MC68HC711PH8 Motorola, MC68HC711PH8 Datasheet - Page 105

MC68HC711PH8
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC711PH8
Description
High-density Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (HCMOS) Microcomputer Unit
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.MC68HC711PH8.pdf
(264 pages)
- Current page: 105 of 264
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
5.7
The SCI transmitter has two status flags. These status flags can be read by software (polled) to
tell when certain conditions exist. Alternatively, a local interrupt enable bit can be set to enable
each of these status conditions to generate interrupt requests. Status flags are automatically set
by hardware logic conditions, but must be cleared by software. This provides an interlock
mechanism that enables logic to know when software has noticed the status indication. The
software clearing sequence for these flags is automatic — functions that are normally performed
in response to the status flags also satisfy the conditions of the clearing sequence.
TDRE and TC flags are normally set when the transmitter is first enabled (TE set to one). The
TDRE flag indicates there is room in the transmit queue to store another data character in the
transmit data register. The TIE bit is the local interrupt mask for TDRE. When TIE is zero, TDRE
must be polled. When TIE and TDRE are one, an interrupt is requested.
The TC flag indicates the transmitter has completed the queue. The TCIE bit is the local interrupt
mask for TC. When TCIE is zero, TC must be polled; when TCIE is one and TC is one, an interrupt
is requested.
Writing a zero to TE requests that the transmitter stop when it can. The transmitter completes any
transmission in progress before shutting down. Only an MCU reset can cause the transmitter to
stop and shut down immediately. If TE is cleared when the transmitter is already idle, the pin
reverts to its general purpose I/O function (synchronized to the bit-rate clock). If anything is being
transmitted when TE is cleared, that character is completed before the pin reverts to general
purpose I/O, but any other characters waiting in the transmit queue are lost. The TC and TDRE
flags are set at the completion of this last character, even though TE has been disabled.
5.7.1
The SCI receiver has seven status flags, three of which can generate interrupt requests. The
status flags are set by the SCI logic in response to specific conditions in the receiver. These flags
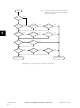
can be read (polled) at any time by software. Refer to Figure 5-3, which shows SCI interrupt
arbitration.
When an overrun takes place, the new character is lost, and the character that was in its way in
the parallel receive data register (RDR) is undisturbed. RDRF is set when a character has been
received and transferred into the parallel RDR. The OR flag is set instead of RDRF if overrun
occurs. A new character is ready to be transferred into the RDR before a previous character is read
from the RDR.
The NF, FE and PF flags provide additional information about the character in the RDR, but do not
generate interrupt requests.
The receiver active flag (RAF) indicates that the receiver is busy.
The last receiver status flag and interrupt source come from the IDLE flag. The RXD line is idle if it has
constantly been at logic one for a full character time. The IDLE flag is set only after the RXD line has
been busy and becomes idle. This prevents repeated interrupts for the time RXD remains idle.
MC68HC11PH8
Status flags and interrupts
Receiver flags
SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE
MOTOROLA
TPG
5-13
5
Related parts for MC68HC711PH8
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola, Inc [VOLTAGE REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
3N2046367254 MOTOROLA SC (XSTRS/R F)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MOTOROLA POWERPC 603e MICROPROCESSOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola Semiconductor Datasheet Library
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifier(POWERTAP III Package)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifirer
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> MTE53N50E
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SCHOTTKY BARRIER RECTIFIER 200 AMPERES 60 VOLT
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN SILICON POWER DARLINGTON TRANSISTOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet: