ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C LATTICE [Lattice Semiconductor], ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C Datasheet

ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C
Related parts for ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C
ISPPACCLK5316S-01T48C Summary of contents
Page 1
October 2007 Features ■ Four Operating Configurations • Zero delay buffer • Zero delay and non-zero delay buffer • Dual non-zero delay buffer • Non-zero delay buffer with output divider ■ 8MHz to 267MHz Input/Output Operation ■ Low Output to ...
Page 2
Lattice Semiconductor General Description The ispClock5300S is an in-system-programmable zero delay universal fan-out buffer for use in clock distribution applications. The ispClock5312S, the first member of the ispClock5300S family, provides single-ended ultra low skew outputs. Each pair ...
Page 3
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 2. ispClock5308S Functional Block Diagram VTT_REFA VTT_REFB REFA_REFP + REFB_REFN 0 1 REFSEL FBK VTT_FBK Figure 3. ispClock5312S Functional Block Diagram VTT_REFA VTT_REFB REFA_REFP + REFB_REFN 0 1 REFSEL FBK VTT_FBK ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet L O ...
Page 4
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 4. ispClock5316S Functional Block Diagram VTT_REFA VTT_REFB REFA_REFP REFB_REFN 0 1 REFSEL FBK VTT_FBK Figure 5. ispClock5320S Functional Block Diagram VTT_REFA VTT_REFB REFA_REFP REFB_REFN 0 1 REFSEL FBK VTT_FBK RESET ...
Page 5
Lattice Semiconductor Absolute Maximum Ratings Core Supply Voltage ...
Page 6
Lattice Semiconductor 2 E CMOS Memory Write/Erase Characteristics Parameter Erase/Reprogram Cycles Performance Characteristics – Power Supply Symbol Parameter 2 I Core Supply Current CCD Incremental I per Active CCD I CCDADDER Output 2 I Analog Supply Current CCA Output Driver ...
Page 7
Lattice Semiconductor Electrical Characteristics – Differential SSTL18 Symbol Parameter V Low-Logic Level Input Voltage Logic Level Input Voltage IH Input Pair Differential Crosspoint V IX Voltage Electrical Characteristics – Differential SSTL2 Symbol Parameter V DC Differential Input ...
Page 8
Lattice Semiconductor DC Electrical Characteristics – Input/Output Loading Symbol Parameter I Input Leakage LK I Input Pull-up Current PU I Input Pull-down Current PD I Tristate Leakage Output OLK C Input Capacitance IN 1. Applies to clock reference inputs when ...
Page 9
Lattice Semiconductor Output Rise and Fall Times – Typical Values Slew 1 (Fastest) Output Type LVTTL 0.54 0.76 LVCMOS 1.8V 0.75 0.69 LVCMOS 2.5V 0.57 0.69 LVCMOS 3.3V 0.55 0.77 SSTL18 0.55 0.40 SSTL2 0.50 0.40 ...
Page 10
Lattice Semiconductor Programmable Input and Output Termination Characteristics Symbol Parameter R Input Resistance IN R Output Resistance OUT Output Resistor R OUT_TEMPCO Temperature Coefficient ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet Conditions Min. Rin=40Ω setting 36 Rin=45Ω setting 40.5 Rin=50Ω setting 45 Rin=55Ω ...
Page 11
Lattice Semiconductor Performance Characteristics – PLL Symbol Parameter Reference and feedback input f f REF, FBK frequency range t Reference and feedback input CLOCKHI, t clock HIGH and LOW times CLOCKLO t Reference and feedback input RINP, t rise and ...
Page 12
Lattice Semiconductor Timing Specifications Skew Matching Symbol Parameter t Output-output Skew SKEW Programmable Skew Control Symbol Parameter t Skew Control Range SKRANGE SK Skew Steps per Range STEPS 2 t Skew Step Size SKSTEP 3 t Skew Time Error SKERR ...
Page 13
Lattice Semiconductor Static Phase Offset vs. Reference Clock Logic Type Reference Clock Logic Symbol (REFA/REFB) LVCMOS 33 LVCMOS 25 LVCMOS 18 SSTL3 t φ – Static Phase Offset SSTL2 ( ) HSTL(1.5V) eHSTL(1.8V) LVDS (2.5V) 1 LVPECL 1. The output ...
Page 14
Lattice Semiconductor JTAG Interface and Programming Mode Symbol Parameter f Maximum TCK Clock Frequency MAX t TCK Clock Pulse Width, High CKH t TCK Clock Pulse Width, Low CKL t Program Enable Delay Time ISPEN t Program Disable Delay Time ...
Page 15
Lattice Semiconductor Timing Diagrams Figure 8. Erase (User Erase or Erase All) Timing Diagram VIH TMS VIL SU1 SU1 CKH CKL VIH TCK VIL State Update-IR Run-Test/Idle (Erase) Figure 9. Programming Timing Diagram VIH ...
Page 16
Lattice Semiconductor Typical Performance Characteristics I vs. f CCD VCO (Normalized to 400MHz) 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 150 200 250 f (MHz) VCO Period Jitter vs. Input/Output Frequency 80 60 V=16 40 V=8 20 V=4 V=2 0 ...
Page 17
Lattice Semiconductor Detailed Description PLL Subsystem The ispClock5300S provides an integral phase-locked-loop (PLL) which may be used to generate output clock sig- nals at lower, higher, or the same frequency as a user-supplied input reference signal. The core functions of ...
Page 18
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 12. PLL Loop Bandwidth vs. Feedback Divider Setting (Nominal) PLL Bandwidth vs. VCO Frequency and V-Divider (Standard Mode) 6.0 5.0 Vdiv=1 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 100 200 300 VCO Frequency (MHz) Dynamic Phase Offset vs. Input ...
Page 19
Lattice Semiconductor When the PLL is selected (PLL_BYPASS=LOW) and locked, the output frequency of each V divider (f culated as: where f is the frequency of V divider the input reference frequency ref V is the ...
Page 20
Lattice Semiconductor • eHSTL • Differential SSTL1.8 • Differential SSTL2 • Differential SSTL3 • Differential HSTL • LVDS • LVPECL (differential, 3.3V) Figure 13. Reference and Feedback Input REFA_REFP REFB_REFN REFSEL FBK VTT_FBK Each input features internal programmable termination resistors ...
Page 21
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 14. Input Receiver Termination Configuration REFA_REFP REFB_REFN Feedback input is terminated to the VTT_FBK pin through a programmable resistor. The following usage guidelines are suggested for interfacing to supported logic families. Differential Receiver + – Single-ended Receiver ...
Page 22
Lattice Semiconductor LVTTL (3.3V), LVCMOS (1.8V, 2.5V, 3.3V) The receiver should be set to LVCMOS or LVTTL mode, and the input signal can be connected to either the REFA or REFB pins. CMOS transmission lines are generally source terminated, so ...
Page 23
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 17. LVDS Input Receiver Configuration LVDS Driver Note that while a floating 100Ω resistor forms a complete termination for an LVDS signal line, additional circuitry may be required to satisfactorily terminate a differential LVPECL signal. This is ...
Page 24
Lattice Semiconductor actual impedance required will be a function of the driver used to generate the signal and the transmission medium used (PCB traces, connectors and cabling). The ispClock5300S’s ability to adjust input impedance over a range of 40Ω to ...
Page 25
Lattice Semiconductor Each of the ispClock5300S’s output driver banks can be configured to support the following logic outputs: • LVTTL • LVCMOS (1.8V, 2.5V, 3.3V) • SSTL2 • SSTL3 • HSTL • eHSTL To provide LVTTL, LVCMOS, SSTL2, SSTL3, HSTL ...
Page 26
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 21. Configuration for SSTL2, SSTL3, and HSTL Output Modes ispClock5300S SSTL/HSTL/eHSTL Mode (SSTL) 20 (HSTL, eHSTL) ispClock5300S Configurations The ispClock5300S device can be configured to operate in four modes. They are: • Zero Delay ...
Page 27
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 22. ispClock5300S configured as Zero Delay Buffer Mode ispClock5300S Single Ended / Differential Clock Input Mixed Zero Delay and Non-Zero Delay Buffer Mode Figure 23 shows the operation of the ispClock5300S in Mixed Zero Delay and Non ...
Page 28
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 23. Mixed Zero Delay and Non Zero Delay Buffer Mode Single Ended / Clock Input Single Ended / Clock Input ispClock5300S V1 PLL V2 V3 Internal Feedback External Feedback 28 ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet ...
Page 29
Lattice Semiconductor Non Zero Delay Buffer Mode 1 In the non zero delay buffer mode as shown in Figure 24 the output routing matrix completely bypasses the PLL. Each of the single ended input reference clocks can be routed to ...
Page 30
Lattice Semiconductor ispClock5300 Operating Configuration Summary The following table summarizes the operating modes of the ispClock5300S. Note: • Whenever the input buffer is configured as differential input, the fan-out buffer paths become unavailable. • Non-zero delay buffer for differential clock ...
Page 31
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 25. Maximum Ambient Temperature vs. Number of Active Output Banks Temperature Derating Curves Outputs LVCMOS33, 3.3V, f (ispClock 5304S, 5308S, 5312S Number of Active ...
Page 32
Lattice Semiconductor (f = 400MHz) to 780ps (f VCO VCO coarse skew mode is selected, an additional divide-by-2 stage is effectively inserted between the VCO and the V- divider bank, as shown in Figure 26. When assigning divider settings in ...
Page 33
Lattice Semiconductor outputs in Figure 27 show how the various sources of skew error stack up in this case. Note that if two or more out- puts are programmed to the same skew setting, then the contribution of the t ...
Page 34
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 29. External Feedback Mode and Timing Relationships Input Reference Clock Other Features RESET and Power-up Functions To ensure proper PLL startup and synchronization of outputs, the ispClock5300S provides both internally gener- ated and user-controllable external reset signals. ...
Page 35
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 30. PAC-Designer Design Entry Screen In-System Programming The ispClock5300S is an In-System Programmable (ISP™) device. This is accomplished by integrating all 2 E CMOS configuration control logic on-chip. Programming is performed through a 4-wire, IEEE 1149.1 compliant ...
Page 36
Lattice Semiconductor Evaluation Fixture Included in the basic ispClock5300S Design Kit is an engineering prototype board that can be connected to the parallel port using a Lattice ispDOWNLOAD ispClock5300S and can be used in real time to ...
Page 37
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 32. ispClock5300S TAP Registers TDI TAP Controller Specifics The TAP is controlled by the Test Clock (TCK) and Test Mode Select (TMS) inputs. These inputs determine whether an Instruction Register or Data Register operation is performed. Driven ...
Page 38
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 33. TAP States Test-Logic-Rst Run-Test/Idle Note: The value shown adjacent to each state transition in this figure represents the signal present at TMS at the time of a rising edge at TCK. When the ...
Page 39
Lattice Semiconductor For ispClock5300S, the instruction word length is eight bits. All ispClock5300S instructions available to users are shown in Table 4. The following table lists the instructions supported by the ispClock5300S JTAG Test Access Port (TAP) controller: Table 4. ...
Page 40
Lattice Semiconductor Figure 34. ispClock5300S Family ID Codes Version (4 bits Configured Version (4 bits Configured Version (4 bits Configured Version (4 bits Configured Version (4 bits Configured MSB XXXX ...
Page 41
Lattice Semiconductor In addition to the four instructions described above, there are 20 unique instructions specified by Lattice for the ispClock5300S. These instructions are primarily used to interface to the various user registers and the E non-volatile memory. Additional instructions ...
Page 42
Lattice Semiconductor Pin Descriptions – ispClock5304S, 5308S, 5312S Pin Name Description VCCO_0 Output Driver ‘0’ VCC VCCO_1 Output Driver ‘1’ VCC VCCO_2 Output Driver ‘2’ VCC VCCO_3 Output Driver ‘3’ VCC VCCO_4 Output Driver ‘4’ VCC VCCO_5 Output Driver ‘5’ ...
Page 43
Lattice Semiconductor Pin Descriptions – ispClock5304S, 5308S, 5312S (Continued) Pin Name Description LOCK PLL Lock indicator, HIGH indicates PLL lock OEX Output Enable X OEY Output Enable Y PLL_BYPASS PLL Bypass RESET Reset PLL NC No internal connection 1. Internal ...
Page 44
Lattice Semiconductor Pin Descriptions – ispClock5316S, 5320S Pin Name VCC_0 Output Driver ‘0’ VCC VCC_1 Output Driver ‘1’ VCC VCC_2 Output Driver ‘2’ VCC VCC_3 Output Driver ‘3’ VCC VCC_4 Output Driver ‘4’ VCC VCC_5 Output Driver ‘5’ VCC VCC_6 ...
Page 45
Lattice Semiconductor Pin Descriptions – ispClock5316S, 5320S (Continued) Pin Name GNDD Digital GND REFA_REFP Clock Reference A/ Positive Differential Input REFB_REFN Clock Reference B/ Negative Differential Input REFSEL Clock Reference Select input (LVCMOS) VTT_REFA Termination voltage for reference input A ...
Page 46
Lattice Semiconductor Detailed Pin Descriptions VCCO_[0..9], GNDO_[0..9] – These pins provide power and ground for each of the output banks. In the case when an output bank is unused, its corresponding VCCO pin may be left unconnected or preferably should ...
Page 47
Lattice Semiconductor Package Diagrams 48-Pin TQFP (Dimensions in Millimeters) PIN 1 INDICATOR 0. SECTION NOTES: 1. DIMENSIONING ...
Page 48
Lattice Semiconductor 64-Pin TQFP (Dimensions in Millimeters) PIN 1 INDICATOR TOP VIEW SIDE VIEW b SEATING PLANE 0. A-B D 64X SECTION B-B NOTES: 1. DIMENSIONING AND ...
Page 49
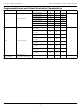
Lattice Semiconductor Part Number Description ispPAC-CLK53XXS - 01 XXXX X Device Family Device Number CLK5304S CLK5308S CLK5312S CLK5316S CLK5320S Ordering Information Conventional Packaging Part Number ispPAC-CLK5320S-01T64C ispPAC-CLK5316S-01T64C ispPAC-CLK5312S-01T48C ispPAC-CLK5308S-01T48C ispPAC-CLK5304S-01T48C Part Number ispPAC-CLK5320S-01T64I ispPAC-CLK5316S-01T64I ispPAC-CLK5312S-01T48I ispPAC-CLK5308S-01T48I ispPAC-CLK5304S-01T48I Lead-Free Packaging Part ...
Page 50
Lattice Semiconductor Lead-Free Packaging (Cont.) Part Number ispPAC-CLK5320S-01TN64I ispPAC-CLK5316S-01TN64I ispPAC-CLK5312S-01TN48I ispPAC-CLK5308S-01TN48I ispPAC-CLK5304S-01TN48I Industrial Clock Outputs Supply Voltage 20 3.3V 16 3.3V 12 3.3V 8 3.3V 4 3.3V 50 ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet Package Pins Lead-Free TQFP 64 Lead-Free TQFP 64 ...
Page 51
Lattice Semiconductor Package Options ispClock5304S: 48-pin TQFP VCCO_0 BANK_0A GND_0 BANK_0B ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet ispPAC-CLK5304S-01T48C ...
Page 52
Lattice Semiconductor ispClock5308S: 48-pin TQFP VCCO_0 BANK_0A GNDO_0 BANK_0B VCCO_1 BANK_1A GNDO_1 BANK_1B ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet ispPAC-CLK5308S-01T48C ...
Page 53
Lattice Semiconductor ispClock5312S: 48-pin TQFP VCCO_0 BANK_0A GNDO_0 BANK_0B VCCO_1 BANK_1A GNDO_1 BANK_1B VCCO_2 BANK_2A GNDO_2 BANK_2B ispClock5300S Family Data Sheet ispPAC-CLK5312S-01T48C VCCO_5 35 BANK_5A 34 ...
Page 54
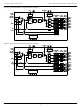
Lattice Semiconductor ispClock5316S: 64-pin TQFP BANK_0A BANK_0B VCCO_1 BANK_1A BANK_1B GNDO_1 VCCO_2 BANK_2A BANK_2B GNDO_2 VCCO_3 BANK_3A BANK_3B GNDO_3 ispPAC-CLK5316S-01T64C ispClock5300S ...
Page 55
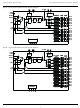
Lattice Semiconductor ispClock5320S: 64-pin TQFP BANK_0A BANK_0B VCCO_1 BANK_1A BANK_1B GNDO_1 VCCO_2 BANK_2A BANK_2B GNDO_2 VCCO_3 BANK_3A BANK_3B GNDO_3 BANK_4A BANK_4B ispPAC-CLK5320S-01T64C ispClock5300S ...
Page 56
Lattice Semiconductor Technical Support Assistance Hotline: 1-800-LATTICE (North America) +1-408-826-6002 (Outside North America) e-mail: isppacs@latticesemi.com Internet: www.latticesemi.com Revision History Date Version April 2006 01.0 May 2006 01.1 June 2006 01.2 October 2006 01.3 October 2007 01.4 Change Summary Initial release. ...