CS5535-UDCF AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), CS5535-UDCF Datasheet - Page 67

CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer Part Number
CS5535-UDCF
Description
Manufacturer
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet
1.CS5535-UDCF.pdf
(579 pages)
Specifications of CS5535-UDCF
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature (max)
85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
CS5535-UDCF
Manufacturer:
AMD
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 67 of 579
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
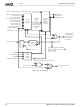
Global Concepts and Features
4.7
4.7.1
There are several places in the Geode CS5535 companion
device where addresses are decoded and routed:
• Physical PCI Bus. The GLPCI_SB decodes PCI bus
• GLIU. The GLIU compares the request addresses
• Typical GeodeLink Device. For most GeodeLink
• Diverse Device. The Diverse Device has the same
4.7.2
From reset, the GLPCI_SB does not actively decode any
cycle. However, it does subtractively decode all cycles.
From reset, any cycle not positively claimed on the PCI bus
is converted to a GLIU request and passed to the GLIU.
Using appropriate setup registers, the GLPCI_SB can be
programmed to actively decode selected I/O and memory
regions. Other than actively claiming, the “convert” and
“pass” operation is the same.
There are control bits in GLPCI_CTL (MSR 51700010h) to
regulate behavior associated with legacy addresses:
• Bits [12:11]: Legacy I/O Space Active Decode. These
• Bit 13: Reject Primary IDE. If this bit is set, the
AMD Geode™ CS5535 Companion Device Data Book
transactions and claims them with a “DEVSEL#” as
appropriate. After claiming a transaction, the GLPCI_SB
converts it to a GLIU request packet. It then passes the
request to the GLIU. It has no routing control or respon-
sibility beyond this point.
against the descriptor settings. It passes the request to
the port associated with the compare hit. Each port is
connected to a specific GeodeLink Device (see Section
4.1.5 "Topology" on page 57 for port assignment). There
are also specific legacy addresses that receive “special”
routing beyond the standard descriptor routing mecha-
nisms.
Devices, further decoding is minimal. If a device
contains only MSRs and a single Native Block (register
group) in I/O or memory space, specific bits within the
request packet can be used to easily select between the
two. If a device contains more than one register group, a
Local Base Address Register (LBAR) for each group is
used. Like a PCI Base Address Register (BAR), an
LBAR compare and hit operation is used to select the
desired group.
decoding responsibilities as a typical GeodeLink Device.
Beyond this programmable LBAR decoding, it has
substantial fixed decoding associated with legacy
addresses.
bits control the degree to which the GLPCI_SB actively
claims I/O region 0000h through 03FFh:
— 00: Subtractive – Claim on fourth clock. (Default.)
— 01: Slow – Claim on third clock.
— 10: Medium – Claim on second clock.
GLPCI_SB will not actively decode the primary IDE
addresses of 01F0h/01F7h and 03F6h.
Memory and I/O Map Overview
Introduction
PCI Bus Decoding
• Bit 14: Reject Secondary IDE. If this bit is set, the
• Bit 15: Reject DMA High Page Active. If this bit is set,
For further details on the GLPCI_CTL register see Section
6.2.2.1 "Global Control (GLPCI_CTRL)" on page 234.
Lastly, there is an “MSR Access Mailbox” located in PCI
Configuration register space. It consists of the following 32-
bit registers:
• MSR Address (PCI Index F4h). Full MSR routing path in
• MSR Data Low (PCI Index F8h). Bits [31:0]: When read,
• MSR Data High (PCI Index FCh). Bits [63:32]: Reads
For further details on the MSR Access Mailbox see Section
6.2.3 "PCI Configuration Registers" on page 240.
4.7.3
From reset, the GLIU passes all request packets to the
Diverse Device, except for the legacy primary IDE
addresses (01F0h/01F7h and 03F6h), these are passed to
the IDE device in the ATAC. There is a GLIU IOD_SC
descriptor to control this primary IDE behavior and it
defaults configured (see Section 6.1.4.2 "IOD Swiss
Cheese Descriptors (GLIU_IOD_SC[x])" on page 226). If
this descriptor is disabled, all requests pass to the Diverse
Device.
Using appropriate MSR setup registers (descriptors), the
GLIU can be programmed to route selected I/O and mem-
ory regions to specific GeodeLink Devices. Any memory or
I/O address that does not hit one of these regions, subtrac-
tively routes to the Diverse Device. Unlike PCI, there is no
performance loss associated with being the subtractive
port.
Operationally, there are five bus masters within the Geode
CS5535 companion device: ATAC, ACC, DD, USBC1, and
USBC2. These masters only generate requests to access
main memory off the Geode GX processor. Therefore, all
their GLIU requests need to be routed to the GLPCI_SB for
presentation to the PCI bus. A set of GLIU P2D_BM
descriptors could be used for this purpose. However, the
Geode CS5535 companion device GLIU is uniquely modi-
fied to route all requests for the listed masters to the
GLPCI_SB will not actively decode the secondary IDE
addresses of 0170h/0177h and 0376h.
the GLPCI_SB will actively decode the I/O range
0480h/048Fh associated with the DMA High Page regis-
ters.
the upper portion plus 14 device address bits in the
lower portion.
an MSR cycle is generated. The 64-bit read returns the
low 32 bits and saves the upper 32 bits for a read to
“Data High”. A write holds the value written as the
current “Data Low”.
return the upper 32 bits of the last MSR value read.
Writes generate an MSR write cycle using the current
value and the “Data Low” value.
GLIU Decoding
31506B
67
Related parts for CS5535-UDCF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6™-2E Embedded Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet: