psd511b1 STMicroelectronics, psd511b1 Datasheet

psd511b1
Available stocks
Related parts for psd511b1
psd511b1 Summary of contents
Page 1
Low Cost Field Programmable Microcontroller Peripherals FEATURES SUMMARY Single Supply Voltage: – 5 V±10% for PSD5XX – 2.7 to 5.5 V for PSD5XX Mbit of UV EPROM Kbit SRAM Input Latches Programmable I/O ports ...
Page 2
Field-Programmable Microcontroller Peripherals 1 Introduction ...........................................................................................................................................................1 2 Key Features ........................................................................................................................................................3 3 Notation ................................................................................................................................................................4 4 ZPSD Background ................................................................................................................................................4 5 Integrated Power Management 6 Design Flow ..........................................................................................................................................................7 7 PSD5XX Family ....................................................................................................................................................8 8 Table 2. PSD5XX Pin Descriptions......................................................................................................................9 9 The PSD5XX Architecture ..................................................................................................................................11 ...
Page 3
Field-Programmable Microcontroller Peripherals 9.5 Power Management Unit ............................................................................................................................58 9.5.1 Standby Mode ..................................................................................................................................58 9.5.2 Power Down .....................................................................................................................................58 9.5.3 Sleep Mode ......................................................................................................................................58 9.5.4 Other Power Saving Options ............................................................................................................61 9.6 PSD5XX Counter/Timer ..............................................................................................................................63 9.6.1 Counter/Timer Operation..................................................................................................................66 9.6.2 Counter/Timer Registers ..................................................................................................................81 9.7 Interrupt Controller ...
Page 4
The PSD5XX family is a microcontroller peripheral that integrates high-performance and user-configurable blocks of EPROM, programmable logic, and SRAM into one part. The Introduction PSD5XX is also loaded with a variety of features, such as Counter/Timers, Interrupt controller, power ...
Page 5
PSD5XX Family Introduction The Peripheral PLD (PPLD) generates outputs to the Counter/Timer unit and the Interrupt Controller. The PPLD outputs to the Counter/Timer enable, disable, or trigger counting or (cont.) time capture. The PPLD outputs to the Interrupt Controller enables ...
Page 6
Introduction The Power Management Unit (PMU) of the PSD5XX enables the user to control the power consumption on selected functional blocks, based on system requirements. For (cont.) microcontrollers that do not generate a chip select input for the PSD, the ...
Page 7
PSD5XX Family Key Features Programmable power management allows: • (cont.) SRAM, EPROM, and ZPLDs to enter standby mode automatically • Disabling of the clock input to the ZPLDs • ZPLDs to enter a special low power mode (Sleep Mode), based ...
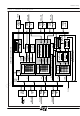
Page 8
Figure 1. PSD5XX Block Diagram PSD5XX Family 5 ...
Page 9
PSD5XX Family 5.0 Upon each address or logic input change to the PSD, the device powers up from low power standby for a short time. Then the PSD consumes only the necessary power to deliver new Integrated logic or memory ...
Page 10
Shown in Figure 3 (below) is the software design flow for a PSD5XX device. PSDsoft—WSI’s software development suite—is used throughout the design phase. You Design Flow start with a design file that is written in PSDabel-a high-level hardware description ...
Page 11
PSD5XX Family 7.0 There are 7 unique devices in the PSD5XX family. The part classifications are based on EPROM size and data bus width. The features of each part are listed in Table 1. PSD5XX Family Table 1. PSD5XX Product ...
Page 12
The following table describes the pin names and pin functions of the PSD5XX. Pins that have multiple names and/or functions are defined by user configuration. Table 2. PSD5XX Pin Pin Name Descriptions ADIO0 – ADIO15 RD WR CSI RESET ...
Page 13
PSD5XX Family Table 2. Pin Name PSD5XX Pin Descriptions PE0 (Cont.) PE1 PE2 PE3 PE4 PE5 PE6 PE7 VSTBY V CC GND 10 Pin Function Type Port PE, pin 0 I/O 1. BHE 2. PSEN 3. WRH 4. UDS 5. ...
Page 14
PSD5XX consists of seven major functional blocks: The PSD5XX ZPLD Blocks Architecture Bus Interface I/O Ports Memory Block Power Management Unit Counter/Timer Interrupt Controller The functions of each block are described in the following sections. Many of the blocks ...
Page 15
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 4. ZPLD Block Diagram Architecture 12 ...
Page 16
The PSD5XX Table 3. ZPLD Input Signals Architecture Signal Name (cont.) PA0 – PA7 PB0 – PB7 PE0 – PE7 PC0 – PC7 PD0 - PD7 PGR0 – PGR3 WDOG2PLD INTR2PLD A8 – A15, A0, A1 RD/E/DS WR/R_W CLKIN RESET ...
Page 17
PSD5XX Family 9.1.1 The DPLD The PSD5XX The DPLD is used for internal address decoding generating the following eight Architecture chip select signals: ES0 – ES3 EPROM selects, block 0 to block 3 RS0 SRAM block select CSIOP I/O Decoder ...
Page 18
The PSD5XX Figure 5. DPLD Logic Array Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 15 ...
Page 19
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX 9.1.2.1 Port A Macrocell Structure Architecture Figure 6a shows the PA Macrocell block, which consists of 8 identical macrocells. Each macrocell output can be connected to its own I/O pin on Port A. There are 3 ...
Page 20
The PSD5XX Figure 6. GPLD Macrocell Input/Output Port Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 17 ...
Page 21
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 6a. PA Macrocell Block Diagram Architecture (cont.) 18 ...
Page 22
The PSD5XX Figure 7. PA Macrocell Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 19 ...
Page 23
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX 9.1.2.2 Port B Macrocell Structure Architecture Figure 8 shows the PB Macrocell block, which consists of 8 identical macrocells. Each macrocell output can be connected to its own I/O pin on Port B. The two inputs, ...
Page 24
The PSD5XX Figure 8. PB Macrocell Block Diagram Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 21 ...
Page 25
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 9. PB Macrocell Architecture (cont.) 22 ...
Page 26
The PSD5XX 9.1.2.3 Port E Macrocell Structure Architecture Figure 10 shows the PE Macrocell block, which consists of 8 identical macrocells. Each macrocell output can be connected to its own I/O pin on Port E. There are 3 user (cont.) ...
Page 27
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 10. PE Macrocell Block Diagram Architecture (cont.) 24 ...
Page 28
The PSD5XX Figure 11. PE Macrocell Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 25 ...
Page 29
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX 9.1.3 The PPLD Architecture The Peripheral Programmable Logic Device (PPLD) provides a powerful mechanism for the user to control the operations of the Counter/Timer and Interrupt Controller. Figure 12 is (cont.) the PPLD block diagram. There ...
Page 30
The PSD5XX Figure 12. PPLD Block Diagram Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 27 ...
Page 31
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 13. Peripheral Macrocell Architecture (cont.) 28 ...
Page 32
The Bus Interface is very flexible and can be configured to interface to most microcontrollers with no glue logic. Table 4 lists some of the bus types to which the Bus Bus Interface is able to interface. Interface Table ...
Page 33
PSD5XX Family Bus 9.2.3 PSD5XX Interface To Non-Multiplexed Bus Interface Figure 16 shows a PSD5XX interfacing to a microcontroller with a non-multiplexed address/data bus. The address bus is connected to the ADIO Port, and the data bus is (Cont.) connected ...
Page 34
Bus Figure 14. Bus Interface – Multiplexed Bus 16-Bit Data Bus Interface (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 31 ...
Page 35
PSD5XX Family Bus Figure 15. ADIO Port, 16-Bit Multiplexed Bus Interface Interface (Cont.) 32 AD0 ADIO–0 AD1 ADIO–1 AD2 ADIO–2 AD3 ADIO–3 AD4 ADIO–4 AD5 ADIO–5 AD6 ADIO–6 AD7 ADIO–7 AD8 ADIO–8 AD9 ADIO–9 AD10 ADIO–10 AD11 ADIO–11 AD12 ADIO–12 ...
Page 36
Bus Figure 16. Bus Interface – Non-Multiplexed 16-Bit Data Interface (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 33 ...
Page 37
PSD5XX Family Bus 9.2.5 Optional Features Interface The PSD5XX provides two optional features to add flexibility to the Bus Interface: (Cont.) 1. Address In Port A can be configured as high order address (A16-A23) inputs to the ZPLD for EPROM ...
Page 38
Figure 17. Interfacing PSD5XX With 80C31 PSD5XX Family 35 ...
Page 39
PSD5XX Family Figure 18. Interfacing PSD5XX With 68HC11 36 ...
Page 40
Figure 19. Interfacing PSD5XX With 80C196 PSD5XX Family 37 ...
Page 41
PSD5XX Family Figure 20. Interfacing PSD5XX With Motorola 68331 38 ...
Page 42
There are 5 programmable 8-bit I/O ports: Port A, Port B, Port C, Port D and Port E. These ports all have multiple operating modes, depending on the configuration. Some of the basic I/O Ports functions are providing input/output ...
Page 43
PSD5XX Family I/O Ports 9.3.3 Address Out (Cont.) For microcontrollers with a multiplexed address/data bus, the I/O ports in Address-Out mode are able to provide latched address outputs (A0 – A15) to external devices. This mode of operation requires the ...
Page 44
I/O Ports 9.3.7 Alternate Function In (Cont.) This mode is per-pin configurable and enables the user to define the pins in Port E to perform Alternate function. Alternate Function includes inputs to Counter/Timers and APD clock. Configuration 1. Select input ...
Page 45
PSD5XX Family I/O Ports 9.3.10 Port Registers (Cont.) There are two sets of registers per I/O port: the Port Configuration Registers (PCR) which consist of four 8-bit registers; and the Port Data Registers (PDR) which include three 8-bit registers. The ...
Page 46
I/O Ports Control Register (Cont.) This register is used in both Standard MCU I/O Mode and Address Out modes. For setting a Standard MCU I/O Mode, a “1” must be written to the corresponding bit in the register. Writing a ...
Page 47
PSD5XX Family I/O Ports Table 15. Register Address Offset (Cont.) Register Name Data In Control Data Out Direction Open Drain Special Function PLD – I/O Macrocell Out Table 15a. Register Address Offset (For 16-bit Motorola Microcontrollers in 16-bit mode. Use ...
Page 48
I/O Ports 9.3.11 Port A – Functionality and Structure (Cont.) Port A is the most flexible of all the I/O ports. It can be configured to perform one or more of the following functions: Standard MCU I/O Mode PLD I/O ...
Page 49
PSD5XX Family The PSD5XX Figure 21. Port A Pin Structure Architecture (cont.) 46 ...
Page 50
The PSD5XX Figure 22. Port B Pin Structure Architecture (cont.) PSD5XX Family 47 ...
Page 51
PSD5XX Family I/O Ports 9.3.13 Port C and Port D – Functionality and Structure (Cont.) Port C and D are identical in function and structure and each can be configured to perform one or more of the following operating modes: ...
Page 52
I/O Ports Figure 23. Port C Pin Structure (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 49 ...
Page 53
PSD5XX Family I/O Ports Figure 24. Port D Pin Structure (Cont.) 50 ...
Page 54
I/O Ports Figure 25. Port E Pin Structure (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 51 ...
Page 55
PSD5XX Family 9.4 The PSD5XX provides EPROM memory for code storage and SRAM memory for scratch pad usage. Chip selects for the memory blocks come from the DPLD decoding logic and are Memory defined by the user in the PSDsoft ...
Page 56
Memory Figure 26. Memory Block Diagram (128KB EPROM) Block (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 53 ...
Page 57
PSD5XX Family Memory 9.4.4 Memory Select Map For 8031 Application Block The 8031 family of microcontrollers has separate code memory space and data memory space. This feature requires a different Memory Select Map. Two modes of operation are (Cont.) provided ...
Page 58
Memory Figure 27a. 8031 Memory Modes Block (Cont.) PSEN SRCODE–EN Figure 27b. 8031 Memory Modes RD PSEN SRCODE–EN ES0 ES1 ES2 ES3 EPROM DPLD RS0 OE RD SEPARATE SPACE MODE ES0 ES1 ES2 ES3 DPLD RS0 RD PSEN RD COMBINED ...
Page 59
PSD5XX Family Peripheral I/O 9.4.5 Peripheral I/O The Peripheral I/O Mode is one of the operating modes of Port A. In this mode, Port A is connected to the data bus of peripheral devices. Port A is enabled only when ...
Page 60
Peripheral I/O Figure 29. PSD5XX Peripheral I/O Configuration PSD5XX Family 57 ...
Page 61
PSD5XX Family 9.5 The PSD5XX provides many power saving options. By configuring the PMMRs (Power Management Mode Registers), the user can reduce power consumption. Table 17 shows Power the bit configuration of the PMMR0 and PMMR1. The microcontroller is able ...
Page 62
Power Figure 30. Power Management Unit Management Unit (Cont.) APD ENABLE PMMR0 - BIT 2 ALE POLARITY PMMR0 - BIT 1 ALE RESET APD CLK CLKIN CSI Figure 30a. Automatic Power Down Unit (APD) Flow Chart SLEEP –ENABLE PMMR1 - ...
Page 63
PSD5XX Family Power Table 17. Power Management Mode Registers (PMMR0, PMMR1) Management PMMR0 Unit Bit 7 (Cont.) TMR CLK 1 = OFF Bit 0 * Bit ALE Power Down (PD) Polarity Low ALE Power Down ...
Page 64
Power 9.5.4 Other Power Saving Options Management The PSD5XX provides additional power saving options. These options, except the SRAM Standby Mode, can be enabled/disabled by setting up the corresponding bit in the PMMR. Unit (Cont.) EPROM The EPROM power consumption ...
Page 65
PSD5XX Family Power Input Clock Management The PSD5XX provides the option to turn off the clock inputs to save AC power Unit consumption. The clock input (CLKIN) is used as a source for driving the following modules: (Cont.) ZPLD Array ...
Page 66
General Description PSD5XX The PSD5XX contains a powerful set of four 16 bit Counter/Timers, each controlled by Counter/Timer either PPLD outputs, external pins or Software. The Counter/Timers aid the user in counting external events and/or generating accurate delays. These ...
Page 67
PSD5XX Family PSD5XX Figure 31. Counter/Timer Block Diagram Counter/Timer (Cont.) 64 ...
Page 68
PSD5XX Figure 32. Counter/Timer and Interrupt Controller Interface with Other Internal Blocks Counter/Timer (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 65 ...
Page 69
PSD5XX Family PSD5XX 9.6.1 Counter/Timer Operation Counter/Timer There are four identical 16 bit Counter/Timers CNTR0,CNTR1,CNTR2 and CNTR3 and associated Counter/Timer image registers IMG0,IMG1,IMG2 and IMG3. Refer to Table 21 Operation for counter name and register correspondence. All Counter/Timers share a ...
Page 70
PSD5XX Figure 33. Inside of Each CTUx ( Counter/Timer Operation (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 67 ...
Page 71
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.1.2 Waveform Mode Operation In Waveform mode, the Counter/Timer is capable of producing various pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals. The Waveform mode in the PSD5XX is realized using two CTUs (Cont.) (COUNTER/TIMER UNITs) in the following combinations: CTU0 ...
Page 72
Counter/Timer Figure 34. Sample Waveform (PWM) and CTU Time Slots (Using Counters/Timers 0 and 1) Operation (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 69 ...
Page 73
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 35. CTU Control Signals For Waveform Mode Operation (Cont.) 70 ...
Page 74
Counter/Timer 9.6.1.3 Pulse Mode Operation In Pulse mode, the Counter/Timer is capable of generating a one shot pulse. The Pulse width of the generated pulse is defined by the value loaded into the associated Image (Cont.) register of the timer. ...
Page 75
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 36. Sample Pulse-Mode Waveform Operation (Cont.) OUTPUT WAVEFORM TERMINAL COUNT PULSE TRIGGER EVENT 72 CTU ACTIVED BY A CTU INACTIVE LOAD/STORE PULSE CTU INACTIVE ...
Page 76
Counter/Timer Figure 37. CTU Control Signals For Pulse Mode Operation (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 73 ...
Page 77
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 38. CTU Control Signals For Event Count Mode Operation (Cont.) 74 ...
Page 78
Counter/Timer 9.6.1.5 Time Capture Mode Operation In the time capture mode, the Counter/Timer is capable of measuring the time (by counting clock pulses) between events. Figure 39 shows the CTU configuration for (Cont.) time capture. All the Counter/Timer registers must ...
Page 79
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 39. CTU Control Signals For Time Capture Mode Operation (Cont.) 76 ...
Page 80
SET WATCHDOG BIT (BIT 3 OF GLOBAL COMMAND REGISTER) (SELF LATCHING BIT) SOFTWARE LOAD (BIT 2 OF SOFTWARE LOAD/STORE REGISTER) TIMER_CLOCK WATCHDOG GPLD OUTPUT COUNTER OUTPUT (ACTIVE HIGH) GPLD WDOG2PLD TERMINAL COUNT TO INTERRUPT CONTROLLER TERMINAL COUNT TO PORT E ...
Page 81
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.1.7 Terminal Counts (TCs) Operation The terminal counts (TC0 – TC3) generated by the Counter/Timers are made available at Port E as outputs or as feedbacks to the ZPLD. Refer to Table 27a for pin assignments. (Cont.) ...
Page 82
Counter/Timer Counter/Timer Clock Input Operation Table 22. DLCY, Scale Bit and DIV to Generate Different Clock Divisions (Cont.) DLCY ...
Page 83
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 42. Counter Clock Generation Operation (Cont GLOBAL CMD DIVISOR VALUE < 4 CLKIN PIN DELAY CYCLE < 0 SCALE BIT REGISTER RESULTING < = DIV = 280 TIMER CLOCK TO COUNTERS / TIMERS 0 ...
Page 84
Counter/Timer 9.6.2 Counter/Timer Registers Operation Registers CNTR0,CNTR1,CNTR2 and CNTR3 serve as actual counting logic. Registers IMG0,IMG1,IMG2 and IMG3 serve as images of these Counter/Timers. Depending upon the (Cont.) selected mode of operation, a Counter can load a new value or ...
Page 85
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Table 23a. Offset Address Map of Counter/Timer-Unit Registers Registers (For 16-Bit Motorola MCUs in 16-Bit Mode. If 8-Bit Mode is selected, use Table 23.) (Cont.) Address Offset +A8h +A4h +A2h +A0h +9Eh +9Ch +9Ah +98h +96h +94h ...
Page 86
Counter/Timer 9.6.2.1 Global Command Register Registers This is used to specify the operation mode of the Counter/Timer and to start or stop the Counter/Timer. Therefore during the initialization of the Counter/Timer registers, the Global (Cont.) Command Register should always be ...
Page 87
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.2.2 Command Registers for Counter/Timers CMD0, CMD1, CMD2, CMD3: Registers Each of the Counter/Timer units (CTU) has one Command Register associated with it. A description of these various CTU command bits is provided below. Refer to CSIOP ...
Page 88
Counter/Timer Command Registers for Counter/Timers CMD0, CMD1, CMD2, CMD3 (Cont.) Registers Output Polarity Bit (3): (Cont.) Input Polarity Bit (4): Pin / PPLD Macrocell Bit (5): This bit determines whether the Counter/Timer0 gets its Software Gating Bit for Load/Store Commands ...
Page 89
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer Figure 43. Enable/Disable and Load/Store Generation Registers (Cont.) 86 ...
Page 90
Counter/Timer 9.6.2.3 Configuring the Mode of Operation of the Counter/Timers: Registers Using the GLOBAL MODE bit of the Global Command register and MODE SELECT bit of the Command register of Counter/Timers 0 – 3, individual Counter/Timer modes of operation (Cont.) ...
Page 91
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.2.5 Software Load/Store Register: Registers Each bit in this register enables a load to the corresponding Counter/Timer from its associated Image Register in Waveform, Pulse or WatchDog modes. The actual counts (Cont.) are stored in their corresponding ...
Page 92
Counter/Timer 9.6.2.6 Status Flags Register Registers There are eight READ-ONLY status flags. The lower four bits represent Freeze Acknowledge bits. (Cont.) Bit 7 * NOTES: At RESET all these bits intialize as 0's. * FrezAck Bits These Freeze Acknowledge bits ...
Page 93
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.2.7 Load/Store (Cont.) The Load operation transacts an Image Register (e.g. IMG0) write into its Counter/Timer Register (e.g. CNTR0), whereas in the Store operation the Counter/Timer Register (e.g. CNTR0) writes back into the Image Register (e.g. IMG0). ...
Page 94
Counter/Timer Figure 44. PPLD Macrocell For Each Counter/Timer (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 91 ...
Page 95
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.2.11 I/O – Port (Cont.) Ports A, B and E have the capabilities for counter/timer alternate and special functions, e.g. Counter/Timer out, load/store, enable/disable, etc. Refer also to the chapter on I/O ports for ...
Page 96
Counter/Timer I/O – Port (Cont.) Port E: Timer[3:0] _ inputs can have different control functions such as timer LOAD/STORE and/or ENABLE/DISABLE, based on how these pins are configured in the Timer Command Registers. Table 27. The Terminal ...
Page 97
PSD5XX Family Counter/Timer 9.6.2.12 Sample Counter/Timer0 Initialization In PULSE Mode (Cont.) Following is a sample initialization routine for Counter/Timer0 to operate in PULSE mode. The assembly language commands do not correspond to any particular microcontroller. Configure CSIOP for Microcontroller access ...
Page 98
General Description Interrupt The PSD5XX includes logic for sensing, masking, priority decoding and identifying up to eight internal interrupts. The PSD5XX interrupt controller can generate interrupts from two Controller dedicated PPLD product terms, two PPLD Macrocell outputs and four ...
Page 99
PSD5XX Family Interrupt Figure 45. Interrupt Controller Block Diagram Controller (Cont.) 96 ...
Page 100
Interrupt Figure 46. Interrupt Controller Interface With Other Internal Blocks Controller (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 97 ...
Page 101
PSD5XX Family Interrupt Interrupt Operation Controller 9.7.1.1 Command Registers (Cont.) All the eight interrupts can be individually masked using a mask register. Writing “ones” into these mask bits enables the associated interrupts. RESET masks all interrupts. Interrupts can also be ...
Page 102
Interrupt Interrupt Operation Controller Interrupt Edge/Level Select Register (Cont.) Bit 7 Sense7 Bits sense 0 When these bits are set LEVEL sensitive 0 = EDGE sensitive (positive edge) At RESET these bits initialize as 0 i.e., all ...
Page 103
PSD5XX Family Interrupt Interrupt Operation Controller 9.7.2 Input/Output (Cont.) Interrupt inputs INT4 and INT5 originate from two dedicated PPLD product terms PT2INT4 and PT2INT5. Interrupt inputs INT6 and INT7 originate from the outputs of the PPLD Macrocells MC2INT6 and MC2INT7 ...
Page 104
Interrupt Figure 47. PPLD Interrupt Macrocell Controller (Cont.) PSD5XX Family 101 ...
Page 105
PSD5XX Family Interrupt Figure 48. Interrupt Flowchart Controller (Cont.) 102 INTERRUPT INITIALIZATION CLEAR ALL PENDING BITS (READ CLEAR REGISTER DEFINE EDGE OR LEVEL SENSITIVE CONFIGURE INTERRUPT SOURCE PLD AND / OR TIMER COUNT i.e. UNMASK REQD INTRPT CONTINUE EXECUTING MAIN ...
Page 106
The Page Register is 4 bits wide and consists of four D flip flops.The outputs of the Register (PGR0 – PGR3) are connected to the input bus of the ZPLD. By including the four outputs Page as inputs to ...
Page 107
PSD5XX Family 12.0 The CSIOP signal, which is generated by the DPLD, selects the internal I/O devices or registers. The CSIOP signal takes up 256 bytes of address space and is defined by the user System in the PSDSoft Software. ...
Page 108
System Table 31. Other Register Address Offset Configuration Register Name (Cont.) INTR. MASK INTR. REQUEST LATCH PMMR1 STATUS FLAGS SOFTWARE LOAD/STORE CMD3 CMD1 CNTR3 CNTR2 CNTR1 CNTR0 IMG3 IMG2 IMG1 IMG0 Address Register Name Offset PAGE REGISTER INTR. READ CLEAR ...
Page 109
PSD5XX Family System Table 31a. Other Register Address Offset (For 16-Bit Motorola MCUs in 16-Bit Mode. If 8-Bit Mode is selected, use Table 31.) Configuration (Cont.) Register Name INTR. MASK INTR. REQUEST LATCH PMMR1 STATUS FLAGS SOFTWARE LOAD/STORE CMD3 CMD1 ...
Page 110
System Table 33. Other Register Function Configuration Register Name (Cont.) PAGE REGISTER INTR. READ CLEAR INTR. EDGE/LEVEL INTR. MASK INTR. REQUEST LATCH INTR. PRIORITY STATUS VM PMMR0 PMMR1 STATUS FLAGS GLOBAL COMMAND DLCY SOFTWARE LOAD/STORE FREEZE COMMAND CMD3 – 0 ...
Page 111
PSD5XX Family System 12.1 Reset Input Configuration The reset input to the PSD5XX (RESET active low signal which resets some of the internal devices and configuration registers. The Timing Diagram in the AC/DC (Cont.) characterization section shows the ...
Page 112
Absolute Maximum Ratings Specifications Symbol T STG NOTE: Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the ...
Page 113
PSD5XX Family Specifications 13.4 AC/DC Parameters (cont.) The following tables describe the AC/DC parameters of the PSD5XX family: DC Electrical Specification AC Timing Specification • ZPLD Timing – Combinatorial Delays – Synchronous Clock Mode – Asynchronous Clock Mode • Microcontroller ...
Page 114
Figure 51. ZPLD Typical I Specifications (cont.) 13.5 Example of PSD5XX Typical Power Calculation at V Conditions Composite PLD input frequency (Freq PLD MHz MCU ALE frequency (Freq ALE) % EPROM Access % SRAM access % I/O access ...
Page 115
PSD5XX Family 13.6 DC Characteristics Symbol Parameter V Supply Voltage CC V High Level Input Voltage IH V Low Level Input Voltage IL V Reset High Level Input Voltage IH1 V Reset Low Level Input Voltage IL1 V Reset Pin ...
Page 116
AC/DC Parameters – ZPLD Timing Parameters Combinatorial Delays (5 V ± 10% Versions) Symbol Parameter I/O Input or Feedback Combinatorial Output Registered Input to t RPD Combinatorial Output t Input to Output Enable EA t Input ...
Page 117
PSD5XX Family AC/DC Parameters – ZPLD Timing Parameters Asynchronous Clock Mode (5 V ± 10% , Note 1) Symbol Parameter Maximum Frequency External Feedback Maximum Frequency f Internal Feedback MAXA (f ) CNTA Maximum Frequency Pipelined Data t Input Setup ...
Page 118
Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters Explanation of AC Symbols for Non ZPLD Timing. Example: t Time from Address Valid to ALE Invalid. AVLX A – Address L – Logic Level Low or ALE C – Power Down N – ...
Page 119
PSD5XX Family Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters Write Timing (5 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter t ALE or AS Pulse Width LVLX t Address Setup Time AVLX t Address Hold Time LXAX Address Valid to t AVWL Leading Edge of ...
Page 120
Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters Port A Peripheral Data Mode Read Timing Symbol Parameter t Address Valid to AVQV (PA) Data Valid t CS Valid to Data SLQV (PA) Valid RD to Data Valid t RLQV (PA Data ...
Page 121
PSD5XX Family Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters Power Down and Reset Timing Symbol Parameter t ALE Access Time from LVDV Power Down ALE or CSI Access Time t LVDV1 from Sleep ZPLD Propagation Delay t LVDV2 in Sleep Mode ZPLD ...
Page 122
AC/DC Parameters – ZPLD Timing Parameters Counter/Timer Timing (5 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter f Maximum Frequency MAX t Clock High Time CHCL t Clock Low Time CLCH t Clock to Output Delay CHPV t Clock to Watchdog CHPV1 Output ...
Page 123
PSD5XX Family 13.9 DC Characteristics (ZPSD5XXV Versions) (3.0 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter V Supply Voltage CC V High Level Input Voltage IH V Low Level Input Voltage IL V Reset High Level Input Voltage IH1 V Reset Low Level ...
Page 124
AC/DC Parameters – ZPLD Timing Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Combinatorial Delays (3.0 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter I/O Input or Feedback Combinatorial Output Registered Input to t RPD Combinatorial Output t Input to Output Enable EA t ...
Page 125
PSD5XX Family Symbol Parameter Maximum Frequency External Feedback Maximum Frequency f Internal Feedback (f MAXA Maximum Frequency Pipelined Data t Input Setup Time SA t Input Hold Time HA t Clock High Time CHA t Clock Low Time CLA t ...
Page 126
Microcontroller Interface –AC/DC Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Explanation of AC Symbols for Non ZPLD Timing. Example: t Time from Address Valid to ALE Invalid. AVLX A – Address L – Logic Level Low or ALE C – Power Down N ...
Page 127
PSD5XX Family Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Write Timing (3.0 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter t ALE or AS Pulse Width LVLX t Address Setup Time AVLX t Address Hold Time LXAX Address Valid to Leading t AVWL ...
Page 128
Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Port A Peripheral Data Mode Read Timing Symbol Parameter t Address Valid to Data Valid AVQV (PA Valid to Data Valid SLQV (PA Data Valid RLQV (PA) t ...
Page 129
PSD5XX Family Microcontroller Interface – AC/DC Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Power Down and Reset Timing Symbol Parameter ALE Access Time from t LVDV Power Down ALE or CSI Access Time t LVDV1 from Sleep ZPLD Propagation Delay t LVDV2 in Sleep ...
Page 130
AC/DC Parameters – ZPLD Timing Parameters (ZPSD5XXV Versions) Counter/Timer Timing (3.0 V ± 10%) Symbol Parameter f Maximum Frequency MAX t Clock High Time CHCL t Clock Low Time CLCH t Clock to Output Delay CHPV t Clock to Watchdog ...
Page 131
PSD5XX Family 14.0 Timing Diagrams Figure 52. Read Timing ALE/ (BHE) MULTIPLEXED BUS ADDRESS (BHE/SIZ0) NON-MULTIPLEXED BUS DATA NON-MULTIPLEXED BUS CSI RD (PSEN, DS) (LDS, UDS AVPV 128 t AVLX t LXAX t ...
Page 132
Figure 53. Write Timing ALE/AS A/D (BHE) MULTIPLEXED BUS ADDRESS (BHE, SIZ0) NON-MULTIPLEXED BUS DATA NON-MULTIPLEXED BUS CSI WR (WRH, WRL) (LDS, UDS) (DS AVLX t LXAX t LVLX ADDRESS VALID t AVWL ADDRESS VALID t ...
Page 133
PSD5XX Family Figure 54. Peripheral I/O Read Timing ALE/AS A/D BUS CSI RD Figure 55. Peripheral I/O Write Timing ALE / BUS WR 130 ADDRESS t AVQV ( PA) t SLQV ( PA) t RLQV ( PA) ...
Page 134
Figure 56. Combinatorial Timing – ZPLD INPUT (FROM PORT ANY OUTPUT INPUT (FROM PORT A) ANY OUTPUT Figure 57. Synchronous Clock Mode Timing – ZPLD CLKIN INPUT REGISTERED OUTPUT tPD tRPD ...
Page 135
PSD5XX Family Figure 58. Asynchronous Clock Mode Timing (Product-Term Clock, PB Macrocell Only) CLOCK INPUT REGISTERED OUTPUT Figure 59. Input to Output Disable/Enable INPUT INPUT TO OUTPUT ENABLE/DISABLE Figure 60. Asynchronous Reset/Preset RESET/PRESET INPUT REGISTER OUTPUT 132 tCHA tCLA tSA ...
Page 136
Figure 61. Reset Timing Figure 62. Key to Switching Waveforms WAVEFORMS T1 T2 INPUTS STEADY INPUT MAY CHANGE FROM MAY CHANGE FROM DON'T CARE OUTPUTS ONLY PSD5XX Family OUTPUTS STEADY OUTPUT WILL BE CHANGING ...
Page 137
PSD5XX Family 15 ° MHz A Pin Symbol Capacitance OUT C VPP NOTES: 1. These parameters are only sampled and are not 100% tested. 16.0 Figure 63. AC Testing Input/Output Waveform ...
Page 138
PSD5XX Pin No. Pin Assignments 68-Pin PLDCC/CLDCC Package 1 GND 2 ADIO_7 3 ADIO_6 4 ADIO_5 5 ADIO_4 6 ADIO_3 7 ADIO_2 8 ADIO_1 9 ADIO_0 10 PC7 11 PC6 12 PC5 13 PC4 14 PC3 15 PC2 16 ...
Page 139
PSD5XX Family PSD5XX Pin Assignments 136 80-Pin Pin No. TQFP Package 1 PC7 2 PC6 3 PC5 4 PC4 5 PC3 6 PC2 7 PC1 8 PC0 GND 12 GND 13 PA7 14 ...
Page 140
Package Information Figure 65. Drawing J5 – 68-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLDCC) (Package Type J) Figure 66. Drawing L5 – 68-Pin Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier (CLDCC) with Window (Package Type ...
Page 141
PSD5XX Family Figure 67. Drawing U2 – 80-Pin Plastic Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP) (Package Type U) (TOP VIEW) 138 PC7 1 PC6 2 PC5 3 PC4 4 PC3 5 PC2 6 PC1 7 PC0 ...
Page 142
Drawing J5 – 68-Pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLDCC) (Package Type Family: Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier Millimeters Symbol Min A 4.19 A1 2.41 A2 3.71 B 0.33 B1 0.66 ...
Page 143
PSD5XX Family Drawing L5 – 68-Pin Pocketed Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier (CLDCC) – CERQUAD (Package Type Family: Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier – CERQUAD Symbol Min A 3.94 A1 2.29 A2 3.05 B 0.43 ...
Page 144
Drawing U2 – 80-Pin Plastic Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP) (Package Type Index 3 Mark B Family: Plastic Thin Quad Flatpack (TQFP) Millimeters Symbol Min 0° A – A1 0.54 A2 1.15 B 0.30 ...
Page 145
... PSD5XX Family – Selector Guide Part # MCU PSD ZPSD ZPSDV Data Path Inputs Interface PSD511B1 ZPSD511B1 ZPSD511B1V 8 PLUS2 61 PSD501B1 ZPSD501B1 ZPSD501B1V 16/8 PLUS2 61 ZPSD512B0 8 PSD512B1 ZPSD512B1 ZPSD512B1V 8 PLUS2 61 PSD502B1 ZPSD502B1 ZPSD502B1V 16/8 PLUS2 61 PSD513B1 ZPSD513B1 ZPSD513B1V 8 PLUS2 61 PSD503B1 ZPSD503B1 ZPSD503B1V 16/8 PLUS2 61 PLDs/Decoders I/O Memory ...
Page 146
PSD5XX 20.2 Part Number Construction Ordering Information Z PSD 20.3 Ordering Information Part Number PSD501B1-C-70J PSD501B1-C-70L PSD501B1-C-70U PSD501B1-C-90JI PSD501B1-C-90UI PSD501B1-C-15J PSD501B1-C-15L PSD501B1-C-15U PSD502B1-C-70J PSD502B1-C-70L PSD502B1-C-70U PSD502B1-C-90JI PSD502B1-C-90UI PSD502B1-C-15J PSD502B1-C-15L PSD502B1-C-15U I 413A2 V -A -20 J Speed (ns) Package Type ...
Page 147
... PSD503B1-C-90JI PSD503B1-C-90UI PSD503B1-C-15J PSD503B1-C-15L PSD503B1-C-15U PSD511B1-C-70J PSD511B1-C-70L PSD511B1-C-70U PSD511B1-C-90JI PSD511B1-C-90UI PSD511B1-C-15J PSD511B1-C-15L PSD511B1-C-15U PSD512B1-C-70J PSD512B1-C-70L PSD512B1-C-70U PSD512B1-C-90JI PSD512B1-C-90UI PSD512B1-C-15J PSD512B1-C-15L PSD512B1-C-15U ...
Page 148
PSD5XX Ordering Information Product Ordering Information Part Number (cont.) ZPSD501B1-C-70J ZPSD501B1-C-70L ZPSD501B1-C-70U ZPSD501B1-C-90JI ZPSD501B1-C-90UI ZPSD501B1-C-15J ZPSD501B1-C-15L ZPSD501B1-C-15U ZPSD501B1V-C-20J ZPSD501B1V-C-20JI ZPSD501B1V-C-20L ZPSD501B1V-C-20U ZPSD501B1V-C-20UI ZPSD501B1V-C-25J ZPSD501B1V-C-25L ZPSD501B1V-C-25U ZPSD502B1-C-70J ZPSD502B1-C-70L ZPSD502B1-C-70U ZPSD502B1-C-90JI ZPSD502B1-C-90UI ZPSD502B1-C-15J ZPSD502B1-C-15L ZPSD502B1-C-15U ZPSD502B1V-C-20J ZPSD502B1V-C-20JI ZPSD502B1V-C-20L ZPSD502B1V-C-20U ZPSD502B1V-C-20UI ZPSD502B1V-C-25J ZPSD502B1V-C-25L ...
Page 149
... ZPSD511B1-C-70L ZPSD511B1-C-70U ZPSD511B1-C-90JI ZPSD511B1-C-90UI ZPSD511B1-C-15J ZPSD511B1-C-15L ZPSD511B1-C-15U ZPSD511B1V-C-20J ZPSD511B1V-C-20JI ZPSD511B1V-C-20L ZPSD511B1V-C-20U ZPSD511B1V-C-20UI ZPSD511B1V-C-25J ZPSD511B1V-C-25L ZPSD511B1V-C-25U ZPSD512B0-C-70J ZPSD512B0-C-70L ZPSD512B0-C-70U ZPSD512B0-C-90JI ZPSD512B0-C-90UI ZPSD512B0-C-15J ...
Page 150
PSD5XX Ordering Information Product Ordering Information Part Number (cont.) ZPSD512B1V-C-20J ZPSD512B1V-C-20JI ZPSD512B1V-C-20L ZPSD512B1V-C-20U ZPSD512B1V-C-20UI ZPSD512B1V-C-25J ZPSD512B1V-C-25L ZPSD512B1V-C-25U ZPSD513B1-C-70J ZPSD513B1-C-70L ZPSD513B1-C-70U ZPSD513B1-C-90JI ZPSD513B1-C-90UI ZPSD513B1-C-15J ZPSD513B1-C-15L ZPSD513B1-C-15U ZPSD513B1V-C-20J ZPSD513B1V-C-20JI ZPSD513B1V-C-20L ZPSD513B1V-C-20U ZPSD513B1V-C-20UI ZPSD513B1V-C-25J ZPSD513B1V-C-25L ZPSD513B1V-C-25U Operating Speed Temperature (ns) Package Type 200 ...
Page 151
PSD5XX Family 21.0 PSD5XX Functional Change: Process A change has been implemented in the most recent silicon that improves the way that the Image Register is updated. This change only applies to Event Count Mode for counter units Change Notice, ...
Page 152
PSD5XX, ZPSD5XX REVISION HISTORY Table 1. Document Revision History Date Rev. Apr-1994 1.0 PSD5XX: Document written in the WSI format. Initial release Jun-1995 1.1 ZPSD5XX: Updated Specifications Mar-1997 1.2 ZPSD5XX Updated specifications May-1998 1.3 PSD5XX, ZPSD5XX Updated specifications, various speed ...
Page 153
... The ST logo is registered trademark of STMicroelectronics All other names are the property of their respective owners STMicroelectronics group of companies Australia - Brazil - Canada - China - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States. ...