CS5535-UDCF AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), CS5535-UDCF Datasheet - Page 57

CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer Part Number
CS5535-UDCF
Description
Manufacturer
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet
1.CS5535-UDCF.pdf
(579 pages)
Specifications of CS5535-UDCF
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer:
AMD
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 57 of 579
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
Global Concepts and Features
4.1.4
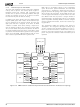
Two additional signals are needed to complete this
GeodeLink architecture overview: Asynchronous System
Management Interrupt (ASMI) and Error. Each GeodeLink
Device outputs these ASMI and Error signals.
An ASMI is much like a legacy interrupt, except it invokes
the SMM handler. As the name suggests, an ASMI is an
asynchronous event, while an SSMI is synchronous to the
instruction that generated it.
The Error signal simply indicates some type of unexpected
error has occurred. A device asserts this signal when an
unexpected error occurs. In a normal operating system,
this would not be asserted. For example, a disk read error
or ethernet network error would be signaled using normal
GeodeLink packet mechanisms. This signal is reserved for
the truly unexpected.
Each GeodeLink Device has mechanisms for enabling and
mapping multiple internal sources down to these singular
outputs. The mechanism consists of the logical “OR” of all
enabled sources. The GLIU receives the ASMI and Error
AMD Geode™ CS5535 Companion Device Data Book
GLPCI_SB
ASMI and Error
USBC1
USBC2
GLCP
ATAC
ACC
DD
& Error
& Error
& Error
& Error
& Error
& Error
& Error
& Error
Figure 4-2. GeodeLink™ Architecture ASMI and Error Routing
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
ASMI
GLIU ASMI & Error
pair from each GeodeLink Device. It has the same “OR”
and enable mechanism that finally results in a single ASMI
and Error pair for the whole component (see Figure 4-2).
The ASMI is routed to the processor, while the Error is
routed to the GLCP. Within the GLCP, the Error signal can
be mapped into an ASMI for routing back into the GLIU.
4.1.5
The connection of the GLIU to the seven GeodeLink
Devices of the Geode CS5535 companion device is illus-
trated in Figure 4-3. Note the port number of the
GeodeLink Device; by design convention, the GLIU is
always Port 0. Part of the Physical to Device (P2D)
descriptor is a port number. When there is a hit on the
descriptor address, the port number indicates which
GeodeLink Device to route the packet to. If there is no hit,
then the packet is routed to the default port. For the Geode
CS5535 companion device, the default is always Port 4,
that is, the Diverse Device (DD).
Topology
Companion Device ASMI to Processor
GLCP Debug or conversion to ASM
Companion Device Error to
31506B
57
Related parts for CS5535-UDCF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6™-2E Embedded Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet: