MC9S08AC16CFJE Freescale Semiconductor, MC9S08AC16CFJE Datasheet - Page 223
MC9S08AC16CFJE
Manufacturer Part Number
MC9S08AC16CFJE
Description
IC MCU 8BIT 16K FLASH 32-LQFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HCS08r
Specifications of MC9S08AC16CFJE
Core Processor
HCS08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
40MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
22
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
1K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 6x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
32-LQFP
Processor Series
S08AC
Core
HCS08
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
1 KB
Interface Type
SCI/SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
40 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
22
Number Of Timers
8
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
EWS08
Development Tools By Supplier
DEMO9S08AC60E, DEMOACEX, DEMOACKIT, DCF51AC256, DC9S08AC128, DC9S08AC16, DC9S08AC60, DEMO51AC256KIT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
6-ch x 10-bit
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC9S08AC16CFJE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC9S08AC16CFJER
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 223 of 336
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
12.5.2
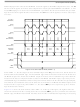
There are three flag bits, two interrupt mask bits, and one interrupt vector associated with the SPI system.
The SPI interrupt enable mask (SPIE) enables interrupts from the SPI receiver full flag (SPRF) and mode
fault flag (MODF). The SPI transmit interrupt enable mask (SPTIE) enables interrupts from the SPI
transmit buffer empty flag (SPTEF). When one of the flag bits is set, and the associated interrupt mask bit
is set, a hardware interrupt request is sent to the CPU. If the interrupt mask bits are cleared, software can
poll the associated flag bits instead of using interrupts. The SPI interrupt service routine (ISR) should
check the flag bits to determine what event caused the interrupt. The service routine should also clear the
flag bit(s) before returning from the ISR (usually near the beginning of the ISR).
12.5.3
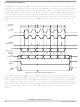
A mode fault occurs and the mode fault flag (MODF) becomes set when a master SPI device detects an
error on the SS pin (provided the SS pin is configured as the mode fault input signal). The SS pin is
configured to be the mode fault input signal when MSTR = 1, mode fault enable is set (MODFEN = 1),
and slave select output enable is clear (SSOE = 0).
The mode fault detection feature can be used in a system where more than one SPI device might become
a master at the same time. The error is detected when a master’s SS pin is low, indicating that some other
SPI device is trying to address this master as if it were a slave. This could indicate a harmful output driver
conflict, so the mode fault logic is designed to disable all SPI output drivers when such an error is detected.
When a mode fault is detected, MODF is set and MSTR is cleared to change the SPI configuration back
to slave mode. The output drivers on the SPSCK, MOSI, and MISO (if not bidirectional mode) are
disabled.
MODF is cleared by reading it while it is set, then writing to the SPI control register 1 (SPI1C1). User
software should verify the error condition has been corrected before changing the SPI back to master
mode.
Freescale Semiconductor
SPI Interrupts
Mode Fault Detection
MC9S08AC16 Series Data Sheet, Rev. 8
Serial Peripheral Interface (S08SPIV3)
223
Related parts for MC9S08AC16CFJE
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: