PIC18F14K50-I/SS Microchip Technology, PIC18F14K50-I/SS Datasheet - Page 47

PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Description
IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX16 20-SSOP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 18Fr
Datasheets
1.PIC18F13K50-ISS.pdf
(420 pages)
2.PIC18F13K50-ISS.pdf
(10 pages)
3.PIC18F13K50-ISS.pdf
(2 pages)
4.PIC18F14K50-ISS.pdf
(4 pages)
5.PIC18F14K50-IP.pdf
(422 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
16KB (8K x 16)
Package / Case
20-SSOP
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
48MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
14
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
768 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 11x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Processor Series
PIC18F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Data Ram Size
768 B
Interface Type
EUSART, I2C, MSSP, SPI, USB
Maximum Clock Frequency
48 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
15
Number Of Timers
4
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52715-96, 52716-328, 52717-734, 52712-325, EWPIC18
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 11 Channel
Package
20SSOP
Device Core
PIC
Family Name
PIC18
Maximum Speed
48 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
3.3|5 V
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
AC244023 - PROC EXTENS PAK PIC18F1XK50DV164126 - KIT DEVELOPMENT USB W/PICKIT 2DM164127 - KIT DEVELOPMENT USB 18F14/13K50AC164112 - VOLTAGE LIMITER MPLAB ICD2 VPPXLT20SS-1 - SOCKET TRANSITION 18DIP 20SSOPAC164307 - MODULE SKT FOR PM3 28SSOP
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Manufacturer:
IR
Quantity:
14 500
Part Number:
PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
- PIC18F13K50-ISS PDF datasheet
- PIC18F13K50-ISS PDF datasheet #2
- PIC18F13K50-ISS PDF datasheet #3
- PIC18F14K50-ISS PDF datasheet #4
- PIC18F14K50-IP PDF datasheet #5
- Current page: 47 of 420
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
3.4.3.1
At the core of indirect addressing are three sets of reg-
isters: FSR0, FSR1 and FSR2. Each represents a pair
of 8-bit registers, FSRnH and FSRnL. Each FSR pair
holds a 12-bit value, therefore the four upper bits of the
FSRnH register are not used. The 12-bit FSR value can
address the entire range of the data memory in a linear
fashion. The FSR register pairs, then, serve as pointers
to data memory locations.
Indirect addressing is accomplished with a set of
Indirect File Operands, INDF0 through INDF2. These
can be thought of as “virtual” registers: they are
mapped in the SFR space but are not physically
implemented. Reading or writing to a particular INDF
register actually accesses its corresponding FSR
register pair. A read from INDF1, for example, reads
the data at the address indicated by FSR1H:FSR1L.
Instructions that use the INDF registers as operands
actually use the contents of their corresponding FSR as
a pointer to the instruction’s target. The INDF operand
is just a convenient way of using the pointer.
Because indirect addressing uses a full 12-bit address,
data RAM banking is not necessary. Thus, the current
contents of the BSR and the Access RAM bit have no
effect on determining the target address.
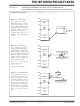
FIGURE 3-8:
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
Using an instruction with one of the
indirect addressing registers as the
operand....
...uses the 12-bit address stored in
the FSR pair associated with that
register....
...to determine the data memory
location to be used in that operation.
In this case, the FSR1 pair contains
ECCh. This means the contents of
location ECCh will be added to that
of the W register and stored back in
ECCh.
FSR Registers and the INDF
Operand
INDIRECT ADDRESSING
x x x x 1 1 1 0
7
PIC18F1XK50/PIC18LF1XK50
ADDWF, INDF1, 1
Preliminary
FSR1H:FSR1L
0
7
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
3.4.3.2
In addition to the INDF operand, each FSR register pair
also has four additional indirect operands. Like INDF,
these are “virtual” registers which cannot be directly
read or written. Accessing these registers actually
accesses the location to which the associated FSR
register pair points, and also performs a specific action
on the FSR value. They are:
• POSTDEC: accesses the location to which the
• POSTINC: accesses the location to which the
• PREINC: automatically increments the FSR by 1,
• PLUSW: adds the signed value of the W register
In this context, accessing an INDF register uses the
value in the associated FSR register without changing
it. Similarly, accessing a PLUSW register gives the
FSR value an offset by that in the W register; however,
neither W nor the FSR is actually changed in the
operation. Accessing the other virtual registers
changes the value of the FSR register.
FSR points, then automatically decrements the
FSR by 1 afterwards
FSR points, then automatically increments the
FSR by 1 afterwards
then uses the location to which the FSR points in
the operation
(range of -127 to 128) to that of the FSR and uses
the location to which the result points in the
operation.
FSR Registers and POSTINC,
POSTDEC, PREINC and PLUSW
0
FFFh
E00h
000h
100h
200h
300h
F00h
Data Memory
Bank 13
Bank 14
Bank 15
through
DS41350E-page 47
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 3
Related parts for PIC18F14K50-I/SS
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: