PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML Microchip Technology, PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML Datasheet
PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML
Specifications of PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML
Available stocks
Related parts for PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML
PIC24FJ64GB002-I/ML Summary of contents
Page 1
... PIC24FJ64GB004 Family 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 28/44-Pin, 16-Bit, Flash Microcontrollers with USB On-The-Go (OTG) and nanoWatt XLP Technology Data Sheet DS39940D ...
Page 2
... PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries. SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies. ...
Page 3
... Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Power Management Modes: • Selectable Power Management modes with nanoWatt XLP Technology for Extremely Low Power: - Deep Sleep mode allows near total power-down (20 nA typical and 500 nA with RTCC or WDT), ...
Page 4
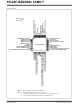
... Configurable Open-Drain Outputs on Digital I/O Pins • External Interrupt Sources 1 28 MCLR AN9/C3INA/VBUSCHG/RP15/VBUSST/CN11/RB15 4 25 AN10/C3INB/ AN11/C1INC/RP13/PMRD/REFO/SESSEND/CN13/RB13 USB PGEC2/D-/VMIO/RP11/CN15/RB11 PGED2/D+/VPIO/RP10/CN16/RB10 CAP OSCO/CLKO/PMA0/CN29/RA3 10 19 DISVREG 11 18 TDO/SDA1/RP9/PMD3/RCV/CN21/RB9 12 17 TCK/USBOEN/SCL1/RP8/PMD4/CN22/RB8 TDI/RP7/PMD5/INT0/CN23/RB7 TMS/USBID/CN27/RB5 V BUS ® /V /VBUSON/RP14/CN12/RB14 REF CPCON /V DDCORE 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 5
... OSCO/CLKO/PMA0/CN29/RA3 Legend: RPn represents remappable peripheral pins. Note 1: Gray shading indicates 5.5V tolerant input pins. 2: Alternative multiplexing for SDA1 and SCL1 when the I2C1SEL bit is set. 3: The back pad on QFN devices should be connected to V 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY ...
Page 6
... Gray shading indicates 5.5V tolerant input pins. 2: Alternative multiplexing for SDA1 and SCL1 when the I2C1SEL bit is set. 3: The back pad on QFN devices should be connected to V DS39940D-page PIC24FJXXGB004 USB SOSCI/C2IND/RP4/CN1/RB4 TDO/PMA8/RA8 OSCO/CLKO/CN29/RA3 OSCI/CLKI/C1IND/PMCS1/CN30/RA2 AN8/RP18/PMA2/CN10/RC2 AN7/RP17/CN9/RC1 AN6/RP16/CN8/RC0 AN5/C1INA/DMLN/RTCC/SCL2/RP3/PMWR/CN7/RB3 AN4/C1INB/DPLN/SDA2/RP2/PMD2/CN6/RB2 . SS 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 7
... Instruction Set Summary .......................................................................................................................................................... 297 29.0 Electrical Characteristics .......................................................................................................................................................... 305 30.0 Packaging Information.............................................................................................................................................................. 327 Appendix A: Revision History............................................................................................................................................................. 341 The Microchip Web Site ..................................................................................................................................................................... 349 Customer Change Notification Service .............................................................................................................................................. 349 Customer Support .............................................................................................................................................................................. 349 Reader Response .............................................................................................................................................................................. 350 Product Identification System ............................................................................................................................................................ 351 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY DS39940D-page 7 ...
Page 8
... When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are using. Customer Notification System Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products. DS39940D-page 8 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 9
... DEVICE OVERVIEW This document contains device-specific information for the following devices: • PIC24FJ32GB002 • PIC24FJ32GB004 • PIC24FJ64GB002 • PIC24FJ64GB004 This family expands on the existing line of Microchip‘s 16-bit microcontrollers, combining an expanded peripheral feature set and enhanced computational performance with a new connectivity option: USB On-The-Go (OTG) ...
Page 10
... This information is provided in the pinout diagrams in the beginning of this data sheet. Multiplexed features are sorted by the priority given to a feature, with the highest priority peripheral being listed first. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 11
... Analog Comparators CTMU Interface Resets (and delays) Instruction Set Packages Note 1: Peripherals are accessible through remappable pins. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY PIC24FJ32GB002 PIC24FJ64GB002 PIC24FJ32GB004 PIC24FJ64GB004 DC – 32 MHz 32K 64K 11,008 22,016 8,192 45 (41/4) Ports A and B 19 ...
Page 12
... Inst Register Divide Control Signals Support Reg Array Multiplier (2) MCLR 10-Bit (3) (3) RTCC Comparators ADC SPI UART I2C (3) (3) 1/2 1/2 1/2 (1) PORTA 16 (9 I/O) PORTB (14 I/ (1) PORTC (10 I/ (1) RP RP0:RP25 16-Bit ALU 16 USB OTG PMP/PSP CTMU 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 13
... C3INB 25 22 C3INC 2 27 C3IND 3 28 CLKI 9 6 CLKO 10 7 Legend: TTL = TTL input buffer ANA = Analog level input/output 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Input I/O Buffer 19 I ANA A/D Analog Inputs ANA 21 I ANA 22 I ANA 23 I ANA ...
Page 14
... USB Differential Minus Line (internal transceiver — D- External Pull-up Control Output — D- External Pull-down Control Output — D+ External Pull-up Control Output — D+ External Pull-down Control Output Voltage Regulator Disable Schmitt Trigger input buffer C™ C/SMBus input buffer Description 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 15
... PMD6 3 28 PMD7 2 27 PMRD 24 21 PMWR 7 4 Legend: TTL = TTL input buffer ANA = Analog level input/output 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Input I/O Buffer External Interrupt Input Master Clear (device Reset) Input. This line is brought low to cause a Reset. 30 ...
Page 16
... PORTB Digital I/ I/O ST PORTC Digital I/ USB Receive Input (from external transceiver — Reference Clock Output Schmitt Trigger input buffer C™ C/SMBus input buffer Description 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 17
... T1CK 12 9 TCK 17 14 TDI 16 13 TDO 18 15 TMS 14 11 USBID 14 11 USBOEN 17 14 Legend: TTL = TTL input buffer ANA = Analog level input/output 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Input I/O Buffer 21 I/O ST Remappable Peripheral (input or output I/O ST ...
Page 18
... A/D and Comparator Reference Voltage (low) Input ANA A/D and Comparator Reference Voltage (high) Input. P — Ground Reference for Logic and I/O Pins — USB Voltage (3.3V Schmitt Trigger input buffer C™ C/SMBus input buffer Description Control Output BUS PWM/Charge Output. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 19
... REF REF reference for analog modules is implemented Note: The AV and AV pins must always connected, regardless of whether any of the analog modules are being used. The minimum mandatory connections are shown in Figure 2-1. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY FIGURE 2- MCLR (2) C6 ...
Page 20
... The DD may be beneficial. A typical ) and fast signal transitions must IL is replaced for normal run-time EXAMPLE OF MCLR PIN CONNECTIONS R1 R2 MCLR PIC24FXXXX JP C1 and V specifications are met and V specifications are met. IL 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 21
... When the regulator is disabled, the V CAP must be tied to a voltage supply at the V Refer to Section 29.0 “Electrical Characteristics” for information on V and DDCORE 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY FIGURE 2- 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.01 Note: Data for Murata GRM21BF50J106ZE01 shown. ...
Page 22
... Copper Pour (tied to ground) OSCO GND Devices” OSCI DEVICE PINS SUGGESTED PLACEMENT OF THE OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT Primary Oscillator Crystal DEVICE PINS OSCI ` OSCO GND ` SOSCO SOSC I ` Sec Oscillator: C2 Top Layer Copper Pour (tied to ground) C2 Oscillator Crystal C1 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 23
... Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY If your application needs to use certain A/D pins as analog input pins during the debug session, the user application must modify the appropriate bits during initialization of the ADC module, as follows: • ...
Page 24
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 24 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 25
... Register Indirect modes. Each group offers up to seven addressing modes. Instructions are associated with predefined addressing modes depending upon their functional requirements. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY For most instructions, the core is capable of executing a data (or program data) memory read, a working reg- ister (data) read, a data memory write and a program (instruction) memory read per instruction cycle ...
Page 26
... Decode & Control Control Signals to Various Blocks DS39940D-page 26 Data Bus Data Latch PCL Data RAM Address Loop Latch Control Logic 16 RAGU WAGU EA MUX ROM Latch 16 Instruction Reg Hardware Multiplier Register Array Divide Support 16-Bit ALU Peripheral Modules 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 27
... W10 W11 W12 W13 W14 W15 22 Registers or bits shaded for PUSH.S and POP.S instructions. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Description Working Register Array 23-Bit Program Counter ALU STATUS Register Stack Pointer Limit Value Register Table Memory Page Address Register ...
Page 28
... Level (IPL). The value in parentheses indicates the IPL when IPL3 = 1. DS39940D-page 28 U-0 U-0 — — (1) R-0 R/W Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1,2) U-0 U-0 R/W-0 — — DC bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 29
... Data for the ALU operation can come from the W register array, or data memory, depending on the addressing mode of the instruction. Likewise, output data from the ALU can be written to the W register array or a data memory location. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — ...
Page 30
... All multi-bit shift instructions only support Register Direct Addressing for both the operand source and result destination. A full summary of instructions that use the shift operation is provided below in Table 3-2. Description 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 31
... Device Config Registers Reserved DEVID (2) Note: Memory areas are not shown to scale. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY from either the 23-bit Program Counter (PC) during pro- gram execution, or from table operation or data space remapping, as described in Section 4.3 “Interfacing Program and Data Memory Spaces”. ...
Page 32
... TABLE 4-1: Device PIC24FJ32GB0 PIC24FJ64GB0 least significant word Instruction Width FLASH CONFIGURATION WORDS FOR PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY DEVICES Program Configuration Memory Word (Words) Addresses 0057F8h: 11,008 0057FEh 00ABF8h: 22,016 00ABFEh PC Address (LSW Address) 0 000000h 000002h 000004h 000006h 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 33
... FFFFh Note: Data memory areas are not shown to scale. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY PIC24FJ64GB004 family devices implement a total of 16 Kbytes of data memory. Should an EA point to a location outside of this area, an all zero word or byte will be returned. ...
Page 34
... CRC/Comp Comparators System/DS NVM/PMD — xxA0 xxC0 xxE0 Interrupts — Compare — — I/O — — — USB — — — — PPS — — — — 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 35
TABLE 4-3: CPU CORE REGISTERS MAP File Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Name WREG0 0000 WREG1 0002 WREG2 0004 WREG3 0006 WREG4 0008 WREG5 000A WREG6 000C WREG7 000E WREG8 0010 WREG9 0012 WREG10 0014 WREG11 ...
Page 36
TABLE 4-4: ICN REGISTER MAP File Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Name CNEN1 0060 CN15IE — CN13IE CN12IE (1) CNEN2 0062 — CN30IE CN29IE CN28IE CNPU1 0068 CN15PUE — CN13PUE CN12PUE CN11PUE CN10PUE (1) CNPU2 006A ...
Page 37
TABLE 4-5: INTERRUPT CONTROLLER REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 INTCON1 0080 NSTDIS — — — INTCON2 0082 ALTIVT DISI — — IFS0 0084 — — AD1IF U1TXIF IFS1 0086 U2TXIF U2RXIF INT2IF ...
Page 38
TABLE 4-6: TIMER REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 TMR1 0100 PR1 0102 T1CON 0104 TON — TSIDL — TMR2 0106 TMR3HLD 0108 TMR3 010A PR2 010C PR3 010E T2CON 0110 TON — ...
Page 39
TABLE 4-7: INPUT CAPTURE REGISTER MAP File Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Name IC1CON1 0140 — — ICSIDL ICTSEL2 ICTSEL1 ICTSEL0 IC1CON2 0142 — — — — IC1BUF 0144 IC1TMR 0146 IC2CON1 0148 — — ICSIDL ...
Page 40
TABLE 4-8: OUTPUT COMPARE REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 OC1CON1 0190 — — OCSIDL OCTSEL2 OCTSEL1 OCTSEL0 OC1CON2 0192 FLTMD FLTOUT FLTTRIEN OCINV OC1RS 0194 OC1R 0196 OC1TMR 0198 OC2CON1 019A — ...
Page 41
TABLE 4-9: I C™ REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 I2C1RCV 0200 — — — — I2C1TRN 0202 — — — — I2C1BRG 0204 — — — — I2C1CON 0206 I2CEN — ...
Page 42
TABLE 4-11: SPI REGISTER MAPS File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 SPI1STAT 0240 SPIEN — SPISIDL — SPI1CON1 0242 — — — DISSCK SPI1CON2 0244 FRMEN SPIFSD SPIFPOL — SPI1BUF 0248 SPI2STAT 0260 SPIEN — ...
Page 43
TABLE 4-15: PAD CONFIGURATION REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 PADCFG1 02FC — — — — Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘0’. Reset values are shown in hexadecimal. TABLE 4-16: ADC REGISTER ...
Page 44
TABLE 4-18: USB OTG REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 U1OTGIR 0480 — — — — U1OTGIE 0482 — — — — U1OTGSTAT 0484 — — — — U1OTGCON 0486 — ...
Page 45
TABLE 4-18: USB OTG REGISTER MAP (CONTINUED) File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 U1EP0 04AA — — — — U1EP1 04AC — — — — U1EP2 04AE — — — — U1EP3 04B0 ...
Page 46
TABLE 4-20: REAL-TIME CLOCK AND CALENDAR REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 ALRMVAL 0620 ALCFGRPT 0622 ALRMEN CHIME AMASK3 AMASK2 RTCVAL 0624 RCFGCAL 0626 RTCEN — RTCWREN RTCSYNC HALFSEC Legend: — = unimplemented, ...
Page 47
TABLE 4-23: PERIPHERAL PIN SELECT REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 RPINR0 0680 — — — INT1R4 RPINR1 0682 — — — — RPINR3 0686 — — — T3CKR4 RPINR4 0688 — — ...
Page 48
TABLE 4-24: SYSTEM REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 RCON 0740 TRAPR IOPUWR — — OSCCON 0742 — COSC2 COSC1 COSC0 CLKDIV 0744 ROI DOZE2 DOZE1 DOZE0 OSCTUN 0748 — — — — ...
Page 49
TABLE 4-27: PMD REGISTER MAP File Name Addr Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 PMD1 0770 T5MD T4MD T3MD T2MD PMD2 0772 — — — IC5MD PMD3 0774 — — — — PMD4 0776 — — — — ...
Page 50
... Table 4-28 and Figure 4-5 show how the program EA is created for table operations and remapping accesses from the data EA. Here, P<23:0> refers to a program space word, whereas D<15:0> refers to a data space word. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 51
... Note 1: The LSb of program space addresses is always fixed as ‘0’ in order to maintain word alignment of data in the program and data spaces. 2: Table operations are not required to be word-aligned. Table read operations are permitted in the configuration memory space. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Program Space Address <23> ...
Page 52
... TBLRDL.B (Wn<0> TBLRDL.W The address for the table operation is determined by the data EA within the page defined by the TBLPAG register. 800000h Only read operations are shown; write operations are also valid in the user memory area. Data EA<15:0> 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 53
... PSVPAG is mapped into the upper half of the data memory space.... 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 24-bit program word are used to contain the data. The upper 8 bits of any program space locations used as data should be programmed with ‘1111 ‘0000 0000’ to force a NOP. This prevents possible issues should the area of code ever be accidentally executed ...
Page 54
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 54 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 55
... Using Table Instruction User/Configuration Space Select 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY RTSP is accomplished using TBLRD (table read) and TBLWT (table write) instructions. With RTSP, the user may write program memory data in blocks of 64 instruc- tions (192 bytes time and erase program memory in blocks of 512 instructions (1536 bytes time. Manual” ...
Page 56
... A complete programming sequence is necessary for programming or erasing the internal Flash in RTSP mode. During a programming or erase operation, the processor stalls (waits) until the operation is finished. Setting the WR bit (NVMCON<15>) starts the operation and the WR bit is automatically cleared when the operation is finished. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 57
... Memory row program operation (ERASE = operation (ERASE = 1) Note 1: These bits can only be reset on POR. 2: All other combinations of NVMOP<3:0> are unimplemented. 3: Available in ICSP™ mode only. Refer to the device programming specification. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY (1) U-0 U-0 — — ...
Page 58
... Initialize in-page EA[15:0] pointer ; Set base address of erase block ; Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; Write the 55 key ; ; Write the AA key ; Start the erase sequence ; Insert two NOPs after the erase ; command is asserted 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 59
... MOV #LOW_WORD_31, W2 MOV #HIGH_BYTE_31, W3 TBLWTL W2, [W0] TBLWTH W3, [W0] 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY // Address of row to write // Initialize PM Page Boundary SFR // Initialize lower word of address // Set base address of erase block // with dummy latch write // Initialize NVMCON // Block all interrupts with priority <7 ...
Page 60
... Initialize lower word of address // Write to address low word // Write to upper byte // Increment address ; Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; Write the 55 key ; ; Write the AA key ; Start the erase sequence ; ; ; and wait for completed 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 61
... TBLWT instructions to write latches __builtin_tblwtl(offset, progDataL); __builtin_tblwth(offset, progDataH); asm(“DISI #5”); __builtin_write_NVM(); 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY instructions write the desired data into the write latches and specify the lower 16 bits of the program memory address to write to. To configure the NVMCON register for a word write, set the NVMOP bits (NVMCON< ...
Page 62
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 62 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 63
... Enable Voltage Regulator Trap Conflict Illegal Opcode Configuration Mismatch Uninitialized W Register 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Any active source of Reset will make the SYSRST signal active. Many registers associated with the CPU and peripherals are forced to a known Reset state. ...
Page 64
... U-0 R/CO-0, HS — — DPSLP R/W-0, HS R/W-0, HS R/W-0, HS (2) WDTO SLEEP HS = Hardware Settable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (2) Preliminary R/W-0, HS R/W-0 CM PMSLP bit 8 R/W-1, HS R/W-1, HS IDLE BOR POR bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 65
... FNOSC Configuration bits (CW2<10:8>) BOR MCLR COSC Control bits (OSCCON<14:12>) WDTO SWR 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY (1) (CONTINUED) Setting Event 6.2 Device Reset Times The Reset times for various types of device Reset are summarized in Table 6-3. Note that the System Reset signal, SYSRST, is released after the POR and PWRT delay times expire ...
Page 66
... RST PWRT OST RST PWRT RST PWRT RST PWRT RST PWRT RST PWRT FRC RST PWRT RST PWRT FRC T RST ). DD Preliminary 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Notes Delay — FRC LPRC LOCK + LOCK OST + LOCK — FRC LPRC LOCK + LOCK OST ...
Page 67
... FRC Oscillator and the user can switch to the desired crystal oscillator in the Trap Service Routine (TSR). 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 6.3 Special Function Register Reset ...
Page 68
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 68 Preliminary 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 69
... PIC24FJ64GB004 family devices non-maskable traps and unique interrupts. These are summarized in Table 7-1 and Table 7-2. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 7.1.1 ALTERNATE INTERRUPT VECTOR TABLE The Alternate Interrupt Vector Table (AIVT) is located after the IVT, as shown in Figure 7-1. Access to the ...
Page 70
... Alternate Interrupt Vector Table (AIVT) 00017Ch 00017Eh 000180h 0001FEh 000200h AIVT Address 000104h Reserved 000106h Oscillator Failure 000108h Address Error 00010Ah Stack Error 00010Ch Math Error 00010Eh Reserved 000110h Reserved 000112h Reserved (1) (1) Trap Source 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 71
... SPI2 Error SPI2 Event Timer1 Timer2 Timer3 Timer4 Timer5 UART1 Error UART1 Receiver UART1 Transmitter UART2 Error UART2 Receiver UART2 Transmitter USB Interrupt 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Vector AIVT IVT Address Address 13 00002Eh 00012Eh 18 000038h 000138h 67 00009Ah 00019Ah ...
Page 72
... ISR is used for multiple vectors – such as when ISR remapping is used in boot- loader applications. It also could be used to check if another interrupt is pending while in an ISR. All interrupt registers are described in Register 7-1 through Register 7-35, on the following pages. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 73
... See Register 3-2 for the description of the remaining bit(s) that are not dedicated to interrupt control functions. 2: The IPL3 bit is concatenated with the IPL<2:0> bits (SR<7:5>) to form the CPU interrupt priority level. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 — ...
Page 74
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 74 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 MATHERR ADDRERR STKERR U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared U-0 U-0 — — bit 8 R/W-0 U-0 OSCFAIL — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 75
... INT1EP: External Interrupt 1 Edge Detect Polarity Select bit 1 = Interrupt on negative edge 0 = Interrupt on positive edge bit 0 INT0EP: External Interrupt 0 Edge Detect Polarity Select bit 1 = Interrupt on negative edge 0 = Interrupt on positive edge 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — ...
Page 76
... Interrupt request has not occurred DS39940D-page 76 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 U1TXIF U1RXIF SPI1IF U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — T1IF OC1IF U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 SPF1IF T3IF bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 IC1IF INT0IF bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 77
... MI2C1IF: Master I2C1 Event Interrupt Flag Status bit 1 = Interrupt request has occurred 0 = Interrupt request has not occurred bit 0 SI2C1IF: Slave I2C1 Event Interrupt Flag Status bit 1 = Interrupt request has occurred 0 = Interrupt request has not occurred 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 T5IF T4IF ...
Page 78
... Interrupt request has not occurred DS39940D-page 78 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 U-0 OC5IF — bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 SPI2IF SPF2IF bit Bit is unknown ...
Page 79
... Interrupt request has not occurred bit 1 SI2C2IF: Slave I2C2 Event Interrupt Flag Status bit 1 = Interrupt request has occurred 0 = Interrupt request has not occurred bit 0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — ...
Page 80
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 80 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — CRCIF U2ERIF U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. U-0 R/W-0 — LVDIF bit 8 R/W-0 U-0 U1ERIF — bit Bit is unknown ...
Page 81
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 6 USB1IF: USB1 (USB OTG) Interrupt Flag Status bit 1 = Interrupt request has occurred 0 = Interrupt request has not occurred bit 5-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — ...
Page 82
... Interrupt request is not enabled DS39940D-page 82 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 U1TXIE U1RXIE SPI1IE U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — T1IE OC1IE U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 SPF1IE T3IE bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 IC1IE INT0IE bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 83
... Interrupt request is enabled 0 = Interrupt request is not enabled Note external interrupt is enabled, the interrupt input must also be configured to an available RPn or PRIx pin. See Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) ...
Page 84
... Interrupt request is not enabled DS39940D-page 84 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 U-0 OC5IE — bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 SPI2IE SPF2IE bit Bit is unknown ...
Page 85
... Interrupt request is enabled 0 = Interrupt request is not enabled bit 1 SI2C2IE: Slave I2C2 Event Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Interrupt request is enabled 0 = Interrupt request is not enabled bit 0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 ...
Page 86
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 86 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — CRCIE U2ERIE U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. U-0 R/W-0 — LVDIE bit 8 R/W-0 U-0 U1ERIE — bit Bit is unknown ...
Page 87
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 6 USB1IE: USB1 (USB OTG) Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Interrupt request is enabled 0 = Interrupt request is not enabled bit 5-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 ...
Page 88
... Interrupt source is disabled DS39940D-page 88 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 T1IP0 — OC1IP2 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 IC1IP0 — INT0IP2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 OC1IP1 OC1IP0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 INT0IP1 INT0IP0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 89
... IC2IP<2:0>: Input Capture Channel 2 Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 T2IP0 — OC2IP2 R/W-0 ...
Page 90
... Interrupt source is disabled DS39940D-page 90 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 U1RXIP0 — SPI1IP2 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 SPF1IP0 — T3IP2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 SPI1IP1 SPI1IP0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 T3IP1 T3IP0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 91
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 2-0 U1TXIP<2:0>: UART1 Transmitter Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 ...
Page 92
... Interrupt source is disabled DS39940D-page 92 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 CNIP0 — CMIP2 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 MI2C1IP0 — SI2C1IP2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 CMIP1 CMIP0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 SI2C1IP1 SI2C1IP0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 93
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 2-0 INT1IP<2:0>: External Interrupt 1 Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 ...
Page 94
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 94 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 T4IP0 — OC4IP2 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 OC3IP0 — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 OC4IP1 OC4IP0 bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 95
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 2-0 T5IP<2:0>: Timer5 Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 U2TXIP0 — U2RXIP2 R/W-0 ...
Page 96
... Interrupt source is disabled DS39940D-page 96 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 SPI2IP0 — SPF2IP2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared U-0 U-0 — — bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 SPF2IP1 SPF2IP0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 97
... IC3IP<2:0>: Input Capture Channel 3 Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 IC5IP0 — IC4IP2 R/W-0 ...
Page 98
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 98 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 U-0 U-0 OC5IP0 — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared U-0 U-0 — — bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 99
... PMPIP<2:0>: Parallel Master Port Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 ...
Page 100
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 100 U-0 U-0 R/W-1 — — MI2C2IP2 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 SI2C2IP0 — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 MI2C2IP1 MI2C2IP0 bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 101
... RTCIP<2:0>: Real-Time Clock/Calendar Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled bit 7-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 R/W-1 — — RTCIP2 U-0 ...
Page 102
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 102 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-1 CRCIP0 — U2ERIP2 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 U1ERIP0 — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 U2ERIP1 U2ERIP0 bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 103
... CTMUIP<2:0>: CTMU Interrupt Priority bits 111 = Interrupt is Priority 7 (highest priority interrupt) • • • 001 = Interrupt is Priority 1 000 = Interrupt source is disabled bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — U-0 ...
Page 104
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 104 U-0 U-0 R/W-0 — — USB1IP2 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-0 USB1IP1 USB1IP0 bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown ...
Page 105
... VECNUM<6:0>: Pending Interrupt Vector ID bits (pending vector number is VECNUM + 8) 0111111 = Interrupt vector pending is Number 135 • • • 0000001 = Interrupt vector pending is Number 9 0000000 = Interrupt vector pending is Number 8 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 R-0 R-0 — ILR3 ILR2 ...
Page 106
... Note that only user interrupts with a priority level less can be disabled. Trap sources (Level 8-15) cannot be disabled. The DISI instruction provides a convenient way to disable interrupts of Priority Levels 1-6 for a fixed period of time. Level 7 interrupt sources are not disabled by the DISI instruction. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 107
... Secondary Oscillator SOSCO SOSCEN Enable SOSCI Oscillator 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY • An on-chip USB PLL block to provide a stable 48 MHz clock for the USB module, as well as a range of frequency options for the system clock • Software-controllable switching between various clock sources • ...
Page 108
... FCKSM<1:0> bits are both programmed (‘00’). Oscillator Source POSCMD<1:0> Internal 11 Internal xx Internal 11 Secondary 11 Primary 01 Primary 00 Primary 10 Primary 01 Primary 00 Internal 11 Internal 11 bits, POSCMD<1:0> (Configuration Configuration bits (Configuration FNOSC<2:0> Notes 1, 2 111 1 110 1 101 1 100 011 011 010 010 010 1 001 1 000 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 109
... IOL1WAY Configuration bit is ‘1’, once the IOLOCK bit is set, it cannot be cleared. 3: Also resets to ‘0’ during any valid clock switch or whenever a non-PLL Clock mode is selected. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY The OSCCON register (Register 8-1) is the main con- trol register for the oscillator ...
Page 110
... The state of the IOLOCK bit can only be changed once an unlocking sequence has been executed. In addition, if the IOL1WAY Configuration bit is ‘1’, once the IOLOCK bit is set, it cannot be cleared. 3: Also resets to ‘0’ during any valid clock switch or whenever a non-PLL Clock mode is selected. DS39940D-page 110 (2) (3) 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 111
... Disable PLL bit 4-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ Note 1: This bit is automatically cleared when the ROI bit is set and an interrupt occurs. 2: This setting is not allowed while the USB module is enabled. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) DOZE0 ...
Page 112
... FNOSCx Configuration bits. The OSWEN control bit (OSCCON<0>) has no effect when clock switching is disabled held at ‘0’ at all times. U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) (1) (1) TUN2 TUN1 TUN0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 113
... In these instances, the application must switch to FRC mode as a transition clock source between the two PLL modes. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY A recommended code sequence for a clock switch includes the following: 1. Disable interrupts during the OSCCON register unlock and write sequence ...
Page 114
... HSPLL, ECPLL 5 (100) HSPLL, ECPLL 4 (011) HSPLL, ECPLL 3 (010) HSPLL, ECPLL 2 (001) XTPLL, ECPLL 1 (000) XTPLL, ECPLL 48 MHz Clock for USB Module PLL Output 4 for System Clock 10 CPDIV<1:0> 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 115
... Unless proper care is taken in the design and layout of the SOSC circuit, this external noise may introduce inaccuracies into the oscillator’s period. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY In general, the crystal circuit connections should be as short as possible also good practice to surround the crystal circuit with a ground loop or ground plane ...
Page 116
... Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ DS39940D-page 116 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 ROSEL RODIV3 RODIV2 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 RODIV1 RODIV0 bit 8 U-0 U-0 — — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 117
... BSET DSCON, #DSEN ; Enable Deep Sleep PWRSAV #SLEEP_MODE ; Put the device into Deep SLEEP mode 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY The assembly syntax of the PWRSAV instruction is shown in Example 9-1. Note: SLEEP_MODE and IDLE_MODE are con- stants defined in the assembler include file for the selected device. Manual” ...
Page 118
... Enable Deep Sleep mode by setting the DSEN bit (DSCON<15>). 6. Enter Deep Sleep mode by immediately issuing a PWRSAV #0 instruction. Any time the DSEN bit is set, all bits in the DSWAKE register will be automatically cleared. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. CY WDT” for ...
Page 119
... PWRSAV instruction, in the event that the PWRSAV instruction is skipped and the device does not enter Deep Sleep mode. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Examples for implementing these cases are shown in Example 9- recommended that an assembler, or in-line C routine, be used in these cases to ensure that the code executes in the number of cycles required ...
Page 120
... Deep Sleep remain as output pins during Deep Sleep. While in this mode, they continue to drive the output level determined by their corresponding LAT bit at the time of entry into Deep Sleep. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. has dropped . This specifica well RST ...
Page 121
... For more details on the CW4 Configuration register and DSWDT configuration options, refer to Section 26.0 “Special Features”. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 9.2.4.8 Switching Clocks in Deep Sleep Mode Both the RTCC and the DSWDT may run from either SOSC or the LPRC clock source ...
Page 122
... The DSEN bit is automatically cleared. 11. Read and clear the DPSLP status bit in RCON, and the DSWAKE status bits. 12. Read the DSGPRx registers (optional). 13. Once all state related configurations are complete, clear the RELEASE bit. 14. Application resumes normal operation. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 123
... These bits are reset only in the case of a POR event outside of Deep Sleep mode. 2: Reset value is ‘0’ for initial power-on POR only and ‘1’ for Deep Sleep POR. 3: This is a status bit only; a DSBOR event will NOT cause a wake-up from Deep Sleep. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — ...
Page 124
... R/W-0, HS R/W-0, HS R/W-0, HS (1) (1) DSWDT DSRTC DSMCLR U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (2) U-0 R/W-0, HS (1) — DSINT0 bit 8 U-0 R/W-0, HS (1) (2) — DSPOR bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 125
... Enabling the automatic return to full-speed CPU operation on interrupts is enabled by setting the ROI bit (CLKDIV<15>). By default, interrupt events have no effect on Doze mode operation. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 9.4 Selective Peripheral Module Control Idle and Doze modes allow users to substantially reduce power consumption by slowing or stopping the CPU clock ...
Page 126
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 126 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 127
... CK WR PORT Data Latch Read LAT Read PORT 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY When a peripheral is enabled and the peripheral is actively driving an associated pin, the use of the pin as a general purpose output pin is disabled. The I/O pin may be read, but the output driver for the parallel port bit will be disabled ...
Page 128
... Tolerate Port or Pin Description d Input PORTA<4:0> V Only V DD levels are tolerated. PORTB<15:13> PORTB<4:0> (1) PORTC<3:0> (1) PORTA<10:7> 5.5V Tolerates input levels above V PORTB<11:7> most standard logic. PORTB<5> (1) PORTC<9:4> Note 1: Not available on 28-pin devices. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. on these pins input DD , useful for DD ...
Page 129
... I/O pins. Peripheral Pin Select is performed in software and generally does not require the device to be reprogrammed. Hardware 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY safeguards are included that prevent accidental or spurious changes to the peripheral mapping once it has been established ...
Page 130
... T5CK RPINR4 U1CTS RPINR18 U1RX RPINR18 U2CTS RPINR19 U2RX RPINR19 (1) Function Mapping Bits INT1R<5:0> INT2R<5:0> IC1R<5:0> IC2R<5:0> IC3R<5:0> IC4R<5:0> IC5R<5:0> OCFAR<5:0> OCFBR<5:0> SCK1R<5:0> SDI1R<5:0> SS1R<5:0> SCK2R<5:0> SDI2R<5:0> SS2R<5:0> T2CKR<5:0> T3CKR<5:0> T4CKR<5:0> T5CKR<5:0> U1CTSR<5:0> U1RXR<5:0> U2CTSR<5:0> U2RXR<5:0> 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 131
... The NULL function is assigned to all RPn outputs at device Reset and disables the RPn output function. ® 3: IrDA BCLK functionality uses this output. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY the bit field corresponds to one of the peripherals and that peripheral’s output is mapped to the pin (see Table 10-3). ...
Page 132
... Reset. In the default (unprogrammed) state, IOL1WAY is set, restricting users to one write session. Programming IOL1WAY allows users unlimited access (with the proper use of the unlock sequence) to the Peripheral Pin Select registers. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 133
... RPn pin function. I/O pins with unused RPn functions should be configured with the null peripheral output. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY The assignment of a peripheral to a particular pin does not automatically perform any other configuration of the pin’ ...
Page 134
... Configure Input Functions (Table 9-1) // Assign U1RX To Pin RP0 RPINR18bits.U1RXR = 0; // Assign U1CTS To Pin RP1 RPINR18bits.U1CTSR = 1; // Configure Output Functions (Table 9-2) // Assign U1TX To Pin RP2 RPOR1bits.RP2R = 3; // Assign U1RTS To Pin RP3 RPOR1bits.RP3R = 4; //lock registers __builtin_write_OSCCONL(OSCCON | 0x40); DS39940D-page 134 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 135
... Bit is set bit 15-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 INT1R<4:0>: Assign External Interrupt 2 (INT2) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Note: Input and output register values can only be changed if IOLOCK (OSCCON<6> See Section 10.4.4.1 “Control Register Lock” ...
Page 136
... T4CKR4 T4CKR3 T4CKR2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-1 R/W-1 T3CKR1 T3CKR0 bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 T2CKR1 T2CKR0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-1 R/W-1 T5CKR1 T5CKR0 bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 T4CKR1 T4CKR0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 137
... IC4R<4:0>: Assign Input Capture 4 (IC4) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 IC3R<4:0>: Assign Input Capture 3 (IC3) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 IC2R4 ...
Page 138
... OCFAR4 OCFAR3 OCFAR2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared U-0 U-0 — — bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 IC5R1 IC5R0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-1 R/W-1 OCFBR1 OCFBR0 bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 OCFAR1 OCFAR0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 139
... U2CTSR<4:0>: Assign UART2 Clear to Send (U2CTS) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 U2RXR<4:0>: Assign UART2 Receive (U2RX) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 U1CTSR4 ...
Page 140
... SS1R4 SS1R3 SS1R2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-1 R/W-1 SCK1R1 SCK1R0 bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 SDI1R1 SDI1R0 bit Bit is unknown U-0 U-0 — — bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-1 SS1R1 SS1R0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 141
... W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 15-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 SS2R<4:0>: Assign SPI2 Slave Select Input (SS2IN) to Corresponding RPn or RPIn Pin bits 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 SCK2R4 SCK2R3 SCK2R2 ...
Page 142
... RP0R4 RP0R3 RP0R2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 RP3R1 RP3R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP2R1 RP2R0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-0 R/W-0 RP1R1 RP1R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP0R1 RP0R0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 143
... Peripheral output number n is assigned to pin, RP7 (see Table 10-3 for peripheral function numbers). bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 RP6R<4:0>: RP6 Output Pin Mapping bits Peripheral output number n is assigned to pin, RP6 (see Table 10-3 for peripheral function numbers). 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP5R4 ...
Page 144
... RP10R4 RP10R3 RP10R2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 RP9R1 RP9R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP8R1 RP8R0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-0 R/W-0 RP11R1 RP11R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP10R1 RP10R0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 145
... Peripheral output number n is assigned to pin, RP0 (see Table 10-3 for peripheral function numbers). bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’ bit 4-0 RP14R<4:0>: RP14 Output Pin Mapping bits Peripheral output number n is assigned to pin, RP14 (see Table 10-3 for peripheral function numbers). 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP13R4 ...
Page 146
... RP18R4 RP18R3 RP18R2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) R/W-0 R/W-0 RP17R1 RP17R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP16R1 RP16R0 bit Bit is unknown (1) R/W-0 R/W-0 RP19R1 RP19R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP18R1 RP18R0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 147
... RP22R<4:0>: RP22 Output Pin Mapping bits Peripheral output number n is assigned to pin, RP22 (see Table 10-3 for peripheral function numbers). Note 1: This register is unimplemented in 28-pin devices; all bits read as ‘0’. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 ...
Page 148
... This register is unimplemented in 28-pin devices; all bits read as ‘0’. DS39940D-page 148 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP25R4 RP25R3 RP25R2 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP24R4 RP24R3 RP24R2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) R/W-0 R/W-0 RP25R1 RP25R0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 RP24R1 RP24R0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 149
... SOSCO/ T1CK SOSCI TGATE 1 Set T1IF 0 Reset Equal 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY Figure 11-1 presents a block diagram of the 16-bit timer module. To configure Timer1 for operation: 1. Set the TON bit (= 1). 2. Select the timer prescaler ratio using the TCKPS<1:0> bits. ...
Page 150
... DS39940D-page 150 (1) U-0 U-0 — — R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 TCKPS0 — TSYNC U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared /2) U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — bit 8 R/W-0 U-0 TCS — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 151
... Timer2 and Timer4 clock and gate inputs are utilized for the 32-bit timer modules, but an interrupt is generated with the Timer3 or Timer5 interrupt flags. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY To configure Timer2/3 or Timer4/5 for 32-bit operation: 1. Set the T32 bit (T2CON<3> or T4CON<3> = 1). ...
Page 152
... The ADC event trigger is available only on Timer 2/3 in 32-bit mode and Timer 3 in 16-bit mode. DS39940D-page 152 Gate Sync PR3 PR2 (PR5) (PR4) Comparator LSB TMR2 TMR3 (TMR4) (TMR5) 16 (1) ( TMR3HLD (TMR5HLD) TCKPS<1:0> 2 TON 1x Prescaler 1, 8, 64, 256 01 00 (2) TGATE (2) TCS Sync 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 153
... Note 1: The timer clock input must be assigned to an available RPn pin before use. Please see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2: The ADC event trigger is available only on Timer3. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 1x Gate Sync ...
Page 154
... DS39940D-page 154 U-0 U-0 — — R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) TCKPS0 T32 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (2) /2) (3) U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — bit 8 U-0 R/W-0 U-0 (2) — TCS — bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 155
... If TCS = 1, RPINRx (TxCK) must be configured to an available RPn pin. See Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 3: Changing the value of TyCON while the timer is running (TON = 1) causes the timer prescale counter to reset and is not recommended. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 (1) — ...
Page 156
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 156 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 157
... Reset Trigger and Sync Sources Note 1: The ICx inputs must be assigned to an available RPn pin before use. Please see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 13.1 General Operating Modes 13.1.1 ...
Page 158
... ICyBUF for the msw). At least one capture value is available in the FIFO buffer when the odd module’s ICBNE bit (ICxCON1<3>) becomes set. Continue to read the buffer registers until ICBNE is cleared (perform automatically by hardware). IC32 bits for both modules to configure Trigger or 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 159
... Input capture module turned off Note 1: The ICx input must also be configured to an available RPn pin. For more information, see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)”. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 ICTSEL2 ...
Page 160
... DS39940D-page 160 U-0 U-0 — — R/W-0 R/W-1 SYNCSEL4 SYNCSEL3 SYNCSEL2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (1) (1) U-0 U-0 R/W-0 — — IC32 bit 8 R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-1 SYNCSEL1 SYNCSEL0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 161
... Compare or PWM events are generated each time a match between the internal counter and one of the Period registers occurs. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY In Synchronous mode, the module begins performing its compare or PWM operation as soon as its selected clock source is enabled. Whenever an event occurs on the selected sync source, the module’ ...
Page 162
... Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. DS39940D-page 162 OCxCON1 OCxCON2 OCxR Match Event Comparator OCxTMR Reset Match Event Comparator OCxRS Preliminary DCBx OCMx OCINV OCTRIS FLTOUT FLTTRIEN FLTMD ENFLTx OCFLTx (1) OCx Pin OC Output and Fault Logic OCFA/ OCFB/ CxOUT OCx Interrupt 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 163
... Trigger mode operation starts after a trigger source event occurs. 7. Set the OCM<2:0> bits for the appropriate compare operation (= 0xx). 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY For 32-bit cascaded operation, these steps are also necessary: 1. Set the OC32 (OCyCON2< ...
Page 164
... OCxR and DCB<1:0> Buffers Comparator Match Event OCxTMR Rollover Reset Comparator Match Event OCxRS Buffer Rollover/Reset OCxRS Preliminary OCMx OCINV OCTRIS FLTOUT FLTTRIEN FLTMD ENFLTx OCFLTx DCB<1:0> (1) OCx Pin OC Output Timing and Fault Logic OCFA/OCFB/CxOUT OCx Interrupt 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 165
... Note 1: Based Doze mode and PLL are disabled. CY OSC 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 14.3.2 PWM DUTY CYCLE The PWM duty cycle is specified by writing to the OCxRS and OCxR registers. The OCxRS and OCxR registers can be written to at any time, but the duty cycle value is not latched until a period is complete ...
Page 166
... Hz 122 Hz 977 FFFFh 7FFFh 0FFFh 244 Hz 488 Hz 3.9 kHz FFFFh 7FFFh 0FFFh Preliminary ( MHz) CY 3.9 kHz 31.3 kHz 125 kHz 03FFh 007Fh 001Fh ( MHz) CY 15.6 kHz 125 kHz 500 kHz 03FFh 007Fh 001Fh 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 167
... The OCx output must also be configured to an available RPn pin. For more information, see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)”. 2: The comparator module used for Fault input varies with the OCx module. OC1 and OC2 use Comparator 1; OC3 and OC4 use Comparator 2; OC5 uses Comparator 3. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 ...
Page 168
... The OCx output must also be configured to an available RPn pin. For more information, see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)”. 2: The comparator module used for Fault input varies with the OCx module. OC1 and OC2 use Comparator 1; OC3 and OC4 use Comparator 2; OC5 uses Comparator 3. DS39940D-page 168 (1) Preliminary 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 169
... SYNCSEL setting. 2: Use these inputs as trigger sources only and never as sync sources. 3: These bits affect the rising edge when OCINV = 1. The bits have no effect when the OCM bits (OCxCON1<1:0>) = 001. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 (3) OCINV — ...
Page 170
... Use these inputs as trigger sources only and never as sync sources. 3: These bits affect the rising edge when OCINV = 1. The bits have no effect when the OCM bits (OCxCON1<1:0>) = 001. DS39940D-page 170 (1) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) Preliminary 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 171
... Enhanced Buffer mode. The module also supports a basic framed SPI protocol while operating in either Master or Slave mode. A total of four framed SPI configurations are supported. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY The SPI serial interface consists of four pins: • SDIx: Serial Data Input • ...
Page 172
... Clear the SPIROV bit (SPIxSTAT<6>). 7. Enable SPI operation by setting the SPIEN bit (SPIxSTAT<15>). 1:1 to 1:8 Secondary Prescaler Select Edge Shift Control Transfer Write SPIxBUF 16 Internal Data Bus registers with MSTEN 1:1/4/16/64 Primary F CY Prescaler SPIxCON1<1:0> SPIxCON1<4:2> Enable Master Clock 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 173
... SDOx bit 0 SDIx SPIxSR Transfer 8-Level FIFO Receive Buffer SPIxBUF Read SPIxBUF 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY To set up the SPI module for the Enhanced Buffer Slave mode of operation: 1. Clear the SPIxBUF register using interrupts: a) Clear the SPIxIF bit in the respective IFS register ...
Page 174
... U-0 U-0 — — SPIBEC2 R/W-0 R/W-0 SISEL2 SISEL1 HS = Hardware Settable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) R-0 R-0 R-0 SPIBEC1 SPIBEC0 bit 8 R/W-0 R-0 R-0 SISEL0 SPITBF SPIRBF bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 175
... Automatically cleared in hardware when a buffer location is available for a transfer from SPIxSR. Note 1: If SPIEN = 1, these functions must be assigned to available RPn pins before use. See Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY DS39940D-page 175 ...
Page 176
... R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) (2) DISSCK DISSDO MODE16 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 SPRE2 SPRE1 SPRE0 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (2) (3) (4) R/W-0 R/W-0 (3) SMP CKE bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 PPRE1 PPRE0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 177
... Frame sync pulse coincides with first bit clock 0 = Frame sync pulse precedes first bit clock bit 0 SPIBEN: Enhanced Buffer Enable bit 1 = Enhanced buffer enabled 0 = Enhanced buffer disabled (Legacy mode) 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY U-0 U-0 U-0 — — ...
Page 178
... SDIx SDIx SDOx Serial Clock SCKx SCKx (1) SSx SSx SSEN (SPIxCON1<7> MSTEN (SPIxCON1<5> and SPIBEN (SPIxCON2<0> (SPIxRXB) Shift Register (SPIxSR) LSb (SPIxTXB) SPIx Buffer (2) (SPIxBUF) Shift Register (SPIxSR) MSb LSb 8-Level FIFO Buffer SPIx Buffer (2) (SPIxBUF) 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 179
... FIGURE 15-7: SPI SLAVE, FRAME MASTER CONNECTION DIAGRAM PIC24F (SPI Slave, Frame Master) FIGURE 15-8: SPI SLAVE, FRAME SLAVE CONNECTION DIAGRAM PIC24F (SPI Slave, Frame Slave) 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY PROCESSOR 2 SDOx SDIx SDIx SDOx Serial Clock SCKx ...
Page 180
... Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 181
... Bus Repeater mode, allowing the acceptance of all messages as a slave regardless of the address • Automatic SCL A block diagram of the module is shown in Figure 16-1. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 16.1 Communicating as a Master in a Single Master Environment The details of sending a message in Master mode depends on the communications protocol for the device being communicated with ...
Page 182
... Bit Detect Start and Stop Bit Generation Collision Detect Acknowledge Generation Clock Stretching I2CxTRN LSB Reload Control Internal Data Bus Read Write I2CxMSK Read Write Read Write I2CxSTAT Read Write I2CxCON Read Write Read Write I2CxBRG Read 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 183
... The address bits listed here will never cause an address match, independent of address mask settings. 2: The address will be Acknowledged only if GCEN = match on this address can only occur on the upper byte in 10-Bit Addressing mode. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 16.3 Slave Address Masking The I2CxMSK register (Register 16-3) designates address bit positions as “ ...
Page 184
... R/W-0, HC R/W-0, HC R/W-0, HC ACKEN RCEN PEN U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2 C pins are controlled by port functions Slave slave slave) R/W-0 R/W-0 DISSLW SMEN bit 8 R/W-0, HC R/W-0, HC RSEN SEN bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 185
... Repeated Start condition not in progress bit 0 SEN: Start Condition Enabled bit (when operating Initiates Start condition on SDAx and SCLx pins. Hardware clear at end of master Start sequence Start condition not in progress 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 2 C master. Applicable during master receive.) 2 ...
Page 186
... HS = Hardware Settable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared 2 C slave) R-0, HSC R-0, HSC GCSTAT ADD10 bit 8 R-0, HSC R-0, HSC RBF TBF bit 0 HSC = Hardware Settable/Clearable bit x = Bit is unknown 2 C module is busy 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 187
... Hardware set when I2CxRCV is written with received byte. Hardware clear when software reads I2CxRCV. bit 0 TBF: Transmit Buffer Full Status bit 1 = Transmit in progress, I2CxTRN is full 0 = Transmit complete, I2CxTRN is empty Hardware set when software writes I2CxTRN. Hardware clear at completion of data transmission. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 2 C slave device address byte. ...
Page 188
... Disable masking for bit x; bit match required in this position DS39940D-page 188 U-0 U-0 U-0 — — — R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 AMSK4 AMSK3 AMSK2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 AMSK9 AMSK8 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 AMSK1 AMSK0 bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 189
... Note: The UART inputs and outputs must all be assigned to available RPn pins before use. Please see Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY • Fully Integrated Baud Rate Generator with 16-Bit Prescaler • ...
Page 190
... BRG timer to be reset (cleared). This ensures the BRG does not wait for a timer overflow before generating the new baud rate. /(16 * 65536). UART BAUD RATE WITH (1,2) BRGH = • (UxBRG + – • Baud Rate denotes the instruction cycle clock = F /2, Doze mode CY OSC /4 CY (1) 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 191
... Write ‘55h’ to UxTXREG; this loads the Sync character into the transmit FIFO. 5. After the Break has been sent, the UTXBRK bit is reset by hardware. The Sync character now transmits. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY 17.5 Receiving in 8-Bit or 9-Bit Data Mode 1. ...
Page 192
... DS39940D-page 192 R/W-0 R/W-0 U-0 (2) IREN RTSMD — R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 RXINV BRGH PDSEL1 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (2) R/W-0 R/W-0 UEN1 UEN0 bit 8 R/W-0 R/W-0 PDSEL0 STSEL bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 193
... If UARTEN = 1, the peripheral inputs and outputs must be configured to an available RPn pin. See Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2: This feature is only available for the 16x BRG mode (BRGH = 0). 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY DS39940D-page 193 ...
Page 194
... R/W-0, HC R/W-0 — UTXBRK UTXEN R-1 R-0 R-0 RIDLE PERR FERR HC = Hardware Clearable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (2) R-0 R-1 (2) UTXBF TRMT bit 8 R/C-0 R-0 OERR URXDA bit Bit is unknown 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 195
... Value of bit only affects the transmit properties of the module when the IrDA encoder is enabled (IREN = 1 UARTEN = 1, the peripheral inputs and outputs must be configured to an available RPn pin. See Section 10.4 “Peripheral Pin Select (PPS)” for more information. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY DS39940D-page 195 ...
Page 196
... PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY NOTES: DS39940D-page 196 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 197
... Configurations for on-chip bus pull-up and pull-down resistors A simplified block diagram of the USB OTG module is shown in Figure 18-1. 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY The USB OTG module can function as a USB periph- eral device USB host, and may dynamically switch between Device and Host modes under soft- ware control ...
Page 198
... Note 1: Pins are multiplexed with digital I/O and other device features. DS39940D-page 198 Transceiver Host Pull-down USB SIE External Transceiver Interface USB Voltage Comparators V BUS Boost Assist 48 MHz USB Clock Registers and Control Interface System RAM 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 199
... USB. Note that an attach indication is added to indicate when the USB has been connected and the host is actively powering V 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC24FJ64GB004 FAMILY To meet compliance specifications, the USB module (and the pull-up resistor) should not be enabled until the host actively drives V tolerant I/O pins may be used for this purpose ...
Page 200
... V DD MCP1253 V GND IN SELECT C+ 10 µF 1 µF C- SHND V PGOOD OUT 40 k and is not able to BUS and regu- BUS on or off as BUS ® PIC Microcontroller USB A/D pin V BUS ® PIC Microcontroller I/O I/O V BUS 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...