MPC564MZP66 Freescale Semiconductor, MPC564MZP66 Datasheet - Page 610
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC564MZP66
Description
IC MCU 512K FLASH 66MHZ 388-BGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
MPC5xxr
Specifications of MPC564MZP66
Core Processor
PowerPC
Core Size
32-Bit
Speed
66MHz
Connectivity
CAN, EBI/EMI, SCI, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
56
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
32K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 2.7 V
Data Converters
A/D 32x10b
Oscillator Type
External
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Package / Case
388-BGA
For Use With
MPC564EVB - KIT EVAL FOR MPC561/562/563/564
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66R2
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 610 of 1420
- Download datasheet (11Mb)
QADC64E Enhanced Mode Operation
Analog supplies should be isolated from digital supplies as much as possible. This necessity stems from
the higher performance requirements often associated with analog circuits. Therefore, deriving an analog
supply from a local digital supply is not recommended. However, if for economic reasons digital and
analog power are derived from a common regulator, filtering of the analog power is recommended in
addition to the bypassing of the supplies already mentioned.
Grounding is the most important factor influencing analog circuit performance in mixed signal systems (or
in stand-alone analog systems). Close attention must be paid not to introduce additional sources of noise
into the analog circuitry. Common sources of noise include ground loops, inductive coupling, and
combining digital and analog grounds together inappropriately.
The problem of how and when to combine digital and analog grounds arises from the large transients
which the digital ground must handle. If the digital ground is not able to handle the large transients, the
current from the large transients can return to ground through the analog ground. It is the excess current
overflowing into the analog ground which causes performance degradation by developing a differential
voltage between the true analog ground and the microcontroller’s ground signal. The end result is that the
ground observed by the analog circuit is no longer true ground and often ends in skewed results.
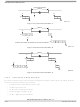
Two similar approaches designed to improve or eliminate the problems associated with grounding excess
transient currents involve star-point ground systems. One approach is to star-point the different grounds at
the power supply origin, thus keeping the ground isolated. Refer to
14-68
An RC low pass filter could be used to isolate the digital and analog supplies
when generated by a common regulator. If multiple high precision analog
circuits are locally employed (i.e., two A/D converters), the analog supplies
should be isolated from each other as sharing supplies introduces the
potential for interference between analog circuits.
MPC561/MPC563 Reference Manual, Rev. 1.2
NOTE
Figure
14-49.
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for MPC564MZP66
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1K0 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 500R 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5K0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 50K 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: