AM7969-175JC AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES), AM7969-175JC Datasheet

AM7969-175JC
Specifications of AM7969-175JC
Available stocks
Related parts for AM7969-175JC
AM7969-175JC Summary of contents
Page 1
... TM TAXIchip Transparent Asynchronous Transmitter/Receiver Interface Am7968/Am7969-125 Am7968/Am7969-175 Technical Manual Integrated Circuits Data Sheet and 1994 ...
Page 2
Advanced Micro Devices reserves the right to make changes in its products without notice in order to improve design or performance characteristics. This publication neither states nor implies any warranty of any kind, including but not limited to implied warrants ...
Page 3
... Chapter 4 Clock Generation and Distribution 4.1 TAXI Transmitter Clock Connections 4.1.1 Local Mode Transmitters 4.2 TAXI Receiver Clock Connections 4.2.1 Cascade Mode Receivers (Am7969-125 only) Chapter 5 Interfacing with the Serial Media 5.1 Very Short Link, DC Coupled 5.2 Terminated, DC Coupled 5.3 Terminated, AC Coupled 5 ...
Page 4
... AMD Chapter 7 Cascade Mode Operation 7.1 Transmit Cascaded Data with a Single TAXI Transmitter 7.2 Receivers In Cascade Mode: Connections (Am7969-125 only) 7.3 Auto-Repeat Configuration 7.4 Unbalanced Configuration (Am7968/Am7969-125 only) Chapter 8 Test Mode 8.1 Transmitter Connections 8.2 Receiver Connections 8.3 Timing Relationships in Test Mode ...
Page 5
... coupled — NRZI 4B/5B, 5B/6B encoding/decoding Drive coaxial cable or twisted pair directly GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Am7968 TAXIchip Transmitter and Am7969 TAXIchip Receiver Chipset is a general-purpose inter- face for very high-speed (4–17.5 Mbyte/s, 40–175 Mbaud serially) point-to-point communications over co- axial or fiber-optic media. The TAXIchip set emulates a pseudo-parallel register. They load data into one side and output it on the other, except in this case, the “ ...
Page 6
... V (ECL) 5 CC2 V (TTL) 6 CC1 7 V (TTL) CC3 RESET 8 9 DMS 10 TLS TSERIN Am7968/Am7969 (X1) (X2) (DMS) Data Mode Select (CNB) Catch Next Byte (IGM) I-Got-Mine (CLK) Clock (DSTRB) Data Strobe (CSTRB) Command Strobe 07370F-2 LCC/PLCC DI2 DI1 24 23 DI0 22 GND1 (TTL) ...
Page 7
... GND = Ground (2) 5 IGM RESET (TTL) CC1 V (CML) 8 CC2 9 SERIN+ 10 SERIN- 11 DMS SERIN+ ACK X1 X2 CLK 07370F GND = Ground (2) Am7968/Am7969 LCC/PLCC DO7 CNB GND2 (CML) 20 GND1 (TTL) 19 CLK Am7969 RESET CNB DMS VLTN DSTRB CSTRB IGM CLK 07370F-8 = Power Supply (2) AMD 07370F-6 3 ...
Page 8
... Standard Products AMD standard products are available in several packages and operating ranges. The ordering number (Valid Combination) is formed by a combination of: AM7968 AM7969 –125 D DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION Am7968 TAXIchip Transmitter Am7969 TAXIchip Receiver Valid Combinations AM7968-125 AM7969-125 DC, JC AM7968-175 AM7969-175 4 C TEMPERATURE RANGE ...
Page 9
... Products List) products are compliant with MIL-STD-883C requirements with exceptions for V order number (Valid Combination) is formed by a combination of: AM7968 -125 /L AM7969 DEVICE NUMBER/DESCRIPTION Am7968 – TAXIchip Transmitter (Local Mode only) Am7969 – TAXIchip Receiver (Local Mode only) Pkg Temps (TC) VCC LCC – 125 C 4 5.5 V LCC – ...
Page 10
... This mode is only used for Automatic Test Equip- ment (ATE) testing at full speed. When this input is left unconnected, it floats to an inter- mediate level which puts the Am7968 Transmitter into its Test Mode 2. In Test Mode 2, the internal clock Am7968/Am7969 CC , the Am7968 CC (Test Mode 1),the serial data ...
Page 11
... The byte rate matches the crystal frequency. During normal operation, the byte rate is set by the crystal frequency. Alternatively, X1 can be driven by an external TTL fre- quency source. In multiple TAXI systems this external source could be another Am7968’s CLK output. powers ECL and Am7968/Am7969 AMD 7 ...
Page 12
... Local mode, and each received byte will be captured, decoded and latched to the outputs. If the CNB input is HIGH, it allows the Am7969 Receiver to capture the first byte after a sync. The Am7969 Re- ceiver will wait for another sync before latching the data out, and capturing another. If CNB is toggled LOW, it will react had decoded a sync byte ...
Page 13
... V. When SERIN– is grounded, the Am7969 is put into Test Mode; SERIN+ becomes a single-ended ECL input, the PLL clock gen- erator is bypassed, and X1 determines the bit rate (rather than the byte rate). Both pins have internal pull down resistors which cause unterminated inputs to stay low ...
Page 14
... Reception of a Sync pattern clears the Command outputs to all 0’s, since Sync is a legal command. Noise-induced bit errors can distort transmitted bit pat- terns. The Am7969 Receiver logic detects most noise- induced transmission errors. Invalid bit patterns are recognized and indicated by the assertion of the viola- tion ( VLTN ) output pin. This signal rises to a logic “ ...
Page 15
... Cascaded. The Am7969 Receivers all have their SERIN+ and SERIN– pins connected to the media (or an optical data link). IGM of each Am7969 is connected to CNB of its down- stream neighbor or is left unconnected on the Receiver farthest downstream. CNB of the first Receiver is tied ...
Page 16
... NRZI. Differential SERIN+/SERIN– inputs can be used to force the Am7969 Receiver into its Test mode. This will allow testing of the logic in the Latches, Decoder, and Shifter without having to first stabilize the the PLL. If SERIN– ...
Page 17
... Oscillator The Am7968 and Am7969 contain an inverting amplifier intended to form the basis of a parallel mode oscillator. The design of this oscillator considered several factors related to its application. The first consideration is the desired frequency accu- racy. This may be subdivided into several areas. An os- ...
Page 18
... Am7968/Am7969 5-Bit 6-Bit Binary Encoded Data* Symbol 00000 110110 00001 010001 00010 100100 00011 100101 00100 010010 00101 010011 00110 010110 00111 010111 01000 100010 01001 110001 01010 110111 01011 100111 01100 110010 ...
Page 19
... S’R 111001 11001 S’S XXXXXX XXXXXX Data 011000 100011 LM (10-bit Sync) 111111 111111 I ’ I ’ 011101 011101 T ’ T ’ 011101 111001 T ’ S ’ Am7968/Am7969 AMD Am7969 Receiver Command Output HEX Binary No Change No Change (Note 2) (Note 2) 0 0000 1 0001 2 0010 3 0011 ...
Page 20
... The working frequency can be varied between 3.3 MHz and 17.5 MHz. The crystal frequency required to achieve the maximum 175 Mbaud on the serial link, and the resultant usable data transfer rate will be: Am7968-125 Input and Am7969-125 Maximum Parallel Throughput 80 ns/pattern (100 Mbit/sec) 88 ns/pattern (102 Mbit/sec) ...
Page 21
... Am7969 Receiver Functional Block Description (Refer to page 1) Crystal Oscillator/Clock Generator The data recovery PLL in the Am7969 must be supplied with a reference frequency at the expected byte rate of the data to be recovered. The source of this frequency can either be the built-in Crystal Oscillator exter- nal clock signal applied through the X ...
Page 22
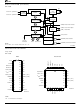
... Transfer Control ACK Logic N Data Source Data Signals Note: N can bits of parallel data; total 12. 18 Am7968 Am7969 Transmission Media Figure 2. TAXIchip System Block Diagram Am7968/Am7969 M Command Destination Command Signals CSTRB Data Path VLTN Control Logic DSTRB N Data Destination Data Signals 07370F-11 ...
Page 23
... IGM CNB VLTN CSTRB DSTRB Data Destination Pin 11 = Don’t Connect = Local Mode Pin 11 = Don’t Connect = Local Mode Figure 3. TAXIchip System in Local Mode Am7968/Am7969 Message Transfer Control Logic Data Command Source Source 9 3 DI0 – DI8 CI0 – CI2 STRB ...
Page 24
... SERIN– SERIN+ RX1 DMS V CC Am7969 Primary RX CNB IGM CLK X2 X1 Figure 4. Cascaded Receiver Clock Connections (Commercial –125 only) 20 SERIN– SERIN+ RX2 DMS Am7969 CNB IGM X2 X1 Crystal OSC Am7968/Am7969 SERIN– SERIN+ RX3 DMS Am7969 CNB IGM N 07370F-13 ...
Page 25
... OPERATING RANGES Commercial (C) Devices Temperature (T – +150 C Supply Voltage (V – +125 C Operating ranges define those limits between which the func- tionality of the device is guaranteed. –0 +7.0 V –0 Max CC –0 +5.5 V 100 mA – +5.0 mA Am7968/Am7969-125 AMD ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + +4 +5 ...
Page 26
... Min ECL Load Min ECL Load CC2 CC3 SEROUT = ECL Pin V (TTL) CC1 Load, DMS = 0 Pin V (ECL) CC2 CC1 CC2 V = Max Pin V (CML) CC3 CC3 Am7968/Am7969-125 Min Max Unit 2.4 V 2.4 V 0.45 V 2.0 V 0.8 V –1.5 V –400 150 A –15 – –1.025 – ...
Page 27
... Am7969-125 TAXIchip Receiver Parameter Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7, DO8/CO3, DO9/CO2, CO0–CO1, DSTRB, CSTRB, IGM, CLK, CNB, VLTN V Output HIGH Voltage OH V Output LOW Voltage OL V Input HIGH Voltage IH V Input LOW Voltage IL V Input Clamp Voltage ...
Page 28
... TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Load TTL Load Am7968/Am7969-125 Min Max Units 8n 25n ...
Page 29
... Am7969-125 TAXIchip Receiver (Notes 13, 14, 22) Parameter No. Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7,DO8/CO3,DO9/CO2,CO0–CO1,DSTRB,CSTRB, IGM,CLK,CNB,VLTN 35 t CLK Period (Note 24 Data Valid to STRB Delay CLK to STRB CLK to STRB PD 38a t STRB to CLK (Note 23 CLK to Data Valid Delay STRB Pulse Width HIGH PW 41 ...
Page 30
... AMD 26 (Page intentionally left blank) Am7968/Am7969-175 ...
Page 31
... OPERATING RANGES Commercial (C) Devices Temperature (T – Supply Voltage (V – +125 C Operating ranges define those limits between which the func- tionality of the device is guaranteed. –0 +7.0 V –0 Max CC –0 +5.5 V +100 mA – +5.0 mA Am7968/Am7969-175 AMD ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . + +4 +5 ...
Page 32
... Min ECL Load Min ECL Load CC2 CC3 SEROUT = ECL Pin V (TTL) CC1 Load, DMS = 0 Pin V (ECL) CC2 CC1 CC2 V = Max Pin V (CML) CC3 CC3 Am7968/Am7969-175 Min Max Unit 2.4 V 2.4 V 0.45 V 2.0 V 0.8 V –1.5 V –400 150 A –15 – –1.025 – ...
Page 33
... Am7969-175 TAXIchip Receiver Parameter Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7, DO8/CO3, DO9/CO2, CO0–CO1, DSTRB, CSTRB, IGM, CLK, CNB, VLTN V Output HIGH Voltage OH V Output LOW Voltage OL V Input HIGH Voltage IH V Input LOW Voltage IL V Input Clamp Voltage ...
Page 34
... TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load ECL Output Load TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Load TTL Load Am7968/Am7969-175 Min Max Units 5 ...
Page 35
... Am7969-175 TAXIchip Receiver (Notes 13, 14, 22) Parameter No. Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7, DO8/CO3, DO9/CO2, CO0–CO1, DSTRB, CSTRB, IGM, CLK, CNB, VLTN 35 t CLK Period (Note 24 Data Valid to STRB Delay CLK to STRB CLK to STRB PD 38a t STRB to CLK (Note 23) ...
Page 36
... AMD 32 (Page intentionally left blank) Am7968/Am7969-125 Military ...
Page 37
... Am7968/Am7969-125 MILITARY ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS StorageTemperature . . . . . . . . . . . . Ambient Temperature Under Bias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Supply Voltage to Ground Potential Continuous . . . . . . . . . . . . DC Voltage Applied to Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DC Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DC Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DC Input Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Rat- ings may cause permanent device failure. Functionality at or above these limits is not implied. Exposure to absolute maxi- mum ratings for extended periods may affect device reliability ...
Page 38
... V = Max (Note –30 to +125 –55 to +125 0. 2 SEROUT = ECL Pin V (TTL) CC1 Load, DMS = 0 Pin V (ECL CC2 CC1 CC2 V = Max CC3 Pin V (CML) CC3 Am7968/Am7969-125 Military Min Max Unit 2.4 V 2.4 V 0.45 V 2.0 V 2.1 V 0.8 V –1.5 V –400 150 A –15 – –1.165 – ...
Page 39
... Am7969-125 Military TAXIchip Receiver Parameter Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7, DO8/CO3, DO9/CO2, CO0–CO1, DSTRB, CSTRB, IGM, CLK, CNB, VLTN V Output HIGH Voltage OH V Output LOW Voltage OL V Input HIGH Voltage IH V Input LOW Voltage IL V Input Clamp Voltage ...
Page 40
... X1 Pulse Width LOW (Note 12 CLK CLK PD 36 Test Conditions TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Output Load on CLK TTL Load TTL Load Am7968/Am7969-125 Military Min Max Units – ...
Page 41
... Am7969-125 Military TAXIchip Receiver (Notes 13, 14, 22) Parameter No. Symbol Parameter Description Bus Interface Signals: DO0–DO7, DO8/CO3, DO9/CO2, CO0–CO1, DSTRB, CSTRB, IGM, CLK, CNB, VLTN 35 t CLK Period (Note 24 Data Valid to STRB Delay CLK to STRB CLK to STRB PD 38a t STRB to CLK (Note 23) ...
Page 42
... When SERIN– is held above 0.25 V and when: THT SERIN– “n” 8 Bit < OPEN THTMAX Test Mode 8 Bit > 2 10; Local Mode 9 Bit < OPEN THTMAX Test Mode 9 Bit > 2 11; Local Mode 10 Bit < OPEN THTMAX Test Mode 10 Bit > 2 12; Local Mode Am7968/Am7969 ...
Page 43
... The limit for this parameter cannot be derived from t 37 and 24. This specification does not apply during reacquisition when CLK stretch can occur. This parameter is guaranteed but is not included in production tests. * Notes listed correspond to the respective references made in the DC Characteristics and the Switching Characteristics tables. Am7968/Am7969 AMD and V for OH OL VCC VCC = 0 ...
Page 44
... This figure is for reference only 07370F-14 Notes < includes scope probe, wiring and stray capacitances without device in test fixture. 2. AMD uses Automatic test equipment load configurations and forcing functions. This figure is for reference only. Am7968/Am7969 OUT – 07370F-15 ECL Output Load ...
Page 45
... TTL Input Waveform ECL Input Waveform WAVEFORM INPUTS Must Be Steady May Change from May Change from Don’t Care Any Change Permitted Does Not Apply Am7968/Am7969 AMD 2 0.2 ns 07370F-16 2 0.2 ns 07370F-17 OUTPUTS Will Be Steady Will Be Changing from Will Be Changing from Changing ...
Page 46
... AMD SWITCHING WAVEFORMS 42 Am7968/Am7969 ...
Page 47
... SWITCHING WAVEFORMS Am7968/Am7969 AMD 43 ...
Page 48
... AMD SWITCHING WAVEFORMS 44 Am7968/Am7969 ...
Page 49
... SWITCHING WAVEFORMS Am7968/Am7969 AMD 45 ...
Page 50
... AMD SWITCHING WAVEFORMS 46 Am7968/Am7969 ...
Page 51
... SWITCHING WAVEFORMS #1 TAXI Am7968/Am7969 AMD #2 TAXI 47 ...
Page 52
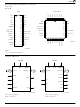
... MIN TOP VIEW .015 .060 SIDE VIEW .050 REF .042 .056 .026 .032 .009 .015 .450 .456 .485 .495 TOP VIEW Am7968/Am7969 .590 .615 .008 .012 .150 MIN 0° 15° 06837D .700 BZ13 CD 028 MAX 1/8/ END VIEW .020 MIN .025 R ...
Page 53
... BOTTOM VIEW .300 BSC .150 BSC .022 .028 .300 BSC .150 BSC .015 MIN TOP VIEW .442 .458 .430 MAX INDEX CORNER .020 X 45 REF. (OPTIONAL) Am7968/Am7969 AMD SIDE VIEW .054 .065 .064 .075 PLANE 2 PLANE 1 07703D CS47 CLT 028 04/28/ ...
Page 54
TAXIchip Technical Manual 1.0 INTRODUCTION Modern electronic systems move data from point-to-point across physical layer bounda- ries using either serial or parallel data links. Parallel data links provide fast data transfers and are compatible with most computer architectures. However, conventional ...
Page 55
... X1 X2 Clock (CLK) Data Mode Select (DMS) Test Serial In (TSERIN) Note: N can bits. Total 12. Figure 1-2 Am7969 TAXI Receiver Block Diagram (SERIN+) Serial In + Media Interface (SERIN–) Serial In – (VLTN) Violation Note: N can bits. Total 12. TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual Data Strobe & ...
Page 56
... TAXI Transmitter will fill the gaps with Syncs, which do not disturb Receiver output data. 2.1 Data and Command The Am7968 TAXI Transmitter and the Am7969 TAXI Receiver interface directly bit data bus. Each TAXlchip has 12 parallel interface lines which are designated as either Command or Data bits ...
Page 57
... Receiver over the serial medium. Cascade mode for Am7968/7969-125 consists of a single Transmitter driving two or more daisy chained (cascaded) Receivers over a single serial medium. Cascade Operation for Am7968/Am7969-175 consists of a single Transmitter driving a single Receiver as shown in Appendix C, TAXI TIPs #13 and #14. ...
Page 58
AMD The TAXIchip set uses 4B/5B or 5B/6B coding, so that m is either and n is either 8-bit mode, each 4-bit nibble is presented to one of two 4B/5B encoders to produce ...
Page 59
Table 3-1 TAXlchip Encoder Patterns 4B/5B ENCODER SCHEME HEX Data Notes: HEX data is parallel input data which is represented by the 4- ...
Page 60
... XXXXXX XXXXXX No STRB 011000 100011 LM (10-bit Sync) (Note 1) 01 111111 111111 10 011101 011101 11 011101 111001 Am7969 Receiver Command Output Mnemonic HEX Binary Data No Change No Change (Note 2) (Note 2) 0 0000 0001 TT 2 0010 ...
Page 61
Violation Logic The TAXI Receiver logic has been designed to detect the most common types of transmission errors. It detects these errors by completely decoding the incoming data patterns, and recognizes the following types of VIOLATIONS: 1. Illegal, reserved ...
Page 62
... If there is no data on the link (if the Transmitter is off there is a quiet line) the data recovery PLL will drift to its natural oscillation frequency. This frequency is determined by component values and tolerances inside the Am7969 receive PLL, and will vary slightly from both the Receiver reference frequency ( the Receiver) and the Transmitter data frequency (X1 of the Transmitter) ...
