AD9268-125EBZ Analog Devices Inc, AD9268-125EBZ Datasheet - Page 28

AD9268-125EBZ
Manufacturer Part Number
AD9268-125EBZ
Description
Dual 16 Bit 125 High SNR ADC
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD9268BCPZ-80.pdf
(44 pages)
Specifications of AD9268-125EBZ
Design Resources
Powering AD9268 with ADP2114 for Increased Efficiency (CN0137)
Number Of Adc's
2
Number Of Bits
16
Sampling Rate (per Second)
125M
Data Interface
Serial, SPI™
Inputs Per Adc
1 Differential
Input Range
1 ~ 2 Vpp
Power (typ) @ Conditions
750mW @ 125MSPS
Voltage Supply Source
Analog and Digital
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Utilized Ic / Part
AD9268
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
AD9268
The signal characteristics must be considered when selecting
a transformer. Most RF transformers saturate at frequencies
below a few megahertz (MHz). Excessive signal power can also
cause core saturation, which leads to distortion.
At input frequencies in the second Nyquist zone and above, the
noise performance of most amplifiers is not adequate to achieve
the true SNR performance of the AD9268. For applications in
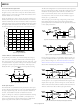
which SNR is a key parameter, differential double balun coupling
is the recommended input configuration (see Figure 68). In this
configuration, the input is ac-coupled, and the CML is provided
to each input through a 33 Ω resistor. These resistors compensate
for losses in the input baluns to provide a 50 Ω impedance to
the driver.
In the double balun and transformer configurations, the value of
the input capacitors and resistors is dependent on the input fre-
quency and source impedance and may need to be reduced or
removed. Table 10 displays recommended values to set the RC
network. At higher input frequencies, good performance can be
ANALOG INPUT
ANALOG INPUT
2V p-p
C
D
0.1µF
P
0.1µF
0.1µF
A
R
D
0Ω
0Ω
Figure 69. Differential Input Configuration Using the AD8352
R
Figure 68. Differential Double Balun Input Configuration
G
S
16
1
2
3
4
5
S
AD8352
V
CC
P
8, 13
14
0.1µF
Rev. A | Page 28 of 44
0.1µF
0.1µF
10
11
33Ω
33Ω
0.1µF
0.1µF
achieved by using a ferrite bead in series with a resistor and
removing the capacitors. However, these values are dependent
on the input signal and should be used only as a starting guide.
Table 10. Example RC Network
Frequency
Range
(MHz)
0 to 100
100 to 200
100 to 300
1
An alternative to using a transformer-coupled input at fre-
quencies in the second Nyquist zone is to use the
differential driver. An example is shown in Figure 69. See the
AD8352 data sheet for more information.
0.1µF
200Ω
200Ω
In this configuration, R1 is a ferrite bead with a value of 10 Ω @ 100 MHz.
0.1µF
R1
R1
0.1µF
C2
C1
C2
R
R
C
R1 Series
(Ω Each)
33
10
10
R2
R2
1
VIN+
VIN–
AD9268
VIN+
VIN–
C1 Differential
(pF)
5
5
Remove
AD9268
VCM
VCM
R2 Series
(Ω Each)
15
10
66
AD8352
C2 Shunt
(pF Each)
15
10
Remove