C8051F320 Silicon Laboratories Inc, C8051F320 Datasheet - Page 177
C8051F320
Manufacturer Part Number
C8051F320
Description
IC 8051 MCU 16K FLASH 32LQFP
Manufacturer
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Series
C8051F32xr
Datasheet
1.C8051F320R.pdf
(256 pages)
Specifications of C8051F320
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
25MHz
Connectivity
SMBus (2-Wire/I²C), SPI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, Temp Sensor, WDT
Number Of I /o
25
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
2.25K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 17x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
32-LQFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
C8051F320
Manufacturer:
SILICON LABS/芯科
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
18 793
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
SILICON
Quantity:
1
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
1 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
SILICON LABS/芯科
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320DK
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
4
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320R
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
C8051F320/1
16.3. SMBus Operation
Two types of data transfers are possible: data transfers from a master transmitter to an addressed slave receiver
(WRITE), and data transfers from an addressed slave transmitter to a master receiver (READ). The master device ini-
tiates both types of data transfers and provides the serial clock pulses on SCL. The SMBus interface may operate as a
master or a slave, and multiple master devices on the same bus are supported. If two or more masters attempt to ini-
tiate a data transfer simultaneously, an arbitration scheme is employed with a single master always winning the arbi-
tration. Note that it is not necessary to specify one device as the Master in a system; any device who transmits a
START and a slave address becomes the master for the duration of that transfer.
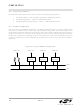
A typical SMBus transaction consists of a START condition followed by an address byte (Bits7-1: 7-bit slave
address; Bit0: R/W direction bit), one or more bytes of data, and a STOP condition. Each byte that is received (by a
master or slave) must be acknowledged (ACK) with a low SDA during a high SCL (see Figure 16.3). If the receiving
device does not ACK, the transmitting device will read a NACK (not acknowledge), which is a high SDA during a
high SCL.
The direction bit (R/W) occupies the least-significant bit position of the address byte. The direction bit is set to logic
1 to indicate a "READ" operation and cleared to logic 0 to indicate a "WRITE" operation.
All transactions are initiated by a master, with one or more addressed slave devices as the target. The master gener-
ates the START condition and then transmits the slave address and direction bit. If the transaction is a WRITE opera-
tion from the master to the slave, the master transmits the data a byte at a time waiting for an ACK from the slave at
the end of each byte. For READ operations, the slave transmits the data waiting for an ACK from the master at the
end of each byte. At the end of the data transfer, the master generates a STOP condition to terminate the transaction
and free the bus. Figure 16.3 illustrates a typical SMBus transaction.
Figure 16.3. SMBus Transaction
SCL
SDA
SLA6
SLA5-0
R/W
D7
D6-0
START
Slave Address + R/W
ACK
Data Byte
NACK
STOP
16.3.1. Arbitration
A master may start a transfer only if the bus is free. The bus is free after a STOP condition or after the SCL and SDA
lines remain high for a specified time (see
Section “16.3.4. SCL High (SMBus Free) Timeout” on page
178). In the
event that two or more devices attempt to begin a transfer at the same time, an arbitration scheme is employed to
force one master to give up the bus. The master devices continue transmitting until one attempts a HIGH while the
other transmits a LOW. Since the bus is open-drain, the bus will be pulled LOW. The master attempting the HIGH
will detect a LOW SDA and lose the arbitration. The winning master continues its transmission without interruption;
the losing master becomes a slave and receives the rest of the transfer if addressed. This arbitration scheme is non-
destructive: one device always wins, and no data is lost.
Rev. 1.1
177