EVAL-AD7450ACB AD [Analog Devices], EVAL-AD7450ACB Datasheet - Page 16

EVAL-AD7450ACB
Manufacturer Part Number
EVAL-AD7450ACB
Description
Differential Input, 1 MSPS 10-Bit and 12-Bit ADCs in an 8-Lead SOT-23
Manufacturer
AD [Analog Devices]
Datasheet
1.EVAL-AD7450ACB.pdf
(28 pages)
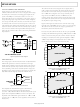
AD7440/AD7450A
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
Figure 26 shows a typical connection diagram for the
AD7440/AD7450A for both 5 V and 3 V supplies. In this setup,
the GND pin is connected to the analog ground plane of the
system. The V
decoupled reference source, depending on the power supply, to
set up the analog input range. The common-mode voltage has
to be set up externally and is the value on which the two inputs
are centered. The conversion result is output in a 16-bit word
with 4 leading zeros followed by the MSB of the 12-bit or 10-bit
result. The 10-bit result of the AD7440 is followed by 2 trailing
zeros. For more details on driving the differential inputs and
setting up the common mode, refer to the Driving Differential
Inputs section.
ANALOG INPUT
The analog input of the AD7440/AD7450A is fully differential.
Differential signals have a number of benefits over single-
ended signals, including noise immunity based on the device’s
common-mode rejection, improvements in distortion perfor-
mance, doubling of the device’s available dynamic range, and
flexibility in input ranges and bias points. Figure 27 defines the
fully differential analog input of the AD7440/AD7450A.
The amplitude of the differential signal is the difference
between the signals applied to the V
(i.e., V
signals each of amplitude V
amplitude of the differential signal is therefore –V
peak-to-peak (2 × V
mode (CM).
V
V
REF
REF
p-p
p-p
*CM IS THE COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE.
IN+
COMMON-MODE
– V
VOLTAGE
IN–
CM*
CM*
REF
). V
Figure 26. Typical Connection Diagram
Figure 27. Differential Input Definitions
0.1
pin is connected to either a 2.5 V or a 2 V
µ
IN+
F
V
V
V
V
REF
IN+
IN–
DD
REF
and V
0.1
). This is true regardless of the common
µ
F
2V/2.5V
AD7450A
REF
AD7440/
IN–
V
V
p-p
V
p-p
REF
REF
REF
that are 180° out of phase. The
are simultaneously driven by two
10
µ
F
IN+
and V
SDATA
V
V
3V/5V
SUPPLY
SCLK
IN+
IN–
GND
AD7450A
AD7440/
CS
IN–
INTERFACE
pins
SERIAL
REF
to +V
µ
C/
REF
µ
Rev. B | Page 16 of 28
P
The common mode is the average of the two signals, that is,
(V
are centered on. This results in the span of each input being
CM ± V
range varies with V
common-mode range decreases. When driving the inputs with
an amplifier, the actual common-mode range is determined by
the amplifier’s output voltage swing.
Figure 28 and Figure 29 show how the common-mode range
typically varies with V
The common mode must be in this range to guarantee the
functionality of the AD7440/AD7450A.
For ease of use, the common mode can be set up to equal V
resulting in the differential signal being ±V
When a conversion takes place, the common mode is rejected,
resulting in a virtually noise-free signal of amplitude –V
+V
case of the AD7450A and 0 to 1024 in the AD7440.
IN+
REF
+ V
, corresponding to the digital codes of 0 to 4096 in the
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
REF
0
0
IN–
0
0
/2. This voltage has to be set up externally, and its
)/2 and is therefore the voltage that the two inputs
Figure 28. Input Common-Mode Range vs. V
Figure 29. Input Common-Mode Range vs. V
0.25
0.5
(V
REF
(V
DD
0.50
DD
. As the value of V
REF
= 5 V and V
1.0
= 3 V and V
COMMON-MODE RANGE
for both a 5 V and a 3 V power supply.
COMMON-MODE RANGE
0.75
1.5
V
V
REF
REF
REF
1.00
REF
(Max) = 3.5 V)
(V)
(V)
(Max) =2V)
2.0
1.25
REF
increases, the
2.5
REF
1.50
centered on V
REF
REF
3.0
1.75
3.25V
1.75V
REF
2.00
2V
3.5
1V
REF
to
REF
,
.