CA3059 Intersil, CA3059 Datasheet - Page 22

CA3059
Manufacturer Part Number
CA3059
Description
ZERO VOLTAGE CROSSING SWITCH
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.CA3059.pdf
(31 pages)
Specifications of CA3059
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
CA3059
Manufacturer:
PHILIPS
Quantity:
563
Part Number:
CA3059
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
In 400Hz applications it may be necessary to widen and shift
the zero-voltage switch output pulse (which is typically 12ms
wide and centered on zero-voltage crossing), to assure that
sufficient latching current is available. The 4K resistor (terminal
No. 12 to common) and the 0.015 F capacitor (terminal No. 5
to common) are used for this adjustment.
Solid-State Traffic Flasher
Another application which illustrates the versatility of the zero-
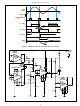
FIGURE 48. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR 400Hz ZERO-VOLTAGE
400Hz
115V
120VAC
INPUT
60Hz
SYNCED
AC
RAMP
LINE
SWITCHED LAMP DIMMER
100
V
COMMON
CC
DIAC PULSE
GENERATION
F
5 MEG
OUT
2W
10K
100 F
15VDC
270K
IN4003
2K
50K
R
RAMP
27K
47K
14
13
8
10 F
50VDC
TECCOR
HT-32
FIGURE 49. SYNCHRONOUS SWITCHING TRAFFIC FLASHER
7
ZVS
V
9
R
1.8K
5
12
13
2
8
7
5K
2W
4K
2W
4
Application Note 6182
0.015
9
6
ZVS
1/2W
F
68K
10
5
C
400Hz
TRIAC
5K
5W
L
11
5
3
22
4
voltage switch, when used with Intersil thyristors, involves
switching traffic control lamps. In this type of application, it is
essential that a triac withstand a current surge of the lamp load
on a continuous basis. This surge results from the difference
between the cold and hot resistance of the tungsten filament. If
it is assumed that triac turn-on is at 90 degrees from the zero-
voltage crossing, the first current surge peak is approximately
ten times the peak steady state rms value.
When the triac randomly switches the lamp, the rate of current
rise di/dt is limited only by the source inductance. The triac di/dt
rating may be exceeded in some power systems. In many
cases, exceeding the rating results in excessive current con-
centrations in a small area of the device which may produce a
hot spot and lead to device failure. Critical applications of this
nature require adequate drive to the triac gate for fast turn on.
In this case, some inductance may be required in the load cir-
cuit to reduce the initial magnitude of the load current when the
triac is passing through the active region. Another method may
be used which involves the switching of the triac at zero line
voltage. This method involves the supply of pulses to the triac
gate only during the presence of zero voltage on the AC line.
Figure 49 shows a circuit in which the lamp loads are switched
at zero line voltage. This approach reduces the initial di/dt,
decreases the required triac surge current ratings, increases
the operating lamp life, and eliminates RFI problems. This cir-
cuit consists of two triacs, a flip-flop (FF-1), the zero-voltage
switch, and a diac pulse generator. The flashing rate in this cir-
cuit is controlled by potentiometer R, which provides between
10 and 120 flashes per minute. The state of FF-1 determines
the triggering of triacs Y
4 generated by the zero crossing circuit. Transistors Q
inhibit these pulses to the gates of the triacs until the triacs turn
FF1
14
7
V
CC
Q
Q
2N697S
“1”
“0”
1/2 CD4013A
(COS/MOS FLIP-FLOP)
5.6K
G
1
or Y
MT
2
MT
by the output pulses at terminal
1
Y
2
1
2N697S
300W LAMP
5.6K
G
1
MT
MT
and Q
1
2
Y
2
2