output Output B L2 Output B PGND 6 TB62209F 2001-09-05 ...
Page 7
... Input circuit (CLK, TORQUE, MDT, CW/CCW, DATA MODE, Decay Mode Input circuit ( RESET , ENABLE, STANDBY input circuit ref Output circuit (MO, PROTECT OUT V SS 150 Ω To Logic IC GND 150 Ω To Logic IC GND 2 150 Ω GND 7 TB62209F To DA circuit GND 2001-09-05 ...
Page 8
... CW/CCW → GB− (OUT Note: Pin assignment above is different at data mode and PWM CLK 34 ENABLE 33 OUT B 32 RESET 31 DATA MODE OUT B 28 PGND TB62209F ( PGND 26 OUT MDT 2 23 MDT 1 22 OUT A 21 TORQUE2 20 TORQUE1 19 PROTECT 8 TB62209F 2001-09-05 ...
Page 9
... Not wired Connect current sensing resistor between this pin and Connect to power ground. The pin functions as a heat sink. Design pattern taking heat into consideration. Connect current sensing resistor between this pin and Not wired Not wired 9 TB62209F Remarks 2001-09-05 ...
Page 10
... In 2-Phase Excitation mode, outputs High level with electrical angle of 0° (phase B: 100%, phase A: 100%). Detects thermal shut down (TSD) and outputs High level. Torque HH: 100% MDT HH: 100% HL: 75% LH: 37.5% LL: 12.5% 10 TB62209F Remarks are generated. DD LH: 85% HL: 70% LL: 50% 2001-09-05 ...
Page 11
... At this time we recommend ENABLE pin be set to Low to prevent misoperation. H: Resets electrical angle. L: Normal operation Forcibly turns all output transistors off. Electrical angle is incremented by one for each CLK input. CLK is reflected at rising edge. Determines chopping frequency. 11 TB62209F Remarks to GND. SS 2001-09-05 ...
Page 12
... For example, used to change the excitation mode to another drive mode during output from MO (electrical angle = 0°). Input Function H Initializes electrical angle to 0° L Normal operation Function 12.5% Mixed Decay mode 37.5% Mixed Decay mode 75% Mixed Decay mode 100% Mixed Decay mode (Fast Decay mode) Comparator Reference Voltage 100% 85% 70% 50% 12 TB62209F 2001-09-05 ...
Page 13
... Locks only at 0° electrical angle 45° → 135° → 225° → 315° → 45° Low-torque, 1-bit micro-step change 0 0 High-torque, 1-bit micro-step change 0 1 2-bit micro-step change 1 0 3-bit micro-step change 1 1 4-bit micro-step change 13 TB62209F Remarks Standby mode 2001-09-05 ...
Page 14
... Note 2: Where 100% and IA = 0%, the electrical angle is 0°. Where and IA = 100%, the electrical angle is +90°. IA (%) Remarks 0 Electrical angle incremented but no current output Electrical angle incremented but no motor rotation 0 due output 100 45° 0 0° 0 0° 0 0° 0 0° 0 0° 14 TB62209F 2001-09-05 ...
Page 15
... D MODE 3 → GB+ (OUT CW/CCW → GB− (OUT GA− Output State L Output off H A+ phase: Low A− phase: High L A+ phase: High A− phase: Low H Output off ( OFF ON (Note) Load L1 L2 OFF OFF ON PGND 15 TB62209F ( OFF ON (Note) Load PGND 2001-09-05 ...
Page 16
... OUT (1) V 5.0 V CLK 5.0 V chop Torque = 100% ref 5 120°C, recommended maximum current usage is below 120° TB62209F Min Typ. Max Unit 4.5 5.0 5 1.2 1.5 A GND 1.0 150 KHz 50 ...
Page 17
... (D- 25°C, Source-Drain j 1 5.0 V OUT (D- 105°C, Drain-Source 1 5.0 V OUT (D- 105°C, Source-Drain j 17 TB62209F = = = = Min Typ. Max Unit 0.4 V GND GND 0.8 − 0.4 200 400 700 mV 1.0 35 ...
Page 18
... Vector θ (θ8) θ (θ7) θ (θ6) θ (θ5) θ (θ4) θ (θ3) θ (θ2) θ (θ1) θ (θ0) 18 TB62209F = = = = 1.0 A) OUT Min Typ. Max Unit 100 100 ...
Page 19
... TSD = operating condition TSD = not operating condition electrical angle = except 0° 12 (IB = 100 Except 0% set electrical angle = 0° (IB = 100 0%) 19 TB62209F = = = = Min Typ. Max Unit 2 µA 1/4.8 1/5.0 1/5.2 ...
Page 20
... Ccp2 = 0.01 µF Output ACTIVE (I = 1.0 A), OUT f chop CR CLK = 800 kHz Ccp = 0.22 µF, Ccp = 0.01 µF t ONG M DD STANDBY = ON → OFF 20 TB62209F Min Typ. Max Unit 120 kHz 100 50 µs 50 ...
Page 21
At constant current control, in current amplitude (pulsating current) Decay mode, a point from can be set using 2-bit parallel data the point where the output current reaches the set current value. RNF is the ...
Page 22
Current value in increasing (Sine wave) • Sine wave in decreasing (When using MIXED DECAY Mode with large attenuation ratio (MDT%) at attenuation) Sine wave in decreasing (When using MIXED DECAY Mode ...
Page 23
When NF is after MIXED DECAY TIMING • In MIXED DECAY MODE, when the output current > the set current value • ...
Page 24
The output current to the motor is in supply voltage mode after the current value set by V Torque reached at the set current value. → ref RS ...
Page 25
When CLK signal is input, the chopping counter (CR-CLK counter) is forced to reset at the next CR-CLK timing. Because of this, compared with a method in which the counter is not reset, response to the input data is ...
Page 26
¸ ...
Page 27
¸ ...
Page 28
¸ ...
Page 29
In Slow Mode, when all output transistors are forced to switch off, coil energy is discharged in the following MODES: As shown in the figure at right, an output transistor has parasitic diodes. To discharge energy from the coil, each ...
Page 30
...
Page 31
= = ...
Page 32
... V and torque = 100% to output I ref or more) is required. At constant current control, this IC chops frequency using the oscillation waveform (saw tooth waveform) determined by external capacitor and resistor as a reference. The TB62209F requires an oscillation frequency of eight times the chopping frequency. The oscillation frequency is calculated as follows ...
Page 33
...
Page 34
OSC-charge delay: Because the rising edge level of the OSC waveform is used for converting the OSC waveform to the internal CR CLK, a delay 1.25 ns (@f waveform and the internal CR CLK. = 100 kHz: ...
Page 35
If drive mode input changes before MO timing • Parallel set signal is reflected. If drive mode input changes after MO timing • Parallel set signal occurs after the rising edge of CLK, therefore not reflected. The drive ...
Page 36
Other parallel set signals can be changed at any time (they are reflected immediately). = ...
Page 37
HSOP36 R only (96°C/W) th (j-a) (2) When mounted on the board (140 mm × × 1.6 mm: 38°C/W: typ.) ...
Page 38
= = µ = µ ...
Page 39
Initial charging • (1) When RESET is released Di1. ( turned OFF turned ON, and Ccp 1 is charged from Ccp 2 via Di2 (3) When the voltage difference between V ...
Page 40
Time taken for capacitor Ccp 2 (charging capacitor) to fill up Ccp 1 (storing capacitor reset is released. The internal IC cannot drive the gates correctly until the voltage of Ccp 1 reaches V ...
Page 41
When driving the stepping motor with and 1.5 A, the logical values for Ccp 1 and Ccp 2 are as shown in the graph below: Choose Ccp 1 and Ccp combined from the ...
Page 42
Low Power Dissipation mode Low Power Dissipation mode turns off phases A and B, and also halts the charge pump. Operation is the same as that when the STANDBY pin is set to Low. (2) Motor Lock mode Motor ...
Page 43
Phase Excitation mode (a) − Electrical angle 360° CLKs ...
Page 44
Phase Excitation mode (b) − − Electrical angle 360° CLKs ...
Page 45
W1-2 Phase Excitation mode − − − − Electrical angle 360° CLKs ...
Page 46
Phase Excitation mode − − − − − − − − Electrical angle 360° CLKs ...
Page 47
Phase Excitation mode − − − − − − − − − − − − − − − Electrical angle 360° CLKs ...
Page 48
For input data, see the current function examples ° ° ° ° θ = θ = ...
Page 49
The values for the devices are all recommended values. For values under each input condition, see the above-mentioned recommended operating conditions. = Ω = µ Because there may be shorts between outputs, shorts to supply, or shorts to ground, be ...
Page 50
...
Page 51
• • • • • ...