ISL6532CR Intersil, ISL6532CR Datasheet - Page 9

ISL6532CR
Manufacturer Part Number
ISL6532CR
Description
IC REG/CTRLR ACPI DUAL DDR 20QFN
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.ISL6532CRZ.pdf
(14 pages)
Specifications of ISL6532CR
Applications
Memory, DDR/DDR2 Regulator
Current - Supply
5.25mA
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
20-QFN
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Voltage - Supply
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ISL6532CRZ
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Active to Shutdown (S0 to S4/S5 Transition)
When the system transitions from active, S0, state to
shutdown, S4/S5, state, the ISL6532 IC disables all
regulators and forces the PGOOD pin and the NCH pin
LOW.
Over/Under Voltage Protection
Both the internal V
protected from faults through internal Over/Under voltage
detection circuitry. If either rail falls below 85% of the targeted
voltage, then an undervoltage event is tripped. An under
voltage will disable all regulators for a period of 3 soft-start
cycles, after which a normal soft-start is initiated. If the output
remains under 85% of target, the regulators will continue to be
disabled and soft-started in a hiccup mode until the fault is
cleared. See Figure 3.
If either rail exceeds 115% of the targeted voltage, then all
outputs are immediately disabled. The ISL6532 will not re-
enable the outputs until either the bias voltage is toggled in
order to initiate a POR or the SLP_S5 signal is forced LOW
and then back to HIGH.
Thermal Protection (S0/S3 State)
If the ISL6532 IC junction temperature reaches a nominal
temperature of 140
ISL6532 will not re-enable the outputs until the junction
temperature drops below 110
is toggled in order to initiate a POR or the SLP_S5 signal is
forced LOW and then back to HIGH.
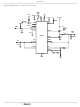
FIGURE 3. V
V
V
DDQ
TT
T0
RESPONSES
TT
/V
DELAY INTERVAL
INTERNAL DELAY
TT
o
DDQ
C, all regulators will be disabled. The
LDO and the V
LDO UNDER VOLTAGE PROTECTION
500mV/DIV
TIME
o
9
C and either the bias voltage
DDQ
.
regulator are
T1
T2
ISL6532
Shoot-Through Protection
A shoot-through condition occurs when both the upper and
lower MOSFETs are turned on simultaneously, effectively
shorting the input voltage to ground. To protect from a shoot-
through condition, the ISL6532 incorporates specialized
circuitry which insures that complementary MOSFETs are
not ON simultaneously.
The adaptive shoot-through protection utilized by the V
regulator looks at the lower gate drive pin, LGATE, and the
upper gate drive pin, UGATE, to determine whether a
MOSFET is ON or OFF. If the voltage from UGATE or from
LGATE to GND is less than 0.8V, then the respective
MOSFET is defined as being OFF and the other MOSFET is
allowed to be turned ON. This method allows the V
regulator to both source and sink current.
Since the voltage of the MOSFET gates are being measured
to determine the state of the MOSFET, the designer is
encouraged to consider the repercussions of introducing
external components between the gate drivers and their
respective MOSFET gates before actually implementing
such measures. Doing so may interfere with the shoot-
through protection.
Application Guidelines
Layout Considerations
Layout is very important in high frequency switching
converter design. With power devices switching efficiently at
250kHz, the resulting current transitions from one device to
another cause voltage spikes across the interconnecting
impedances and parasitic circuit elements. These voltage
spikes can degrade efficiency, radiate noise into the circuit,
and lead to device over-voltage stress. Careful component
layout and printed circuit board design minimizes these
voltage spikes.
As an example, consider the turn-off transition of the upper
MOSFET. Prior to turn-off, the MOSFET is carrying the full
load current. During turn-off, current stops flowing in the
MOSFET and is picked up by the lower MOSFET. Any
parasitic inductance in the switched current path generates a
large voltage spike during the switching interval. Careful
component selection, tight layout of the critical components,
and short, wide traces minimizes the magnitude of voltage
spikes.
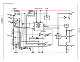
There are two sets of critical components in the ISL6532
switching converter. The switching components are the most
critical because they switch large amounts of energy, and
therefore tend to generate large amounts of noise. Next are
the small signal components which connect to sensitive
nodes or supply critical bypass current and signal coupling.
A multi-layer printed circuit board is recommended. Figure 4
shows the connections of the critical components in the
converter. Note that capacitors C
IN
and C
OUT
could each
DDQ
DDQ