se98pw NXP Semiconductors, se98pw Datasheet
se98pw
Available stocks
Related parts for se98pw
se98pw Summary of contents
Page 1
... To maintain interchangeability with the I specified with the operating voltage of 3 3.6 V. DIMM applications normally use the C-grade accuracy SE98PW or SE98TK temp sensor. For applications requiring the higher B-grade accuracy, the SE98PW/1 or SE98TK/1 is available. 2 C-bus temperature sensor 2 C-bus/SMBus ...
Page 2
... I Enterprise networking I Hard disk drives and other PC peripherals 4. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Type number Topside Package mark Name SE98PW SE98 TSSOP8 SE98TK SE98 HVSON8 SE98_2 Product data sheet 2 C-bus/SMBus compatible 400 kHz 0 (typ./max (typ./max.) + +125 (typ ...
Page 3
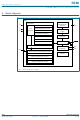
... NXP Semiconductors 5. Block diagram Fig 1. Block diagram of SE98 SE98_2 Product data sheet SE98 REGISTERS CRITICAL TEMPERATURE LIMIT UPPER TEMPERATURE LIMIT LOCK PROTECT LOWER TEMPERATURE LIMIT HYSTERESIS THRESHOLD MANUFACTURER ID DEVICE ID DEVICE CAPABILITY REGISTER CONFIGURATION REGISTER EVENT OUTPUT COMPARATOR/INT MODE EVENT OUTPUT POLARITY ...
Page 4
... In general, application the A0 pin would not damage the pin, but NXP Semiconductors does not guarantee the overvoltage for this pin. SE98_2 Product data sheet SO-DIMM SMBus EVENT SE98PW 3 6 SCL 4 5 SDA 002aab806 Pin description Pin Type Description ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors 7. Functional description 7.1 Serial bus interface The SE98 uses the 2-wire serial bus (I controller. The serial bus consists of a clock (SCL) and data (SDA) signals. The device can operate on either the I mode is defined to have bus speeds from 100 kHz 400 kHz, and the SMBus is from 10 kHz to 100 kHz ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors temperature ( C) critical Upper Boundary Alarm alarm window Lower Boundary Alarm (1) EVENT in Interrupt mode (1) EVENT in Comparator mode software interrupt clear (1) EVENT in ‘Critical Temp only’ mode (1) EVENT pin shown here is active LOW. It can be programmed to be active HIGH. Fig 5. EVENT output for ‘Interrupt’, ‘Comparator’, and ‘Critical Temp only’ modes 7 ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors 7.5 Power-up default condition After power-on, the SE98 is initialized to the following default condition: • Starts monitoring local sensor • EVENT register is cleared—EVENT output is pulled HIGH by external pull-ups • EVENT hysteresis is defaulted • Command pointer is defaulted to ‘00h’ • ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors 7.8 SMBus Alert The SE98 supports SMBus Alert when it is programmed for the Interrupt mode and when the EVENT polarity bit is set to logic 0. The EVENT pin can be ANDed with other EVENT or ALERT signals from other slave devices to signal their intention to communicate with the host controller ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors The data byte has the most significant bit first. At the end of a read, this device can accept either Acknowledge (ACK Acknowledge (NACK) from the Master (No Acknowledge is typically used as a signal for the slave that the Master has read its last byte). It takes this device 125 ms to measure the temperature ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors SCL SDA S START device address and write by host SCL SDA SR device address and read repeated START by host SCL D15 D14 D13 D12 SDA returned most significant byte data A = ACK = Acknowledge bit Not Acknowledge bit Write bit = Read bit = 1. ...
Page 11
... NXP Semiconductors 8. Register descriptions 8.1 Register overview This section describes all the registers used in the SE98. The registers are used for latching the temperature reading, storing the low and high temperature limits, configuring, the hysteresis threshold and the ADC, as well as reporting status. The device uses the Pointer register to access these registers ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors 8.2 Capability register (00h, 16-bit read-only) Table 5. Capability register (address 00h) bit allocation Bit 15 Symbol Reset 0 Access R Bit 7 Symbol RFU[2:0] Reset 0 Access R Table 6. Bit 15:5 4 SE98_2 Product data sheet RFU[10: TRES[1: Capability register (address 00h) bit description ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors 8.3 Configuration register (01h, 16-bit read/write) Table 7. Configuration register (address 01h) bit allocation Bit 15 Symbol Default 0 Access R Bit 7 Symbol CTLB AWLB Default 0 Access R/W R/W Table 8. Bit 15:11 10:9 8 SE98_2 Product data sheet RFU CEVNT ESTAT ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors Table 8. Bit SE98_2 Product data sheet Configuration register (address 01h) bit description Symbol Description CTLB Critical Trip Lock bit. 0 — Critical Alarm Trip register is not locked and can be altered (default). 1 — Critical Alarm Trip register settings cannot be altered. ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors Table 9. Action sets clears Above Critical Trip Above Alarm Window Below Alarm Window Fig 11. Hysteresis: how it works SE98_2 Product data sheet Hysteresis Enable Below Alarm Window Bit (bit 13) Temperature Threshold slope temperature falling T th(low) rising T th(low) temperature critical alarm ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors 8.4 Temperature format The 16-bit value used in the following Trip Point Set and Temperature Read-Back registers is 2’s complement with the Least Significant Bit (LSB) equal to 0.0625 C. For example: • A value of 019Ch will represent 25.75 C • A value of 07C0h will represent 124 C • ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors 8.5.2 Lower Boundary Alarm Trip register (16-bit read/write) The value is the lower threshold temperature value for Alarm mode. The data format is 2’s complement with bit 2 = 0.25 C. RFU bits will always report zero. Interrupts will respond to the presently programmed boundary values. If boundary values are being altered in-system advised to turn off interrupts until a known state can be obtained to avoid superfl ...
Page 18
... Reset Access Table 17. Bit 11:1 0 8.7 Manufacturer’s ID register (16-bit read-only) The manufacture’s ID matches that assigned to NXP Semiconductors PCI SIG (1131h), and is intended for use to identify the manufacturer of the device. Table 18. Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access SE98_2 ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors 8.8 Device ID register The device ID and device revision are A1h and 00h, respectively. Table 19. Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access 8.9 SMBus register Table 20. Bit Symbol Reset Access Bit Symbol Reset Access Table 21. Bit 15:8 7 6:1 0 SE98_2 Product data sheet ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors 9. Application design-in information In a typical application, the SE98 behaves as a slave device and interfaces to the master (or host) via the SCL and SDA lines. The host monitors the EVENT output pin, which is asserted when the temperature reading exceeds the programmed values in the alarm registers. The A0, A1 and A2 pins are directly connected to the shared SPD’ ...
Page 21
... sink V esd T j(max) T stg [1] In general, application the A0 pin would not damage the pin, but NXP Semiconductors does not guarantee the overvoltage for this pin. SE98_2 Product data sheet is the formula to calculate the effect of self-heating j ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors 11. Characteristics Table 23. Characteristics +125 C; unless otherwise specified. DD amb Symbol Parameter T temperature limit accuracy lim(acc) T temperature resolution res I average supply current DD(AV) I standby supply current DD(stb) T conversion period conv E conversion rate error f(conv) I leakage current L V supply voltage DD Table 24 ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors 300 I DD(AV 3 3.3 V 200 3.6 V 100 Fig 14. Supply current versus temperature 15.0 I OL(sink)EVENT_N (mA) 3.3 V 3.6 V 10.0 5 Fig 16. EVENT sink current at 0.4 V versus temperature Sample of 25 devices Fig 18. Temperature Error versus temperature SE98_2 Product data sheet ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors Table 25. SMBus AC characteristics +120 C; unless otherwise specified. These specifications are guaranteed by design. DD amb The AC specifications fully meet or exceed SMBus 2.0 specifications, but allow the bus to interface with the I to 400 kHz. Symbol ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Package outline TSSOP8: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 8 leads; body width 4 pin 1 index 1 e DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions UNIT max. 0.15 0.95 mm 1.1 0.25 0.05 0.85 Notes 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included. 2. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors HVSON8: plastic thermal enhanced very thin small outline package; no leads; 8 terminals; body 0. terminal 1 index area terminal 1 index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) (1) A UNIT max. 0.05 0 0.2 0.00 0.2 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Soldering This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description” . 13.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors 13.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 22. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description” . 14. Abbreviations Table 28. Acronym ADC ARA CDM DIMM HBM 2 I C-bus LSB MM MSB SO-DIMM POR ...
Page 30
... SE98_2 Product data sheet Data sheet status Product data sheet re-written re-written information”: removed type numbers SE98PW/1 and SE98TK/1 information”: ” to “V ”; changed pin name “GND” to “ Figure 2 “Pin configuration for TSSOP8” ...
Page 31
... Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document, including without limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without notice ...
Page 32
... NXP Semiconductors 18. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2.1 General features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2.2 Temperature sensor features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 6 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7.1 Serial bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7.2 Slave address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7.3 EVENT output 7.3.1 Alarm window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 7.3.2 Critical trip 7.4 Conversion rate ...