MC68HC705KJ1CDW Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC705KJ1CDW Datasheet - Page 73
MC68HC705KJ1CDW
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC705KJ1CDW
Description
IC MCU 4MHZ 1.2K OTP 16-SOIC
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC05r
Datasheet
1.MCHRC705KJ1CDWE.pdf
(108 pages)
Specifications of MC68HC705KJ1CDW
Core Processor
HC05
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
4MHz
Peripherals
POR, WDT
Number Of I /o
10
Program Memory Size
1.2KB (1.2K x 8)
Program Memory Type
OTP
Ram Size
64 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 5.5 V
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
16-SOIC (0.300", 7.5mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Data Converters
-
Connectivity
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MC68HC705KJ1CDW
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
8.2.3 COP Watchdog Reset
A timeout of the COP watchdog generates a COP reset. The COP watchdog is part of a software error
detection system and must be cleared periodically to start a new timeout period. To clear the COP
watchdog and prevent a COP reset, write a logic 0 to bit 0 (COPC) of the COP register at location $07F0.
8.2.4 Illegal Address Reset
An opcode fetch from an address not in RAM or EPROM generates a reset.
8.3 Interrupts
The following sources can generate interrupts:
An interrupt temporarily stops the program sequence to process a particular event. An interrupt does not
stop the operation of the instruction being executed, but takes effect when the current instruction
completes its execution. Interrupt processing automatically saves the CPU registers on the stack and
loads the program counter with a user-defined interrupt vector address.
8.3.1 Software Interrupt
The software interrupt (SWI) instruction causes a non-maskable interrupt.
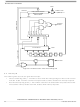
8.3.2 External Interrupt
An interrupt signal on the IRQ/V
current instruction, it tests the IRQ latch. If the IRQ latch is set, the CPU then tests the I bit in the condition
code register. If the I bit is clear, the CPU then begins the interrupt sequence.
The CPU clears the IRQ latch during interrupt processing, so that another interrupt signal on the IRQ/V
pin can latch another interrupt request during the interrupt service routine. As soon as the I bit is cleared
during the return from interrupt, the CPU can recognize the new interrupt request.
IRQ/V
Setting the I bit in the condition code register disables external interrupts.
The port A external interrupt bit (PIRQ) in the mask option register enables pins PA0–PA3 to function as
external interrupt pins.
The external interrupt sensitivity bit (LEVEL) in the mask option register controls interrupt triggering
sensitivity of external interrupt pins. The IRQ/V
negative-edge and low-level triggered. Port A external interrupt pins can be positive-edge triggered only
or both positive-edge and high-level triggered. The level-sensitive triggering option allows multiple
external interrupt sources to be wire-ORed to an external interrupt pin. An external interrupt request,
shown in
Freescale Semiconductor
•
•
•
PP
SWI instruction
External interrupt pins
–
–
Timer
–
–
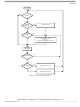
pin interrupt logic.
Figure
IRQ/V
PA0–PA3 pins
Real-time interrupt flag (RTIF)
Timer overflow flag (TOF)
PP
8-5, is latched as long as any source is holding an external interrupt pin low.
MC68HC705KJ1 • MC68HRC705KJ1 • MC68HLC705KJ1 Data Sheet, Rev. 4.1
pin
PP
pin latches an external interrupt request. When the CPU completes its
PP
pin can be negative-edge triggered only or
Figure 8-4
shows the
Interrupts
PP
73