AM79C031JC AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), AM79C031JC Datasheet

AM79C031JC
Specifications of AM79C031JC
Available stocks
Related parts for AM79C031JC
AM79C031JC Summary of contents
Page 1
... When used with two AMD SLICs, the DSLAC device provides software config- urable solutions to the BORSCHT function. Publication# 09875 Rev: J Issue Date: December 1999 ...
Page 2
... Summary of MPI Commands Command Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 Programmable Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 Detailed Description of DSLAC Device Coefficients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Adaptive B Filter Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 Adaptive Filter Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 User Test Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 A-Law and -Law Companding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 Controlling the SLIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 Calculating Coefficients with WinSLAC Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 Physical Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 Revision Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 2 Am79C02/03/031(A) Data Sheet ...
Page 3
LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1 Attenuation Distortion (Single Ended ...
Page 4
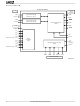
... (02 & 031 only Interface (02 & 031 only Dual SLAC Device SLIC (SLI) Microprocessor Interface CS1 Am79C02/03/031(A) Data Sheet Highway DXA DRA TSCA Time Slot Assigner DXB (TSA) DRB TSCB FS PCLK RST (02 only) (MPI) MCLK CS2 DIN DOUT DCLK Microprocessor 09875H-001 ...
Page 5
ORDERING INFORMATION Standard Products AMD standard products are available in several packages and operating ranges. The order number (Valid Combi- nation) is formed by a combination of the elements below. Am79C02/03/031 A Valid Combinations Am79C02 Am79C03 Am79C031 Note: * Functionality ...
Page 6
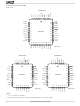
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS Top View AGND 1 RSVD VIN 1 VEE 1 VOUT 1 VCCA 1 VCCA 2 VOUT 2 VEE 2 VIN 2 AGND 2 32-Pin PLCC AGND 6 VIN VEE 1 Am79C031 9 ...
Page 7
... C1 –C5 be used to monitor or control the operation of a SLIC or any other device associated with the 2 2 subscriber line. Lines C11–C51 are associated with Channel 1, and lines C12–C52 are associated with Channel 2. The C51 and C52 lines are available on the Am79C02(A) and Am79C031(A). C51 and C52 are output only on the Am79C031(A) and must be programmed as outputs ...
Page 8
Power supply for the Am79C02: AGND Analog Ground (Channel 1) 1 AGND Analog Ground (Channel 2) 2 DGND Digital Ground (Channel 1) 1 DGND Digital Ground (Channel 2) 2 PGND PCM I/O Ground VCCA +5 V Analog Power Supply (Channel ...
Page 9
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Storage temperature . . . . . . . . .–60°C Ambient operating temperature . .–40°C Ambient relative humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5% to 100% V with ...
Page 10
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS over operating range unless otherwise noted Typical values are for T = 25°C and nominal supply voltages. Minimum and maximum specifications are over the A temperature and supply voltage ranges shown in Operating Ranges. Symbol Parameter Descriptions V ...
Page 11
Transmission Characteristics The gain of the receive path is defined when a 0 dBm0, 1014 Hz PCM sine wave input results in a nominal 1.55 Vrms for µ-law or 1.56 Vrms for A-law analog output. The ...
Page 12
Attenuation Distortion 2 Attenuation (dB) 1 0.125 0 –0.125 (transmit only) 200 300 Figure 1. Attenuation Distortion (Single Ended) Group Delay Distortion For either transmission path, the group delay distortion is within the limits shown in Figure 2. The minimum ...
Page 13
Variation of Gain with Input Level The gain deviation relative to the gain at –10 dBm0 is within the limits shown if Figure 3 for either transmission path when the input is a sine wave signal of frequency 1014 Hz. ...
Page 14
Discrimination against Out-of-Band Input Signals When an out-of-band sine wave signal with frequency f and level A is applied to the analog input, there may be frequency components below 4 kHz at the digital output, caused by the out-of-band signal. ...
Page 15
Discrimination against 12 kHz and 16 kHz Metering Signals If the DSLAC device is used in a metering application where 12 kHz or 16 kHz tone bursts are injected onto the telephone line toward the subscriber, a portion of those ...
Page 16
Overload Compression Figure 7 shows the acceptable region of operation for input signal levels above the reference input power (0 dBm0). The conditions for this figure are: ( < GX PCM input; and (4) measurement analog-to-analog ...
Page 17
... Chip Select Off Time, Input Mode (Note 7) ICSO 10 t Input Data Setup Time IDS 11 t Input Data Hold Time IDH 12 t SLIC Output Latch Valid OLH 13 t Chip Select Setup Time, Output Mode OCSS 14 t Chip Select Hold Time, Output Mode OCSH 15 t ...
Page 18
Master Clock For 2.048 MHz ±100 ppm or 4.096 MHz ±100 ppm operation: No. Symbol 35 t Master Clock Period (2.048 MHz) MCY Master Clock Period (4.096 MHz Rise Time of Clock MCR 37 t Fall Time of ...
Page 19
Microprocessor Interface (Input Mode DCLK Data DIN Valid Outputs C5–C1 Microprocessor Interface (Output Mode DCLK Three-State Data OH DOUT ...
Page 20
PCM Highway Timing for (Transmit on Negative PCLK Edge PCLK 26 FS TSCA/ TSCB 30 DXA/DXB DRA/DRB 20 Time Slot Zero Clock Slot Zero ...
Page 21
PCM Highway Timing for (Transmit on Positive PCLK Edge PCLK 26 FS TSCA/ TSCB DXA/DXB DRA/DRB Note: In this mode, the PCM transmit timing is compatible with other CODEC IC’s. Time Slot Zero ...
Page 22
... Digital (GX and GR) gain blocks are disabled, resulting in unity gain, and analog (AX and AR) gains are set to unity. 4. SLIC input/output direction is set to the Input mode. 5. Normal conditions are selected (see Command 4). 6. The B-filter Adaptive mode is turned off. 7. Both channels placed in Inactive (standby) mode. ...
Page 23
VIN Decimator ADC AX & HPF AISN Analog Loopback * Digital (also uses Loop- RX Cutoff) back (#21) (#13) * Inter DAC polator VOUT * programmable blocks Distortion Correction and Equalization The DSLAC device contains programmable filters ...
Page 24
... A2 AISN where and The AISN gain is used to alter the input impedance of the DSLAC device from the SLIC as given by: Z where G (defined as G 440 gain into an open circuit and G a short circuit. There are two special cases to the formula for h ...
Page 25
... X-filter coefficients – R-filter coefficients – Z-filter coefficients – Adaptive B filter parameters – AISN coefficient – Read/Write SLIC Input/Output – Select A-law or µ-law code – Select Transmit PCM Port – Select Transmit PCM clock edge – Select Transmit PCM delay – ...
Page 26
... Read AISN, PCM delay, Analog Gains 15. 52 Write SLIC Input/Output Register 16. 53 Read SLIC Input/Output Register 17. 54 Write SLIC Input/Output Direction 18. 55 Read SLIC I/O Direction, Power Interrupt Bit, and Channel Status Bit 19. 60 Write Operating Functions 20. 61 Read Operating Functions 21. 70 Write Operating Conditions 22. ...
Page 27
... GX, GR and Z filters are disabled with coefficients retained and AR are set to unity and AISN gain is set The Adaptive B feature is disabled. e) A-law is selected. f) All SLIC I/O lines are configured as inputs. g) Normal conditions are selected (see Command 4 Operation (06h) Command 4. Reset to Normal Conditions (08h) ...
Page 28
MCLK Selection (10h/12h) Command MCLK may be selected to operate from a 2.048 MHz or 4.096 MHz external clock. MCLK selection on either channel affects both channels Write Transmit Time Slot and ...
Page 29
Write Transmit Clock Slot, Receive Clock Slot, and Transmit Clock Edge (44h) Command Input Data TCS: Transmit Clock Slot number 0–7 RCS: Receive Clock Slot number 0–7 XE=0 Transmit on negative edge of PCLK Transmit on ...
Page 30
... Command Input Data C1 through C5 are set The data appears latched on the C1 through C5 SLIC I/O pins, provided they are set in the Output mode (see Command 17). The data sent to any of the pins set to the Input mode are latched, but do not appear at the pins. ...
Page 31
... Read SLIC Input/Output Direction, Channel Status Bit, and Power Interrupt Bit (55h) Command Output Data Power Interruption Channel Status CSTAT = 0 CSTAT = CSTAT RSVD A There has not been a power interruption since the last software reset command. A power interruption has been previously detected requiring the DSLAC device to be completely reprogrammed ...
Page 32
Write Operating Functions (60h) Command Input Data Adaptive B Filter ABF = 0* PCD = 1 A-law/µ-law A A Filter EGR = 0* EGR = 1 GX Filter EGX = 0* EGX = 1 ...
Page 33
Write Operating Conditions (70h) Command Input Data Cut off Transmit Path CTP = 0* CTP = 1 Cut off Receive Path CRP = 0* CRP = 1 High-Pass Filter HPF = 0* HPF = 1 Receive Path Gain RG ...
Page 34
Write GX Filter Coefficients (80h) Command Input Data Byte 1 Input Data Byte 2 The coefficient for the GX filter is defined as 25. Read GX Filter Coefficients (81h) Command Output Data Byte 1 Output Data Byte ...
Page 35
Write Z Filter Coefficients (84h) Command Input Data Byte 1 Input Data Byte 2 Input Data Byte 3 Input Data Byte 4 Input Data Byte 5 Input Data Byte 6 Input Data Byte 7 Input Data Byte 8 Input ...
Page 36
Write B Filter Coefficients (86h) Command Input Data Byte 1 Input Data Byte 2 Input Data Byte 3 Input Data Byte 4 Input Data Byte 5 Input Data Byte 6 Input Data Byte 7 Input Data Byte 8 Input ...
Page 37
Read B Filter Coefficients (87h) Command Output Data Byte 1 Output Data Byte 2 Output Data Byte 3 Output Data Byte 4 Output Data Byte 5 Output Data Byte 6 Output Data Byte 7 Output Data Byte 8 Output ...
Page 38
Read X Filter Coefficients (89h) Command Output Data Byte 1 Output Data Byte 2 Output Data Byte 3 Output Data Byte 4 Output Data Byte 5 Output Data Byte 6 Output Data Byte 7 Output Data Byte 8 Output ...
Page 39
Read R Filter Coefficients (8Bh) Command Output Data Byte 1 Output Data Byte 2 Output Data Byte 3 Output Data Byte 4 Output Data Byte 5 Output Data Byte 6 Output Data Byte 7 Output Data Byte 8 Output ...
Page 40
Read Error Level Threshold (8Fh) Command Output Data Byte 1 40. Write GZ Filter Coefficient (92h) Command Input Data RSVD Reserved. Always write as 0, but 0 is not guaranteed when read. The coefficient, GZ, is defined as: GZ ...
Page 41
Read Adaptive B Filter Coefficients (91h) New to Revision E Command Output data Output data Output data Output data Output data 44. Write Operating Functions 2 (64h) New to Revision E Command Input data Chopper Clock Control CHP = ...
Page 42
... Eq. (6) rithm, which by a series of iterations, minimizes the re- ceive signal that is echoed in the transmit signal (due to mismatches in the SLIC, hybrid, and line). Adaptation applies to the FIR part of the filter only. Preprogrammed coefficients used to initiate the adaptive algorithm must 2 be “ ...
Page 43
In the continuous Adaptation mode, the algorithm is switched on (via MPI Command 19) after a call is con- nected and remains on until the call ends. In this way, the B filter is continually being optimized to the re- ...
Page 44
A-Law and -Law Companding Table 1 and Table 2 show the companding definitions used for A-law and -law PCM encoding Intervals Segment x Interval Segment Number Size End Points 128 ...
Page 45
Intervals Value at Segment x Interval Segment Number Size End Points 256 128 ...
Page 46
... The CHCLK output pin on the DSLAC device drives the CHCLK inputs for AMD switcher type SLICs. The CHCLK output is a 256 kHz or 293 kHz, TTL compatible signal that can drive two SLICs active only when one or both channels are activated; otherwise held high internally. ...
Page 47
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS PL032 .485 .447 .495 .453 .585 Pin 1 I.D. .595 .547 .553 .050 REF. .026 .032 TOP VIEW PL044 .685 .695 .650 .656 Pin 1 I.D. .685 .695 .650 .656 .026 .050 REF .032 TOP VIEW REVISION SUMMARY ...
Page 48
Revision I to Revision J • Page 45, Table 2, changed values in column 7. The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. ("AMD") products. AMD makes no representations or warranties with respect to ...