HEF4047BP,652 NXP Semiconductors, HEF4047BP,652 Datasheet

HEF4047BP,652
Specifications of HEF4047BP,652
933324240652
HEF4047BPN
Related parts for HEF4047BP,652
HEF4047BP,652 Summary of contents
Page 1
DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF, HEC HEF4047B MSI Monostable/astable multivibrator Product specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC04 INTEGRATED ...
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator DESCRIPTION The HEF4047B consists of a gatable astable multivibrator with logic techniques incorporated to permit positive or negative edge-triggered monostable multivibrator action with retriggering and external counting options. Inputs include + TRIGGER, TRIGGER, ASTABLE, ASTABLE, RETRIGGER ...
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator Astable operation is enabled by a HIGH level on the ASTABLE input. The period of the square wave at O and O outputs is a function of the external components employed. ‘True’ input pulses on the ...
Page 4
Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ... (1) Special input protection that allows operating input voltages outside the supply voltage lines. ...
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIONS FUNCTION astable multivibrator free running true gating complement gating monostable multivibrator pos. edge-triggering neg. edge-triggering retriggerable (1) external count down Notes 1. Input pulse to RESET of external counting chip; external counting chip output ...
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator AC CHARACTERISTICS pF; input transition times SS amb L Propagation delays ASTABLE, ASTABLE OSC. OUTPUT HIGH to LOW LOW to HIGH ASTABLE, ASTABLE O, O ...
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator Minimum MR pulse width; HIGH Minimum input pulse width; any input exept MR APPLICATION INFORMATION General features: Monostable (one-shot) or astable (free-running) operation True and complemented buffered outputs Only one external R and C required Monostable ...
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator 1. Astable mode design information a. Unit-to-unit transfer-voltage variations The following analysis presents worst-case variations from unit-to-unit as a function of transfer-voltage (V running (astable) operation – --------------------------- - ...
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator b. Variations due to changes addition to variations from unit-to-unit, the astable period may vary as a function of frequency with respect to V Typical variations are presented graphically in Figs 5 and ...
Page 10
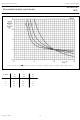
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator Fig.6 Typical O and O period accuracy as a function of supply voltage; astable mode; T CURVE f O kHz A 500 10 B 225 100 C 100 100 D 50 100 January 1995 C R ...
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator 2. Monostable mode design information The following analysis presents worst case variations from unit-to-unit as a function of transfer-voltage (V one-shot (monostalbe) operation ‘ – -------------- ...
Page 12
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator 3. Retrigger mode operation The HEF4047B can be used in the retrigger mode to extend the output pulse duration compare the frequency of an input signal with that of the internal oscillator. In the ...
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator 5. Timing component limitations The capacitor used in the circuit should be non-polarized and have low leakage (i.e. the parallel resistance of the capacitor should be an order of magnitude greater than the external resistor used). ...
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator Fig.10 Power consumption as a function of the output frequency Fig.11 Power consumption as a function of the output frequency January 1995 = 5 V; astable ...
Page 15
Philips Semiconductors Monostable/astable multivibrator Fig.12 Power consumption as a function of the output frequency January 1995 = 15 V; astable mode Product specification HEF4047B MSI ...