PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF Microchip Technology, PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF Datasheet - Page 28

PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Description
IC PIC MCU FLASH 256K 100TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® 24Fr
Datasheets
1.PIC24FJ128GA106-IPT.pdf
(52 pages)
2.PIC24FJ64GB106-IPT.pdf
(16 pages)
3.PIC24FJ64GB106-IPT.pdf
(352 pages)
4.PIC24FJ192GB108-IPT.pdf
(328 pages)
Specifications of PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
256KB (85.5K x 24)
Package / Case
100-TQFP, 100-VQFP
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
32MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART, USB OTG
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
83
Ram Size
16K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Processor Series
PIC24FJ
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
16 bit
Data Ram Size
16 KB
Interface Type
I2C/SPI/UART
Maximum Clock Frequency
32 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
84
Number Of Timers
5
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52713-733, 52714-737, 53276-922, EWDSPIC
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, DM240001, DM240011
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
16-ch x 10-bit
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
876-1004 - PIC24 BREAKOUT BOARDDM240001 - BOARD DEMO PIC24/DSPIC33/PIC32
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
21 000
Company:
Part Number:
PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
214
Company:
Part Number:
PIC24FJ256GB110-I/PF
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
PIC24FJXXXGA1/GB1
4.4
The term “Blank Check” implies verifying that the
device has been successfully erased and has no
programmed memory locations. A blank or erased
memory location is always read as ‘1’.
The Device ID registers (FF0002h:FF0000h) can be
ignored by the Blank Check since this region stores
device information that cannot be erased. The device
Configuration registers are also ignored by the Blank
Check. Additionally, all unimplemented memory space
should be ignored by the Blank Check.
The QBLANK command is used for the Blank Check. It
determines if the code memory is erased by testing
these memory regions. A ‘BLANK’ or ‘NOT BLANK’
response is returned. If it is determined that the device
is not blank, it must be erased before attempting to
program the chip.
4.5
4.5.1
Code memory is programmed with the PROGP
command. PROGP programs one row of code memory
starting from the memory address specified in the
command. The number of PROGP commands
required to program a device depends on the number
of write blocks that must be programmed in the device.
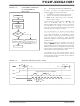
A flowchart for programming the code memory of the
PIC24FJXXXGA1/GB1 families is shown in Figure 4-4.
In this example, all 87K instruction words of a
256 Kbyte device are programmed. First, the number
of commands to send (called ‘RemainingCmds’ in the
flowchart) is set to 1368 and the destination address
(called ‘BaseAddress’) is set to ‘0’. Next, one write
block in the device is programmed with a PROGP
command. Each PROGP command contains data for
one row of code memory of the device. After the first
command is processed successfully, ‘RemainingCmds’
is decremented by 1 and compared with 0. Since there
are more PROGP commands to send, ‘BaseAddress’
is incremented by 80h to point to the next row of
memory.
On the second PROGP command, the second row is
programmed. This process is repeated until the entire
device is programmed. No special handling must be
performed when a panel boundary is crossed.
DS39907A-page 28
Blank Check
Code Memory Programming
PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY
FIGURE 4-4:
4.5.2
After code memory is programmed, the contents of
memory can be verified to ensure that programming
was successful. Verification requires code memory to
be read back and compared against the copy held in
the programmer’s buffer.
The READP command can be used to read back all of
the programmed code memory.
Alternatively, you can have the programmer perform
the verification after the entire device is programmed
using a checksum computation.
BaseAddress + 80h
BaseAddress =
PROGRAMMING VERIFICATION
No
RemainingCmds = 1368
Command to Program
RemainingCmds – 1
BaseAddress = 00h
RemainingCmds =
PROGP response
FLOWCHART FOR
PROGRAMMING CODE
MEMORY
RemainingCmds
Send PROGP
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
BaseAddress
PASS?
Finish
Start
Are
0?
Is
Yes
Yes
Report Error
Failure
No