PRIXP425ABD Intel, PRIXP425ABD Datasheet - Page 28

PRIXP425ABD
Manufacturer Part Number
PRIXP425ABD
Description
Manufacturer
Intel
Datasheet
1.PRIXP425ABD.pdf
(128 pages)
Specifications of PRIXP425ABD
Core Operating Frequency
533MHz
Package Type
BGA
Pin Count
492
Mounting
Surface Mount
Operating Temperature (max)
70C
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PRIXP425ABD
Manufacturer:
NXP
Quantity:
660
Company:
Part Number:
PRIXP425ABD
Manufacturer:
INT31
Quantity:
2 112
Part Number:
PRIXP425ABD
Manufacturer:
INTEL
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
PRIXP425ABDT
Manufacturer:
INTEL
Quantity:
455
2.2.6
2.2.7
2.2.8
Intel
Datasheet
28
®
IXP42X Product Line of Network Processors and IXC1100 Control Plane Processor
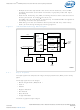
non-cacheable loads until the bus controller can act on them. The FB and the four-entry
pend buffer (PB) work with the D-cache and mini-data cache to provide
“hit-under-miss” capability, allowing the Intel XScale
Data Cache (D-Cache)
The D-cache can contain high-use data such as lookup tables and filter coefficients,
allowing the Intel XScale
processor stalls caused by multi-cycle accesses to external memory.
The 32-Kbyte D-cache is 32-set/32-way associative, where each set contains 32 ways
and each way contains a tag address, a cache line (32 bytes with one parity bit per
byte) of data, two dirty bits (one for each of two eight-byte groupings in a line), and
one valid bit. For each of the 32 sets, zero through 28 ways can be locked, unlocked,
or used as local SRAM. Unlocked ways are replaceable via a round-robin policy.
The D-cache (together with the mini-data cache) can be enabled or disabled. Attribute
bits within the descriptors, contained in the DTLB of the DMMU, provide significant
control over an enabled D-cache. These bits specify cache operating modes such as
read and write allocate, write-back, write-through, and D-cache versus mini-data cache
targeting.
The D-cache (and mini-data cache) work with the load buffer and pend buffer to
provide “hit-under-miss” capability that allows the Intel XScale
other data in the cache after a “miss” is encountered. The D-cache (and mini-data
cache) works in conjunction with the write buffer for data that is to be stored to
memory.
Mini-Data Cache
The mini-data cache can contain frequently changing data streams such as MPEG
video, allowing the Intel XScale
This prevents processor stalls caused by multi-cycle accesses to external memory. The
mini-data cache relieves the D-cache of data “thrashing” caused by frequently
changing data streams.
The 2-Kbyte, mini-data cache is 32-set/two-way associative, where each set contains
two ways and each way contains a tag address, a cache line (32 bytes with one parity
bit per byte) of data, two dirty bits (one for each of two eight-byte groupings in a line),
and a valid bit. The mini-data cache uses a round-robin replacement policy, and cannot
be locked.
The mini-data cache (together with the D-cache) can be enabled or disabled. Attribute
bits contained within a coprocessor register specify operating modes write and/or read
allocate, write-back, and write-through.
The mini-data cache (and D-cache) work with the load buffer and pend buffer to
provide “hit-under-miss” capability that allows the Intel XScale
other data in the cache after a “miss” is encountered. The mini-data cache (and
D-cache) works in conjunction with the write buffer for data that is to be stored to
memory.
Fill Buffer (FB) and Pend Buffer (PB)
The four-entry fill buffer (FB) works with the Intel XScale
the caches while “miss” data is being fetched from memory.
The FB can contain up to four unique “miss” addresses (logical), allowing four “misses”
before the processor is stalled. The PB holds up to four addresses (logical) for
additional “misses” to those addresses that are already in the FB. A coprocessor
register can specify draining of the fill and pend (write) buffers.
Intel
®
®
IXP42X product line and IXC1100 control plane processors—Datasheet
processor access to data at core frequencies. This prevents
®
processor access to data streams at core frequencies.
®
processor to seek other data in
®
processor to hold
Document Number:
®
®
processor to access
processor to access
252479-007US
June 2007