L6227D STMicroelectronics, L6227D Datasheet - Page 17

L6227D
Manufacturer Part Number
L6227D
Description
IC DRVR DUAL FULL BRDG 24-SOIC
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Type
H Bridger
Datasheet
1.L6227DTR.pdf
(22 pages)
Specifications of L6227D
Input Type
Non-Inverting
Number Of Outputs
4
On-state Resistance
730 mOhm
Current - Output / Channel
1.4A
Current - Peak Output
2.8A
Voltage - Supply
8 V ~ 52 V
Operating Temperature
-25°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
24-SOIC (7.5mm Width)
Operating Supply Voltage
8 V to 52 V
Supply Current
1.4 A
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
For Use With
497-6817 - EVAL BOARD FOR L6227Q
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
L6227D
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
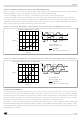
OUTPUT CURRENT CAPABILITY AND IC POWER DISSIPATION
In Fig. 17 and Fig. 18 are shown the approximate relation between the output current and the IC power dissipa-
tion using PWM current control driving two loads, for two different driving types:
– One Full Bridge ON at a time (Fig.17) in which only one load at a time is energized.
– Two Full Bridges ON at the same time (Fig.18) in which two loads at the same time are energized.
For a given output current and driving type the power dissipated by the IC can be easily evaluated, in order to
establish which package should be used and how large must be the on-board copper dissipating area to guar-
antee a safe operating junction temperature (125°C maximum).
Figure 17. IC Power Dissipation versus Output Current with One Full Bridge ON at a time.
Figure 18. IC Power Dissipation versus Output Current with Two Full Bridges ON at the same time.
THERMAL MANAGEMENT
In most applications the power dissipation in the IC is the main factor that sets the maximum current that can be de-
livered by the device in a safe operating condition. Therefore, it has to be taken into account very carefully. Besides
the available space on the PCB, the right package should be chosen considering the power dissipation. Heat sinking
can be achieved using copper on the PCB with proper area and thickness. Figures 20, 21 and 22 show the Junction-
to-Ambient Thermal Resistance values for the PowerSO36, PowerDIP24 and SO24 packages.
For instance, using a PowerSO package with copper slug soldered on a 1.5 mm copper thickness FR4 board
with 6cm
ing methods for this package. Using a multi-layer board with vias to a ground plane, thermal impedance can be
reduced down to 15°C/W.
2
dissipating footprint (copper thickness of 35µm), the R
P
P
TWO FULL BRIDGES ON AT THE SAME TIME
D
D
[W ]
[W]
10
10
8
6
4
2
0
8
6
4
2
0
0
ONE FULL BRIDGE ON AT A TIME
0
0.25 0.5 0.75 1
0.25 0.5 0.75 1
I
I
OUT
OUT
[A ]
[A]
1.25 1.5
1.25 1.5
I
I
I
I
A
B
A
B
th j-amb
Test Conditions:
Supply Volt age = 24 V
Test Conditions:
Supply Voltage = 24V
I
I
OUT
OUT
is about 35°C/W. Fig. 19 shows mount-
No PW M
f
I
SW
No PWM
f
OUT
SW
= 3 0 kHz (slow decay)
= 30 kHz (slow decay)
I
OUT
L6227
17/22