M34282E2GP MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor], M34282E2GP Datasheet - Page 7

M34282E2GP
Manufacturer Part Number
M34282E2GP
Description
SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Manufacturer
MITSUBISHI [Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor]
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
M34282E2GP
Manufacturer:
RENESAS
Quantity:
20 361
Part Number:
M34282E2GP
Manufacturer:
RENSESAS
Quantity:
20 000
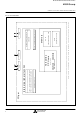
(5) Most significant ROM code reference enable flag (URS)
(6) Stack registers (SKs) and stack pointer (SP)
(7) Skip flag
URS flag controls whether to refer to the contents of the most
significant 1 bit (bit 8) of ROM code when executing the TABP
p instruction. If URS flag is “0,” the contents of the most
significant 1 bit of ROM code is not referred even when
executing the TABP p instruction. However, if URS flag is “1,”
the contents of the most significant 1 bit of ROM code is set to
flag CY when executing the TABP p instruction (Figure 4).
URS flag is “0” after system is released from reset and returned
from RAM back-up mode. It can be set to “1” with the URSC
instruction, but cannot be cleared to “0.”
Stack registers (SKs) are used to temporarily store the contents
of program counter (PC) just before branching until returning
to the original routine when;
• performing a subroutine call, or
• executing the table reference instruction (TABP p).
Stack registers (SKs) are four identical registers, so that
subroutines can be nested up to 4 levels. However, one of
stack registers is used when executing a table reference
instruction. Accordingly, be careful not to over the stack. The
contents of registers SKs are destroyed when 4 levels are
exceeded.
The register SK nesting level is pointed automatically by 2-bit
stack pointer (SP).
Figure 5 shows the stack registers (SKs) structure.
Figure 6 shows the example of operation at subroutine call.
Skip flag controls skip decision for the conditional skip
instructions and continuous described skip instructions.
Note : The 4282 Group just invalidates the next instruction
when a skip is performed. The contents of program
counter is not increased by 2. Accordingly, the number
of cycles does not change even if skip is not performed.
However, the cycle count becomes “1” if the TABP p,
RT, or RTS instruction is skipped.
MITSUBISHI
ELECTRIC
Fig. 5 Stack registers (SKs) structure
Fig. 6 Example of operation at subroutine call
Stack pointer (SP) points “3” at reset or
returning from RAM back-up mode. It points “0”
by executing the first BM instruction, and the
contents of program counter is stored in SK
When the BM instruction is executed after four
stack registers are used ((SP) = 3), (SP) = 0
and the contents of SK
Executing BM
Note:
instruction
0000
0001
0002
Address
SINGLE-CHIP 4-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Returning to the BM instruction execution
address with the RT instruction, and the BM
instruction is equivalent to the NOP instruction.
Main program
Program counter (PC)
16
16
16
NOP
BM SUB1
NOP
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
SK
SK
SK
SK
0
1
2
3
(SP)
(SK
(PC)
(PC)
(SP)
0
Executing RT
is destroyed.
0
instruction
)
0
SUB1
3
0001
(SK
0
)
16
4282 Group
SUB1 :
Subroutine
(SP) = 0
(SP) = 1
(SP) = 2
(SP) = 3
NOP
RT
0
·
·
·
.
7