LFE2M20E-6FN484C LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR, LFE2M20E-6FN484C Datasheet - Page 11
LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Manufacturer Part Number
LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Description
FPGA LatticeECP2M Family 19000 Cells 90nm (CMOS) Technology 1.2V 484-Pin FBGA
Manufacturer
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet
1.LFE2-12SE-6FN256C.pdf
(389 pages)
Specifications of LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Package
484FBGA
Family Name
LatticeECP2M
Device Logic Units
19000
Typical Operating Supply Voltage
1.2 V
Maximum Number Of User I/os
304
Ram Bits
1246208
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Manufacturer:
Lattice
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
350
Company:
Part Number:
LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
LFE2M20E-6FN484C-5I
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
11
Part Number:
LFE2M20E-6FN484C-5I
Manufacturer:
LATTICE
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 11 of 389
- Download datasheet (5Mb)
Lattice Semiconductor
Delay Locked Loops (DLL)
In addition to PLLs, the LatticeECP2/M family of devices has two DLLs per device.
CLKI is the input frequency (generated either from the pin or routing) for the DLL. CLKI feeds into the output muxes
block to bypass the DLL, directly to the DELAY CHAIN block and (directly or through divider circuit) to the reference
input of the Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) input mux. The reference signal for the PFD can also be generated
from the Delay Chain and CLKFB signals. The feedback input to the PFD is generated from the CLKFB pin, CLKI
or from tapped signal from the Delay chain.
The PFD produces a binary number proportional to the phase and frequency difference between the reference and
feedback signals. This binary output of the PFD is fed into a Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). Based on these inputs,
the ALU determines the correct digital control codes to send to the delay chain in order to better match the refer-
ence and feedback signals. This digital code from the ALU is also transmitted via the Digital Control bus (DCNTL)
bus to its associated DLLDELA delay block. The ALUHOLD input allows the user to suspend the ALU output at its
current value. The UDDCNTL signal allows the user to latch the current value on the DCNTL bus.
The DLL has two independent clock outputs, CLKOP and CLKOS. These outputs can individually select one of the
outputs from the tapped delay line. The CLKOS has optional fine phase shift and divider blocks to allow this output
to be further modified, if required. The fine phase shift block allows the CLKOS output to phase shifted a further 45,
22.5 or 11.25 degrees relative to its normal position. Both the CLKOS and CLKOP outputs are available with
optional duty cycle correction. Divide by two and divide by four frequencies are available at CLKOS. The LOCK out-
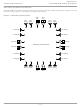
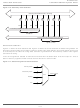
put signal is asserted when the DLL is locked. Figure 2-6 shows the DLL block diagram and Table 2-5 provides a
description of the DLL inputs and outputs.
The user can configure the DLL for many common functions such as time reference delay mode and clock injection
removal mode. Lattice provides primitives in its design tools for these functions. For more information about the
DLL, please see the list of additional technical documentation at the end of this data sheet.
Figure 2-6. Delay Locked Loop Diagram (DLL)
internal), from clock net
(CLKOP) or from a user
ALUHOLD
UDDCNTL
clock (pin or logic)
from CLKOP (DLL
or external pin)
(from routing
CLKFB
RSTN
CLKI
÷4
÷2
Reference
Feedback
Frequency
Detector
Phase
Arithmetic
Logic Unit
2-8
Delay Chain
Delay0
Delay1
Delay2
Delay3
Delay4
LatticeECP2/M Family Data Sheet
Detect
Lock
Output
Muxes
Control
Output
Digital
Cycle
Cycle
Duty
Duty
50%
50%
Architecture
÷4
÷2
9
CLKOP
CLKOS
LOCK
DCNTL
Related parts for LFE2M20E-6FN484C
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
IC, LATTICEECP2M FPGA, 420MHZ, FPBGA-256
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
IC, LATTICEECP2M FPGA, 420MHZ, FPBGA-256
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
FPGA LatticeECP2M Family 19000 Cells 90nm (CMOS) Technology 1.2V 484-Pin FBGA
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
FPGA LatticeECP2M Family 19000 Cells 90nm (CMOS) Technology 1.2V 484-Pin FBGA
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
FPGA LatticeECP2M Family 19000 Cells 90nm (CMOS) Technology 1.2V 256-Pin FBGA
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
FPGA LatticeECP2M Family 19000 Cells 90nm (CMOS) Technology 1.2V 256-Pin FBGA
Manufacturer:
LATTICE SEMICONDUCTOR
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
ISPLSI2032-80LT44Lattice Semiconductor [In-System Programmable High Density PLD]
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
IC PROGRAMMED LATTICE GAL 16V8
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
357-036-542-201 CARDEDGE 36POS DL .156 BLK LOPRO
Manufacturer:
Lattice Semiconductor Corp.
Datasheet: