LM2904MXNOPB National Semiconductor, LM2904MXNOPB Datasheet
LM2904MXNOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM2904MXNOPB
Description
SOP8
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM2904MXNOPB.pdf
(9 pages)
Specifications of LM2904MXNOPB
Date_code
08+
© 2003 National Semiconductor Corporation
RSDS
Design Guidelines Part 2
Overview
This is the second half of the flat panel display design
guidelines. Part 1 focused on the Timing Controller (TCON)
and Column Driver RSDS
voltage references and power supply generation. In a typical
flat panel display, there can be 12 or more different supply
voltages that need to be generated and stabilized to maxi-
mize the panel performance.
DC-DC Conversion
Power supply design is very different from the high-speed
digital design that dominates the rest of the flat panel display
system. National Semiconductor has an industry best sup-
port structure for analog and power supply design including
the award winning WebBench
application notes (AN-556: Introduction to Power Supplie-
sand AN-1149: Layout Guidelines for Switching Power Sup-
plies are particularly helpful). All of National’s documentation
is available on the corporate website (www.national.com) or
through your local National Semiconductor representative.
Panels will normally have only a low voltage digital supply
(typically +3.3V), and will use that supply to generate the
higher voltages needed by the column drivers and the row
drivers. The most common method for developing these
voltages is to use a step-up converter. There are many
variations on the market, and National Semiconductor has a
variety of options designed specifically to meet the needs of
flat panel displays.
In this application note, examples are given that will illustrate
how to use National’s LM2622 and a +3.3V supply to gen-
erate the following voltages:
• +9.0V for Column Driver Analog Supply
• +18.0V for Row Driver "on" Voltage
• −9.0V for Row Driver "off" Voltage
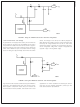
The basic operation of the LM2622 is outlined in Figure 1
and Figure 2. All of the components shown are external to
the device except the switch, which is attached to the circuit
by the SW pin on the IC. In the first cycle, the switch is
closed (shown in Figure 1) and the diode is reverse biased
(the diode acts like an open circuit and has been removed
from the figure). Energy is stored in the inductor and the
current for the load is supplied by C
(shown in Figure 2), the switch is open and the energy stored
in the inductor is transferred to the load and C
details on the operation of the LM2622 and switching power
supplies in general, please see the LM2622 datasheet and
Linear and Switching Voltage Regulator Fundamentals,
which is available on National’s corporate website or through
your National Semiconductor representative.
™
Flat Panel Display
™
interface. Part 2 focuses on the
™
software and numerous
OUT
. In the second cycle
AN200471
OUT
. For more
National Semiconductor
Application Note 1237
April 2003
+9.0V for Column Driver Analog Supply
Normally, the analog supply for the column drivers is be-
tween +8.0V and +10.0V. The LM2622 is capable of gener-
ating a controlled, stable voltage of up to +12.0V from a
+3.3V supply. Column drivers will consume 8-10mA of ana-
log current under worst-case conditions. For XGA and SXGA
applications, the DC-DC converter must be able to supply
100-150mA of current. National’s LM2622 can provide 100-
200mA of current at over 90% efficiency, making it perfectly
suited to supply the column driver analog voltage
Figure 3 shows an example of how to generate +9.0V using
the LM2622. In this configuration, the LM2622 is set to
operate at 600kHz (it can also operate at 1.3MHz if the
FSLCT pin is tied high). The circuit comprising of L1, D1, C3,
and the SW pin of the IC operate as described above in
Figure 1 and Figure 2. The analog output voltage is con-
trolled by the resistor-dividor of R1 and R2. The voltage on
the FB pin is internally fixed at +1.26V, so in order to have a
+9.0V output, resistor values of 51kΩ for R1 and 8.3kΩ for
R2 can be used. Voltages other than +9.0V can be gener-
ated by changing the ratio of R1 and R2.
FIGURE 1. Basic Operation of the LM2622 (switch
FIGURE 2. Basic Operation of the LM2622 (switch
closed)
open)
www.national.com
20047101
20047102