TB6584AFNG(O,EL) Toshiba, TB6584AFNG(O,EL) Datasheet

TB6584AFNG(O,EL)
Specifications of TB6584AFNG(O,EL)
Related parts for TB6584AFNG(O,EL)
TB6584AFNG(O,EL) Summary of contents
Page 1
... TOSHIBA Bi-CMOS Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic 3-Phase Full-Wave Sine-Wave PWM Brushless Motor Controller The TB6584AFNG is designed for motor fan applications for three-phase brushless DC (BLDC) motors. Features • Sine-wave PWM control • Triangular-wave generator (with a carrier frequency of f osc • Lead angle control (0° to 58° separate steps) External setting or automatic internal control • ...
Page 2
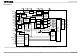
Block Diagram OSC/C 1 OSC/R 2 System clock HUP generator 3 HUM 4 HVP 5 Position HVM 6 estimation HWP 7 HWM Voltage regulator GND refout Power-on ...
Page 3
Pin Configuration OSC/C OSC/R HUP HUM HVP HVM HWP HWM GND RES CW/CCW LPF TB6584AFNG 30 REV ...
Page 4
Pin Description Pin No. Symbol Function 1 OSC/C Oscillator capacitor 2 OSC/R Oscillator resistor 3 HUP Position signal input HUM 5 HVP Position signal input HVM 7 HWP Position signal input HWM 9 GND ...
Page 5
Input/Output Equivalent Circuits Equivalent circuit diagrams may be partially omitted or simplified for explanatory purposes. Pin Symbol HUP Position signal input, U HUM HVP Position signal input, V HVM HWP Position signal input, W HWM Clockwise/counterclockwise rotation CW/CCW L: CW ...
Page 6
Pin Symbol Gain setting (Lead angle control circuitry) OUT Peak hold PH (Lead angle control circuitry) Low pass filter LPF (Lead angle control circuitry) Upper limit for LA UL Current limit control input I DC Reference voltage ...
Page 7
Pin Symbol Reverse rotation detection REV signal FG signal output FG Commutation signal output Commutation signal output Commutation signal output Commutation signal output Commutation signal output Commutation signal output, Z ...
Page 8
Absolute Maximum Ratings Characteristics Supply voltage Input voltage Commutation output current V output current refout Power dissipation Operating temperature Note 1: V pins LA, and UL IN (1) SP Note 2: V pins: HUP, HVP, HWP, HUM, HVM, ...
Page 9
Electrical Characteristics Characteristics Supply current Input current Input voltage Input sensitivity Hall effect Common-mode input inputs voltage Input hysteresis Input delay time Output voltage Output leakage current Output off time (Low-High) Current sensing LA gain setting amp LA limit setting ...
Page 10
Functional Description 1. Basic Operation During startup, the motor is driven by square-wave commutation signals that are generated according to the position signals. When the position signals indicate a rotational speed ( Hz, the TB6584AFNG estimates the rotor ...
Page 11
Dead Time Insertion (cross conduction protection) To prevent a short-circuit between external low-side and high-side power elements during sine-wave PWM drive, a dead time is digitally inserted between the turn-on of one side and the turn-off of the other ...
Page 12
PWM Carrier Frequency The triangular waveform generator provides a carrier frequency of f (The triangular wave is also used to force the switch-on ...
Page 13
Rotating Pulse Output The TB6584AFNG outputs rotating pulse based on hall signal. FGC terminal can switch one pulse per electrical angle or 3 pulses per electrical angle. One pulse per electrical angle is generated from hall signal of U ...
Page 14
Protection-Related Input Pins (1) Overcurrent protection (I If the voltage of the DC-link current exceeds the internal reference voltage, the commutation signals are forced Low. Overcurrent protection is disabled after every carrier period. Reference voltage = 0.5 V (typ.) ...
Page 15
Operation Flow Position signals (Hall sensors) estimation Voltage command System clock CR oscellator generator Note: The conduction period is reduced by the dead time. (carrier_frequency × 92% − phase Position Counter V phase Phase alignment W phase Square-wave ...
Page 16
The position signals from Hall sensors are modulated, and the modulated signals are then compared against a triangular waveform to generate a sinusoidal PWM waveform. The counter measures the period from a given rising (falling) edge of three hall signals ...
Page 17
Forward Rotation Timing Chart (Noninverted hall signal inputs HUM HUP HVM HVP HWP HWM 0 < Hall signals < (120° commutation < Hall signals (180° commutation: Modulated waveforms) S ...
Page 18
Forward Rotation Timing Chart (Inverted hall signal inputs HUM HUP HVM HVP HWP HWM Reverse rotation sensing (120° commutation When CW/CCW = Low, inverted Hall signals put the TB6584AFNG in 120 commutation ...
Page 19
Reverse Rotation Timing Chart (Inverted hall signal inputs) HUM HUP HVM HVP HWP HWM 0 < Hall signals < (120° commutation < Hall signals (180° commutation: Modulated waveforms) S ...
Page 20
Reverse Rotation Timing Chart (Noninverted hall signal inputs) HUM HUP HVM HVP HWP HWM Reverse rotation sensing (120° commutation When CW/CCW = High, noninverted Hall signals put the TB6584AFNG in 120° commutation ...
Page 21
Square-Wave Drive Waveform (Note) Hall signal inputs Output waveforms Note: Square waveforms are used in the above diagram for the sake of simplicity. To obtain an ...
Page 22
Sine-Wave Drive Waveform (CW/CCW = Low) Inside U phase V phase W phase Output waveforms Phase voltage differences V UV (U- (V- (W-U) In sine-wave drive mode, the amplitude of ...
Page 23
Application Circuit Example (R2/R1 OSC/C 1 OSC/R 2 System clock HUP 3 generator HUM 4 HVP 5 HVM 6 HWP 7 HWM Voltage 21 V regulator CC 9 GND ...
Page 24
Package Dimensions Weight: 0.17 g (typ.) TB6584AFNG 24 2010-05-27 ...
Page 25
... Application Circuits The application circuits shown in this document are provided for reference purposes only. Thorough evaluation is required, especially at the mass production design stage. Toshiba does not grant any license to any industrial property rights by providing these examples of application circuits. 6. Test Circuits Components in the test circuits are used only to obtain and confirm the device characteristics. These components and circuits are not guaranteed to prevent malfunction or failure from occurring in the application equipment ...
Page 26
IC Usage Considerations Notes on handling of ICs (1) The absolute maximum ratings of a semiconductor device are a set of ratings that must not be exceeded, even for a moment. Do not exceed any of these ratings. Exceeding the ...
Page 27
... Product shall not be used for or incorporated into any products or systems whose manufacture, use, or sale is prohibited under any applicable laws or regulations. • The information contained herein is presented only as guidance for Product use. No responsibility is assumed by TOSHIBA for any infringement of patents or any other intellectual property rights of third parties that may result from the use of Product. No license to any intellectual property right is granted by this document, whether express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise. • ...