CS5535-UDCF AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), CS5535-UDCF Datasheet - Page 59

CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer Part Number
CS5535-UDCF
Description
Manufacturer
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet
1.CS5535-UDCF.pdf
(579 pages)
Specifications of CS5535-UDCF
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer:
AMD
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 59 of 579
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
Global Concepts and Features
In addition to the “positive” address decode above, each
GLIU has a subtractive port that takes all addresses not
assigned to a specific port. There is always a default sub-
tractive port path to the boot ROM to allow the central pro-
cessor to start executing code from time zero. Thus, from
system reset, there is a default memory address path that
allows the first processor instruction fetch to:
1)
2)
3)
4)
4.1.7
The BIZZARO flag is used to indicate special cycles and
exceptions to normal packet operation. All special cycles
traverse the GLIU system as I/O packets with the BIZ-
ZARO flag set. The special cycles are:
1)
2)
3)
AMD Geode™ CS5535 Companion Device Data Book
Routing
Proceed down through the two Geode GX processor
GLIUs;
cross the PCI bus to the Geode CS5535 companion
device;
proceed down through the Geode CS5535 companion
device GLIU to the default port connected to the DD;
and
access the boot device connected to the DD.
Interrupt Acknowledge: I/O read from address zero.
Shutdown: I/O write to address zero.
Halt: I/O write to address one.
Field 0
[31:29]
Bits
Special Cycles and BIZZARO Flag
Routing
Field 1
[28:26]
Bits
Routing
Field 2
[25:23]
Bits
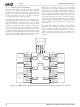
Table 4-1. MSR Routing Conventions
Routing
Field 3
[22:20]
Bits
4.2
An MSR address consists of the fields shown in Table 4-1.
When a GLIU receives an MSR packet, it routes the packet
to the port specified in Field 0 but shifts address bits
[31:14] to the left by three bits and replaces bits [16:14]
with zero. Thus, Field 1 is moved to Field 0, Field 2 is
moved to Field 1, etc. The address field always remains
unchanged and selects one 64-bit MSR per address value,
that is, the address value 0 accesses one 64-bit register,
the address value 1 accesses one 64-bit register, the
address value 2 accesses one 64-bit register, etc. There
are no MSR byte enables. All 64 bits are always written
and read.
Many Geode CS5535 companion device MSRs are only 32
bits in physical size. In these cases, interface logic dis-
cards the upper 32 bits on writes and pads the upper 32
bits on reads. Read padding is undefined. Lastly, Geode
CS5535 companion device GeodeLink Devices only
decode enough bits of the address to select one of N
MSRs, where N is the total number of MSRs in the device.
For example, if a GeodeLink Device has only 16 MSRs,
then the addresses 0x2001, 0x0201, 0x0021, and
0x0x0001 all access MSR number 1, while the addresses
0x200F, 0x020F, 0x002F, and 0x0x000F all access MSR
number 15.
To access a given GeodeLink Device, use Table 4-2 "MSR
Addresses from AMD Geode™ GX Processor" on page 60.
Note the target device addresses:
The xxxx portion refers to the MSR addresses as they
appear any place within Section 6.0 "Register Descrip-
tions" on page 199. To form a complete MSR address,
“OR” an address provided in a register description section
with the appropriate address above.
Routing
Field 4
[19:17]
Bits
GLPCI_SB
GLIU
USBC2
ATAC
DD
ACC
USBC1
GLCP
MSR Addressing
Routing
Field 5
[16:14]
Bits
5100xxxxh
5101xxxxh
5120xxxxh
5130xxxxh
5140xxxxh
5150xxxxh
5160xxxxh
5170xxxxh
31506B
Address
[13:0]
Field
Bits
59
Related parts for CS5535-UDCF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6™-2E Embedded Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet: