MC908AZ32ACFU Freescale Semiconductor, MC908AZ32ACFU Datasheet - Page 209
MC908AZ32ACFU
Manufacturer Part Number
MC908AZ32ACFU
Description
IC MCU 32K FLASH 8.4MHZ 64-QFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC08r
Datasheet
1.MC908AZ32ACFUE.pdf
(324 pages)
Specifications of MC908AZ32ACFU
Core Processor
HC08
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
CAN, SCI, SPI
Peripherals
LVD, POR, PWM
Number Of I /o
40
Program Memory Size
32KB (32K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
512 x 8
Ram Size
1K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 15x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-QFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFU
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
3
Company:
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFU
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFU
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFUE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFUE
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC908AZ32ACFUER
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 209 of 324
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
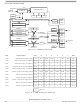
Functional Description
19.3.2 Input Capture
An input capture function has three basic parts: edge select logic, an input capture latch and a 16-bit
counter. Two 8-bit registers, which make up the 16-bit input capture register, are used to latch the value
of the free-running counter after the corresponding input capture edge detector senses a defined
transition. The polarity of the active edge is programmable. The level transition which triggers the counter
transfer is defined by the corresponding input edge bits (ELSxB and ELSxA in TBSC0 through TBSC1
control registers with x referring to the active channel number). When an active edge occurs on the pin of
an input capture channel, the TIMB latches the contents of the TIMB counter into the TIMB channel
registers, TBCHxH–TBCHxL. Input captures can generate TIMB CPU interrupt requests. Software can
determine that an input capture event has occurred by enabling input capture interrupts or by polling the
status flag bit.
The result obtained by an input capture will be two more than the value of the free-running counter on the
rising edge of the internal bus clock preceding the external transition. This delay is required for internal
synchronization.
The free-running counter contents are transferred to the TIMB channel register (TBCHxH–TBCHxL, see
19.8.5 TIMB Channel
Registers) on each proper signal transition regardless of whether the TIMB channel
flag (CH0F–CH1F in TBSC0–TBSC1 registers) is set or clear. When the status flag is set, a CPU interrupt
is generated if enabled. The value of the count latched or “captured” is the time of the event. Because this
value is stored in the input capture register 2 bus cycles after the actual event occurs, user software can
respond to this event at a later time and determine the actual time of the event. However, this must be
done prior to another input capture on the same pin; otherwise, the previous time value will be lost.
By recording the times for successive edges on an incoming signal, software can determine the period
and/or pulse width of the signal. To measure a period, two successive edges of the same polarity are
captured. To measure a pulse width, two alternate polarity edges are captured. Software should track the
overflows at the 16-bit module counter to extend its range.
Another use for the input capture function is to establish a time reference. In this case, an input capture
function is used in conjunction with an output compare function. For example, to activate an output signal
a specified number of clock cycles after detecting an input event (edge), use the input capture function to
record the time at which the edge occurred. A number corresponding to the desired delay is added to this
captured value and stored to an output compare register (see
19.8.5 TIMB Channel
Registers). Because
both input captures and output compares are referenced to the same 16-bit modulo counter, the delay
can be controlled to the resolution of the counter independent of software latencies.
Reset does not affect the contents of the input capture channel register (TBCHxH–TBCHxL).
19.3.3 Output Compare
With the output compare function, the TIMB can generate a periodic pulse with a programmable polarity,
duration and frequency. When the counter reaches the value in the registers of an output compare
channel, the TIMB can set, clear or toggle the channel pin. Output compares can generate TIMB CPU
interrupt requests.
MC68HC908AZ32A Data Sheet, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor
209
Related parts for MC908AZ32ACFU
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: