SAF-C502-2R20N Siemens Semiconductor Group, SAF-C502-2R20N Datasheet
SAF-C502-2R20N
Related parts for SAF-C502-2R20N
SAF-C502-2R20N Summary of contents
Page 1
Microcomputer Components 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller C502 Data Sheet 08.94 ...
Page 2
... USART with programmable 10-bit Baudrate-Generator Six interrupt sources, two priority levels Programmable 15-bit Watchdog Timer Oscillator Watchdog Fast Power On Reset Power Saving Modes P-DIP-40 package and P-LCC-44 package Temperature ranges: SAB-C502 Semiconductor Group T SAB-C502 : 0 ˚ ˚ SAF-C502 : – 40 ˚ ˚ C502 08.94 ...
Page 3
The SAB-C502-L/C502-2R described in this document is compatible with the SAB 80C52 and can be used for all present SAB 80C52 applications. The SAB-C502-2R contains a non-volatile 16 K read/write data memory, four ports, three 16-bit timers/counters, a six source, ...
Page 4
... Q67120-C892 SAF-C502-LN Q67120-C883 SAF-C502-LP Q67120-C893 SAF-C502-2RN Q67120-C886 SAF-C502-2RP Q67120-C894 SAF-C502-L20N Q67120-C887 SAF-C502-L20P Q67120-C895 SAF-C502-2R20N Q67120-C888 SAF-C502-2R20P Q67120-C896 Note: Extended temperature range – 40 ˚C to 110 ˚C (SAH-C502) on request. Semiconductor Group Package Description (8-Bit CMOS microcontroller) P-LCC-44 for external memory 12 MHz P-DIP-40 P-LCC-44 ...
Page 5
Pin Configuration (top view) Semiconductor Group (P-LCC-44) 4 C502 ...
Page 6
Pin Configuration (top view) Semiconductor Group (P-DIP-40) 5 C502 ...
Page 7
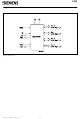
Logic Symbol Semiconductor Group 6 C502 ...
Page 8
Pin Definitions and Functions Symbol Pin Number P-LCC-44 P1.7 – P1.0 9– Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O*) Function P-DIP-40 8–1 I Port bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors. Port ...
Page 9
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number P-LCC-44 P3.0 – P3.7 11, 13– XTAL2 20 *)I = Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O*) Function P-DIP-40 10–17 I/O Port 3 is ...
Page 10
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number P-LCC-44 XTAL1 21 P2.0 – P2.7 24–31 PSEN Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O*) Function P-DIP-40 19 – XTAL1 Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input ...
Page 11
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number P-LCC-44 RESET 10 ALE P0.0 – P0.7 43– N.C. 1, 12, 23 Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O*) ...
Page 12
Functional Description The SAB-C502 is fully compatible to the standard 8051 microcontroller family compatible with the SAB 80C52. While maintaining all architectural and operational characteristics of the SAB 80C52 the SAB-C502 incorporates some enhancements in the Timer2 and ...
Page 13
CPU The SAB-C502 is efficient both as a controller and as an arithmetic processor. It has extensive facilities for binary and BCD arithmetic and excels in its bit-handling capabilities. Efficient use of program memory results from an instruction set consisting ...
Page 14
Special Function Registers All registers, except the program counter and the four general purpose register banks, reside in the special function register area. The 36 special function register (SFR) include pointers and registers that provide an interface between the CPU ...
Page 15
Table 1 Special Function Register in Numeric Order of their Addresses (cont’d) Address Register SYSCON B2 H reserved B3 H reserved B4 H reserved B5 H reserved N6 H reserved B7 H reserved B8 ...
Page 16
Table 2 Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks Block Symbol Name CPU ACC Accumulator B B-Register DPH Data Pointer, High Byte DPL Data Pointer, Low Byte DPSEL Data pointer select register PSW Program Status Word Register SP Stack Pointer Interrupt ...
Page 17
Table 3 Contents of SFR’s, SFR’s in Numeric Order Address Register Bit DPL 83 H DPH 86 H WDTREL 87 H PCON SMOD 88 H TCON TF1 89 H TMOD GATE ...
Page 18
Table 3 Contents of SFRs, SFRs in Numeric Order (cont’d) Address Register Bit SYSCON SRELH C0 H WDCON C8 H T2CON TF2 C9 H T2MOD CA H RC2L CB ...
Page 19
Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Timer/Counter 0 and 1 can be used in four operating modes as listed in table 4: Table 4 Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Operating Modes Mode Description 0 8-bit timer/counter with a divide-by-32 prescaler 1 16-bit timer/counter ...
Page 20
Timer 2 Timer 16-bit Timer/Counter with up/down count feature. It can operate either as timer event counter which is selected by bit C/T2 (T2CON.1). It has three operating modes as shown in table 5. ...
Page 21
Serial Interface (USART) The serial port is full duplex and can operate in four modes (one synchronous mode, three asynchronous modes) as illustrated in table 6. Figure 3 illustrates the block diagram of Baudrate generation for the serial interface. Table ...
Page 22
The possible baudrate can be calculated using the formulas given in table 7. Table 7 Baudrates Baud Rate derived from Oscillator Timer 1 (16-bit timer) (8-bit timer with 8-bit autoreload) Timer 2 Baudrate Generator The internal baudrate generator consists of ...
Page 23
Additional On-Chip RAM - XRAM The SAB-C502 contains another 256byte of On-Chip RAM additional to the 256bytes internal RAM. This RAM is called XRAM (‘eXtended RAM’) in this document. The additional ON-Chip RAM is logically located in the external data ...
Page 24
DPTR outside a) P0/P2 Bus XRAM address b) RD/WR range active c) ext. memory (DPH XCON) is used MOVX @DPTR DPTR within a) P0/P2 Bus XRAM address (WR-Data only) range b) RD/WR inactive (DPH = XCON) c) XRAM is ...
Page 25
Eight Datapointers for Faster External Bus Access The SAB-C502 contains a set of eight 16-bit-Datapointer (DPTR) from which the actual DPTR can be selected. This means that the user’s program may keep up to eight 16-bit addresses resident in these ...
Page 26
Interrupt System The SAB-C502 provides 6 interrupt sources with two priority levels. Figure 4 gives a general overview of the interrupt sources and illustrates the request and control flags. Figure 4 Interrupt Request Sources Semiconductor Group 25 C502 ...
Page 27
Table 11 Interrupt Sources and their Corresponding Interrupt Vectors Source (Request Flags) IE0 TF0 IE1 TF1 TF2 + EXF2 A low-priority interrupt can itself be interrupted by a high-priority interrupt, but not by another low- priority interrupt. ...
Page 28
... Fail Safe Mechanisms The SAB-C502 offers enhanced fail safe mechanisms, which allow an automatic recovery from software upset or hardware failure. 1) Watchdog Timer (15 bit, WDT) 2) Oscillator Watchdog (OWD) 1) Watchdog Timer (WDT) The Watchdog Timer in the SAB-C502 is a 15-bit timer, which is incremented by a count rate of ...
Page 29
Starting and refreshing the WDT Table 13 gives an overview how to start and refresh the WDT. The mentioned bits are located in SFR WDCON. Table 13 Starting and Refreshing the WDT Function Starting WD SETB Refreshing WD SETB ...
Page 30
Oscillator Watchdog (OWD) The OWD consists of an internal RC oscillator which provides the reference frequency for the comparison with the frequency of the on-chip oscillator. Figure 6 shows the block diagram of the oscillator watchdog unit while table ...
Page 31
Fast Internal Resest after Power-On The SAB-C502 can use the oscillator watchdog unit for a fast internal resert procedure after power- on. Normally members of the 8051 family enter their default reset state not before the on-chip oscillator starts. The ...
Page 32
Power Saving Modes Two power down modes are available, the Idle Mode and the Power Down Mode. The bits PDE, PDS and IDLE, IDLS select the Power Down mode or the idle mode, respectively. If the Power Down mode and ...
Page 33
Absolute Maximum Ratings Ambient temperature under bias ( Storage temperature ( T ) ...............................................................................– 65 ˚ 150 ˚ Voltage on pins with respect to ground ( CC Voltage on any pin with respect to ground ( ...
Page 34
... Active mode, 12 MHz 7) 7) Idle mode, 12 MHz Active mode, 20 MHz 7) 7) Idle mode, 20 MHz Power Down Mode Semiconductor Group ˚C for the SAB-C502 – ˚C for the SAF-C502 A Symbol Limit Values min. V – 0 – 0.5 IL1 V – 0.5 IL2 V 0.2 ...
Page 35
Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause spurious noise pulses to be superimposed on the and port 3. The noise is due to external bus capacitance discharging into the port 0 and port 2 pins when these ...
Page 36
... PXIX t *) – 63 PXIZ – PXAV t – 302 AVIV t 0 – AZPL 35 for the SAB-C502 for the SAF-C502 Limit Values Variable Clock 3.5 MHz to 12 MHz CLCL min. max – 40 – CLCL t – 40 – CLCL t – 53 – CLCL – ...
Page 37
AC Characteristics for SAB-C502-L / C502-2R External Data Memory Characteristics Parameter RD pulse width WR pulse width Address hold after ALE RD to valid data in Data hold after RD Data float after RD ALE to valid data in Address ...
Page 38
External Clock Drive Parameter Oscillator period High time Low time Rise time Fall time Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values Variable Clock Freq. = 3.5 MHz to 12 MHz min. t 83.3 CLCL t 20 CHCX t 20 CLCX t – ...
Page 39
... PXIX t *) – 40 PXIZ – PXAV t – 190 AVIV t 0 – AZPL 38 for the SAB-C502 for the SAF-C502 Limit Values Variable Clock 3.5 MHz to 20 MHz CLCL min. max – 40 – CLCL t – 30 – CLCL t – 30 – CLCL – ...
Page 40
AC Characteristics for SAB-C502-L20 / C502-2R20 External Data Memory Characteristics Parameter RD pulse width WR pulse width Address hold after ALE RD to valid data in Data hold after RD Data float after RD ALE to valid data in Address ...
Page 41
External Clock Drive Parameter Oscillator period High time Low time Rise time Fall time Figure 7 Program Memory Read Cycle Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values Variable Clock Freq. = 3.5 MHz to 20 MHz min CLCL t 12 ...
Page 42
Figure 8 Data Memory Read Cycle Semiconductor Group 41 C502 ...
Page 43
Figure 9 Data Memory Write Cycle Semiconductor Group 42 C502 ...
Page 44
ROM Verification Characteristics for SAB-C502-2R ROM Verification Mode 1 Parameter Address to valid data ENABLE to valid data Data float after ENABLE Oscillator frequency Figure 10 ROM Verification Mode 1 Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values min. t – AVQV t ...
Page 45
AC Inputs during testing are driven at measurements are made at Figure 11 AC Testing: Input, Output Waveforms For timing purposes a port pin is no longer floating when a 100 mV change from load voltage occurs and begins to ...
Page 46
Figure 14 Recommended Oscillator Circuits Semiconductor Group 45 C502 ...