MC68HC711xxxx Motorola, MC68HC711xxxx Datasheet - Page 65

MC68HC711xxxx
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC711xxxx
Description
Microcontrollers
Manufacturer
Motorola
Datasheet
1.MC68HC711XXXX.pdf
(268 pages)
- Current page: 65 of 268
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
3.2.2 Analog Converter
3.2.3 Digital Control
3.2.4 Result Registers
3.2.5 A/D Converter Clocks
M68HC11E Family — Rev. 5
MOTOROLA
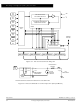
Conversion of an analog input selected by the multiplexer occurs in this block. It
contains a digital-to-analog capacitor (DAC) array, a comparator, and a successive
approximation register (SAR). Each conversion is a sequence of eight comparison
operations, beginning with the most significant bit (MSB). Each comparison
determines the value of a bit in the successive approximation register.
The DAC array performs two functions. It acts as a sample and hold circuit during
the entire conversion sequence and provides comparison voltage to the
comparator during each successive comparison.
The result of each successive comparison is stored in the SAR. When a conversion
sequence is complete, the contents of the SAR are transferred to the appropriate
result register.
A charge pump provides switching voltage to the gates of analog switches in the
multiplexer. Charge pump output must stabilize between 7 and 8 volts within up to
100 µs before the converter can be used. The charge pump is enabled by the
ADPU bit in the OPTION register.
All A/D converter operations are controlled by bits in register ADCTL. In addition to
selecting the analog input to be converted, ADCTL bits indicate conversion status
and control whether single or continuous conversions are performed. Finally, the
ADCTL bits determine whether conversions are performed on single or multiple
channels.
Four 8-bit registers ADR[4:1] store conversion results. Each of these registers can
be accessed by the processor in the CPU. The conversion complete flag (CCF)
indicates when valid data is present in the result registers. The result registers are
written during a portion of the system clock cycle when reads do not occur, so there
is no conflict.
The CSEL bit in the OPTION register selects whether the A/D converter uses the
system E clock or an internal RC oscillator for synchronization. When E-clock
frequency is below 750 kHz, charge leakage in the capacitor array can cause
errors, and the internal oscillator should be used. When the RC clock is used,
additional errors can occur because the comparator is sensitive to the additional
system clock noise.
Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Converter
Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Converter
Data Sheet
Overview
65
Related parts for MC68HC711xxxx
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola, Inc [VOLTAGE REGULATOR]
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
3N2046367254 MOTOROLA SC (XSTRS/R F)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MOTOROLA POWERPC 603e MICROPROCESSOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
Motorola Semiconductor Datasheet Library
Manufacturer:
Motorola

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifier(POWERTAP III Package)
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SWITCHMODE Schottky Power Rectifirer
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> MTE53N50E
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hybrid Power Module
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
SCHOTTKY BARRIER RECTIFIER 200 AMPERES 60 VOLT
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN SILICON POWER DARLINGTON TRANSISTOR
Manufacturer:
Motorola
Datasheet: