DP8572AN National Semiconductor, DP8572AN Datasheet - Page 9

DP8572AN
Manufacturer Part Number
DP8572AN
Description
IC REAL TIME CLOCK W/RAM 24 DIP
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Type
Clock/Calendar/NVSRAMr
Datasheet
1.DP8572AN.pdf
(22 pages)
Specifications of DP8572AN
Memory Size
44B
Time Format
HH:MM:SS:hh (12/24 hr)
Date Format
YY-MM-DD-dd
Interface
Parallel
Voltage - Supply
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
24-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
*DP8572AN
DP8572
DP8572
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
DP8572AN
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA/东芝
Quantity:
20 000
Functional Description
INITIAL POWER-ON of BOTH V
V
the power fail circuitry to function correctly whenever power
is off the V
maximum of 1 M
trol registers will contain random data The first task to be
carried out in an initialization routine is to start the oscillator
by writing to the crystal select bits in the Real Time Mode
Register If the DP8572A is configured for single supply
mode an extra 50
select bits are programmed The user should also ensure
that the RTC is not in test mode (see register descriptions)
REAL TIME CLOCK FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
As shown in Figure 2 the clock has 10 bytes of counters
which count from 1 100 of a second to years Each counter
counts in BCD and is synchronously clocked The count se-
quence of the individual byte counters within the clock is
shown later in Table VII Note that the day of week day of
month day of year and month counters all roll over to 1
The hours counter in 12 hour mode rolls over to 1 and the
AM PM bit toggles when the hours rolls over to 12
(AM
counter
All other counters roll over to 0 Also note that the day of
year counter is 12 bits long and occupies two addresses
Upon initial application of power the counters will contain
random information
READING THE CLOCK VALIDATED READ
Since clocking of the counter occurs asynchronously to
reading of the counter it is possible to read the counter
while it is being incremented (rollover) This may result in an
incorrect time reading Thus to ensure a correct reading of
the entire contents of the clock (or that part of interest) it
must be read without a clock rollover occurring In general
this can be done by checking a rollover bit On this chip the
periodic interrupt status bits can serve this function The
following program steps can be used to accomplish this
1 Initialize program for reading clock
2 Dummy read of periodic status bit to clear it
3 Read counter bytes and store
4 Read rollover bit and test it
5 If rollover occured go to 3
6 If no rollover done
To detect the rollover individual periodic status bits can be
polled The periodic bit chosen should be equal to the high-
est frequency counter register to be read That is if only
SECONDS through HOURS counters are read then the
SECONDS periodic bit should be used
READING THE CLOCK INTERRUPT DRIVEN
Enabling the periodic interrupt mask bits cause interrupts
just as the clock rolls over Enabling the desired update rate
and providing an interrupt service routine that executes in
less than 10 ms enables clock reading without checking for
a rollover
READING THE CLOCK LATCHED READ
Another method to read the clock that does not require
checking the rollover bit is to write a one into the Time
BB
and V
e
0 PM
CC
CC
may be applied in any sequence In order for
e
pin must see a path to ground through a
1) The AM PM bit is bit D7 in the hours
The user should be aware that the con-
A may be consumed until the crystal
BB
and V
(Continued)
CC
9
Save Enable bit (D7) of the Time Save Control Register and
then to write a zero Writing a one into this bit will enable the
clock contents to be duplicated in the Time Save RAM
Changing the bit from a one to a zero will freeze and store
the contents of the clock in Time Save RAM The time then
can be read without concern for clock rollover since inter-
nal logic takes care of synchronization of the clock Be-
cause only the bits used by the clock counters will be
latched the Time Save RAM should be cleared prior to use
to ensure that random data stored in the unused bits do not
confuse the host microprocessor This bit can also provide
time save at power failure see the Additional Supply Man-
agement Functions section With the Time Save Enable bit
at a logical 0 the Time Save RAM may be used as RAM if
the latched read function is not necessary
INITIALIZING AND WRITING TO THE
CALENDAR-CLOCK
Upon initial application of power to the RTC or when making
time corrections the time must be written into the clock To
correctly write the time to the counters the clock would
normally be stopped by writing the Start Stop bit in the Real
Time Mode Register to a zero This stops the clock from
counting and disables the carry circuitry When initializing
the clock’s Real Time Mode Register it is recommended
that first the various mode bits be written while maintaining
the Start Stop bit reset and then writing to the register a
second time with the Start Stop bit set
The above method is useful when the entire clock is being
corrected If one location is being updated the clock need
not be stopped since this will reset the prescaler and time
will be lost An ideal example of this is correcting the hours
for daylight savings time To write to the clock ‘‘on the fly’’
the best method is to wait for the 1 100 of a second period-
ic interrupt Then wait an additional 16
the data to the clock
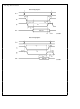
PRESCALER OSCILLATOR FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION
Feeding the counter chain is a programmable prescaler
which divides the crystal oscillator frequency to 32 kHz and
further to 100 Hz for the counter chain (see Figure 3 ) The
crystal frequency that can be selected are 32 kHz 32 768
kHz 4 9152 MHz and 4 194304 MHz
FIGURE 3 Programmable Clock Prescaler Block
s and then write
TL F 9980 – 8