CS5535-UDCF AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), CS5535-UDCF Datasheet - Page 167

CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer Part Number
CS5535-UDCF
Description
Manufacturer
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet
1.CS5535-UDCF.pdf
(579 pages)
Specifications of CS5535-UDCF
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer:
AMD
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 167 of 579
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
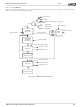
Multi-Function General Purpose Timer
5.16.1
The 15-bit prescaler is a binary down counter, dividing
down the incoming clock, and provides 15 outputs for the
MFGPTs. The frequency of these outputs ranges from 2
to 2
ing clock high, so these outputs function as increment
enables for the MFGPTs. The prescaler resets to 0000
and starts decrementing after reset. The prescaler output
vector, psclr_out[14:0], is based on prescaler counter
psclr_cnt[14:0], where psclr_out[i] = &(~psclr_cnt[i:0]) (i.e.,
prescaler output bit i is asserted if the prescaler counter
from bit i down to bit 0 are all low). When the prescaler
reaches 0000
time.
The external clock for the prescaler is activated if there is
one or more MFGPTs activated using it as its clock source;
it is also activated for MFGPT I/O register writes and syn-
chronous counter reads (only for 14.318 MHz) when the
MFGPT being written has already selected the 14.318 MHz
clock as its clock source. Whenever the external clock is
activated, the prescaler counts. Therefore, multiple
MFGPTs and register access can affect the prescaler
counting. From the point of view of the MFGPT, once the
MFGPT is disabled and then re-enabled, it cannot be
determined exactly when the prescaler carry-out occurs as
it does not know how long the prescaler has been stopped,
if at all.
5.16.2
The I/O register write data is first stored in I/O register sub-
modules before being transferred over to the MFGPTs.
There are two types of I/O register sub-modules, one for
the Working power domain and one for the Standby power
domain. The main difference is that for the Working power
domain, except for the counter register, the register values
here and the register values in the timer are the same. For
the Standby power domain, the register values in the I/O
register sub-module cannot be relied upon except during
write, as this logic could have been powered down in
Standby mode and the register data is therefore invalid.
For the Standby power domain, the read always comes
from the timer directly.
5.16.2.1 MFGPT Register Set
There are four software accessible I/O registers per
MFGPT: Up Counter, Comparator 1 Value, Comparator 2
Value, and Setup registers. (See Section 6.17 "Multi-Func-
tion General Purpose Timer Register Descriptions" on
page 483 for register details.) Writes to these registers are
first stored here and then transferred to a separate copy of
the register in the timer. For MFGPT0 to MFGPT5, read of
these registers, except for the counter, comes from the
registers here, while read of the counter register comes
from the timer. For MFGPT6 and MFGPT7, reads of these
registers comes from the copy inside the timer. (TW Note:
Restate reason or be more precise in reference.)
AMD Geode™ CS5535 Companion Device Data Book
-15
of the input frequency and each pulse is one incom-
Prescaler
I/O Registers Block
16
, all prescaler outputs are asserted at that
16
-1
5.16.2.2 Setup Register
The Setup Register contains the following control fields
that control the MFGPT operation:
• Counter Enable. Enables the Up Counter to count (it
• Clock Select. Instructs the clock switch logic to use the
• Scale Factor. Selects the prescaler divide scale factor
• Stop Enable. Enables the Up Counter to stop counting
• External Enable. Enables the Up Counter to be cleared
• Reverse Enable. Flips the order of the Up Counter
• Compare 1 Mode. Controls the Compare 1 output.
• Compare 2 Mode. Same as Compare 1 Mode, except
All of the above fields, except Count Enable, are write-once
only.
does not enable/disable other MFGPT functions).
32 kHz clock as the MFGPT clock if low or the 14.318
MHz clock if high, once this register has been written
(only for MFGPT0 to MFGPT5).
for Up Counter to increment.
during a system power management Sleep mode (for
MFGPT0 to MFGPT5) or Standby mode (for MFGPT6
and MFGPT7).
and restarted rather than performing the next increment
each time there is a low to high transition detected on
the GPIO input associated with the timer. An asynchro-
nous edge-detector catches the transition; the signal is
then synchronized and sent to clear the counter
synchronously. Therefore, the clear does not occur
immediately on the transition.
outputs going to the Compare 1 circuit so that bit 0
becomes bit 15, bit 1 becomes bit 14, etc. This allows
the timer logic to generate a PDM signal instead of a
PWM signal. To properly generate a PDM signal, the
Compare 2 Value should be set to FFFF
Compare 1 Value to establish the density.
There are four cases:
this controls the Compare 2 output. The Up Counter is
directly compared against the Compare 2 Value (i.e.,
without going through Bit Reverse logic).
00: Disabled. Output is low.
01: Compare on Equal. The compare output goes high
when the Up Counter value, after going through Bit
Reverse logic, is the same value as the Compare 1
Value.
10: Compare on GE. The compare output goes high
when the Up Counter value, after going through Bit
Reverse logic, is greater than or equal to the Compare
1 Value.
11: Event. Same as “Compare on GE”, but an event is
also created. This event can be read and cleared via
the MFGPT Setup Register and is used to generate
interrupt and reset.
31506B
16
to allow the
167
Related parts for CS5535-UDCF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6™-2E Embedded Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet: