LM4947TLEVAL National Semiconductor, LM4947TLEVAL Datasheet
LM4947TLEVAL
Specifications of LM4947TLEVAL
Related parts for LM4947TLEVAL
LM4947TLEVAL Summary of contents
Page 1
... BTL (3.3V) ■ THD+N at 1kHz, 37mW into 32Ω SE (3.3V) ■ Single Supply Operation ( ■ Single Supply Operation Boomer® registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation. © 2007 National Semiconductor Corporation Features ■ Control Interface ■ programmable National 3D Audio ■ ...
Page 2
Typical Application FIGURE 1. Typical Audio Amplifier Application Circuit-Output Capacitor-less FIGURE 2. Typical Audio Amplifier Application Circuit-Single Ended www.national.com 2 201735d3 201735d4 ...
Page 3
Connection Diagrams 25-Bump micro SMD Top View micro SMD Marking 20173507 Top View XY - Date Code TT - Die Traceability G - Boomer Family 201735d2 www.national.com ...
Page 4
Pin Descriptions Bump Name Description A1 R Right Input Channel 2 or Right Differential Input - IN2 A2 L Left Input Channel 1 or Left Differential Input + IN1 A3 MIN+ Mono Channel Non-inverting Input A4 RHP Right Headphone 3D ...
Page 5
... Absolute Maximum Ratings If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications. Supply Voltage Storage Temperature Input Voltage ESD Susceptibility (Note 3) ESD Machine model (Note 6) Junction Temperature ( Solder Information Electrical Characteristics 3.3V The following specifications apply for V ...
Page 6
Symbol Parameter Power Supply Rejection Ratio Loudspeaker out PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio R and L OUT OUT η Class D Efficiency CMRR Common-Mode-Rejection Ratio XTALK Crosstalk T Wake-Up Time from Shutdown WU Volume Control Step Size Error Digital Volume ...
Page 7
Electrical Characteristics 5V The following specifications apply for V Symbol Parameter I Quiescent Supply Current DDQ I Shutdown Current SD V Output Offset Voltage OS P Output Power O THD+N Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise N Output Noise OUT (Notes ...
Page 8
Symbol Parameter Power Supply Rejection Ratio Loudspeaker out PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio R and L OUT OUT η Class D Efficiency CMRR Common-Mode Rejection Ratio XTALK Crosstalk T Wake-Up Time from Shutdown WU Volume Control Step Size Error Digital ...
Page 9
(Notes 2, 7) The following specifications apply for V Symbol Parameter t Clock Period 1 t Clock Setup Time 2 t Data Hold Time 3 t Start Condition Time 4 t Stop Condition Time 5 V SPI ...
Page 10
Note 1: See AN-450 "Surface Mounting and their effects on Product Reliability" for other methods of soldering surface mount devices. Note 2: Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For ...
Page 11
Typical Performance Characteristics THD+N vs Output Power = 8Ω 1kHz V = 3.3V Mode 1, MONO THD+N vs Output Power = 8Ω 1kHz V = 3.3V Mode 5, MONO THD+N ...
Page 12
THD+N vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz, Diff 3.3V Mode 4, SE THD+N vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz, Diff 3.3V Mode 6, SE ...
Page 13
THD+N vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz, Diff 5V Mode 2, OCL 20173555 THD+N vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz, Diff 5V Mode 4, ...
Page 14
THD+N vs Frequency = 8Ω 3.3V Diff In, Mode 1 THD+N vs Frequency = 8Ω 3.3V Diff In, Mode 3 THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω ...
Page 15
THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω 3.3V 12mW Mode 4,7, SE 20173531 THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω 3.3V 12mW Mode 6, SE 20173533 THD+N vs ...
Page 16
THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω 5V Diff In, Mode 2, OCL THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω 5V Diff In, Mode 4,7, OCL THD+N vs Frequency = 32Ω, P ...
Page 17
PSRR vs Frequency V = 3.3V 0dB DD V Mode 1, MONO 20173516 PSRR vs Frequency V = 3.3V 0dB DD V Mode 2, SE 20173518 PSRR vs Frequency V = 3.3V 0dB DD ...
Page 18
PSRR vs Frequency V = 3.3V Mode 5, MONO PSRR vs Frequency V = 3.3V Mode 6, SE PSRR vs Frequency Mode 1, MONO www.national.com = 0dB 20173522 ...
Page 19
PSRR vs Frequency 0dB DD V Mode 2, SE 201735a8 PSRR vs Frequency 0dB DD V Mode 4, OCL 201735b0 PSRR vs Frequency 0dB DD ...
Page 20
PSRR vs Frequency Mode 6, SE Power Dissipation vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz V = 3.3V Mode 7, OCL Power Dissipation vs Output Power = 8Ω ...
Page 21
Power Dissipation vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz V = 3.3V Mode 20173598 Power Dissipation vs Output Power = 32Ω 1kHz Mode 7, ...
Page 22
Crosstalk vs Frequency = 32Ω 3.3V Mode 4, OCL Crosstalk vs Frequency = 32Ω 5V Mode 4, OCL Supply Current vs Supply Voltage No Load, Mode 7, OCL ...
Page 23
Supply Current vs Supply Voltage No Load, Mode MONO 201735d1 Supply Current vs Supply Voltage No Load, Mode Headphone SE 20173581 Output Power vs Supply Voltage = 32Ω, Mode OCL R ...
Page 24
Output Power vs Supply Voltage = 32Ω, Mode 7, OCL R L Efficiency vs Output Power = 8Ω, Mode BTL V = 3.3V www.national.com Output Power vs Supply Voltage R L 20173590 Efficiency vs ...
Page 25
Application Information PIN DESCRIPTION SDA: This is the serial data input pin. SCL: This is the clock input pin. ID_ENB: This is the address select input pin COMPATIBLE INTERFACE The LM4947 uses a serial ...
Page 26
Low Medium High Maximum Select L and R Stereo Pair IN1 IN1 Select L and R Stereo Pair IN2 IN2 Select L +L and R +R Stereo Pair IN1 IN2 IN1 IN2 Sets Stereo Inputs to Differential X = Don't ...
Page 27
Volume Step xVC4 ...
Page 28
Output MC2 MC1 MC0 Mode Number Note: L and R are selected by modes from Table ...
Page 29
AC gain where M represents some ratio of the nominal internal resistor, 20kΩ (see exam- ple below). (3D 2π M)(20kΩ 3dB C (nF) ...
Page 30
Further allowance should be made for increased ambient temperatures. The above examples assume that a device is a surface mount part operating around the maximum power dissipation point. Since internal power dissipation is a ...
Page 31
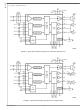
DEMO BOARD SCHEMATIC 31 www.national.com ...
Page 32
Revision History Rev 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 www.national.com Date 06/16/06 Initial release. 06/19/06 Changed the Class D Efficiency (n) on Typical limit (from 79 to 86) on the 5V specification table. 06/22/06 Added more ...
Page 33
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted X = 2.517 ± 0. – Bump micro SMD Order Number LM4947TL NS Package Number TLA25BBA Dimensions are in millimeters = 2.517 ± 0. 0.600 ± 0.10 2 ...
Page 34
... For more National Semiconductor product information and proven design tools, visit the following Web sites at: Products Amplifiers www.national.com/amplifiers Audio www.national.com/audio Clock Conditioners www.national.com/timing Data Converters www.national.com/adc Displays www.national.com/displays Ethernet www.national.com/ethernet Interface www.national.com/interface LVDS www.national.com/lvds Power Management www.national.com/power Switching Regulators www.national.com/switchers LDOs www ...