Page 63
... Am7968/Am7969-125 Data Width PLL Multiplier Am7968/Am7969-175 Data Width PLL Multiplier The source of byte rate frequency can be either from the built-in crystal oscillator or from a TTL clock signal. The maximum allowable mismatch between Transmitter and Receiver frequency sources is 0 ...
Page 64
... In addition to the bit synchronization accomplished by the PLL, the logic will maintain byte synchronization (framing) with the incoming data 60 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual Typical Crystal Specification 4.0 MHz –17.5 MHz +0.1% Parallel 1.00 ppm (max) Low Profile 10 ppm RESET Am7968 or, Am7969 12330E-5 ...
Page 65
... TAXI Receivers. 5.0 INTERFACING WITH THE SERIAL MEDIA The Am7968/Am7969 TAXlchip set is capable of providing a high speed point-to-point serial link over fiber-optic, coaxial, or twisted pair media. The choice of the appropriate medium depends primarily on line length and data rate. This chapter discusses the issues involved in media choice and the requirements for driving different types of media ...
Page 66
AMD common mode range. The average DC value of the input signal is therefore relatively unimportant. There are three broad classes of TAXl-to-media interface: 1. Very short (<3 link length), usually DC coupled. 2. Terminated, DC coupled. 3. Terminated, AC ...
Page 67
TAXIchip set in order for the DC connection to work. If the supply voltage or the logic levels are incompatible connection must be used. 5.2 Terminated, DC Coupled ...
Page 68
AMD threshold level of the receiver’s differential amplifier. Once the Receiver recognizes the state change, variations in the falling edge are not significant. To avoid edge rate variations due to driver turn-off, we must equate the voltage to which the ...
Page 69
Figure 5-5. In Figure 5-5a, the average DC fluctuates between 40% and 60% of the maximum level (+10% of midpoint). After the signal is capacitively coupled (Figure 5-5b), the average DC component ...
Page 70
... TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual Fiber Optic Transmitter Optical Source Source: Driver LED or Electronics Laser Diode TAXI /Optical Interface Fiber Optic Receiver Optical Detector: Receiver PIN or Electronics Avalanche Photodiode = + Data Command Am7968 Transmitter Transceiver Am7969 Receiver Data Command 12330E-13 = GND) and if the two components ...
Page 71
For DC-coupled interconnections in which the distance between the TAXIchip set and the optical module is less than 3 , transmission line terminations are not necessary. All that is required is the appropriate ECL pull-down as shown in Figure 5-7 ...
Page 72
AMD 5.5.2 AC-Coupled TAXl-Fiber Optic Transceiver Interface Some applications will require the TAXIchip set to optical transceiver interconnection to be AC-coupled. AC coupling should be used in the following situations: a) when the TAXIchip set and optical components are driven ...
Page 73
Because of the resultant lower system costs, coaxial cable is the recommended serial medium for short-to-moderate length links. At longer lengths, the advantages of fiber optic transmission (low attenuation, immunity to EMI and ground loops, etc.) make it the media ...
Page 74
AMD Sample Values Using RG-58A/U, 50 following component values: 5.7 Interfacing to Twisted-Pair Cable Another low cost alternative twisted pair cable. Twisted pair cable is generally more lossy than coaxial cable making it suitable only for short distances. To reduce ...
Page 75
Sample Values Using IBM Type 1 STP 150 shielded twisted pair cable, a successful TAXI link was established using the following component values 101 R2 = 291 R3 = 300 C = 0.1 F 6.0 BOARD LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS ...
Page 76
... Use of strip lines for serial signals is recommended. 72 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual V Plane Leads must be very short 5 (less than 1 Normal Overshoot < 0.5 V Jog or Glitch Normal Undershoot < 0 Plane Receiver Am7969 7 V CC1 (TTL GND1 20 V CC2 8 (CML GND2 12330E-19 12330E-20 ...
Page 77
When terminating serial lines to or from the TAXls ensure that the Vcc rail or ground tap is not at a noisy location. Resistors can couple noise from a power supply rail into the Serial lines. Vcc to Ground ...
Page 78
... Receiver gets the second byte, and so on. Performing this reset operation with latches would require additional logic to decode a Sync command which in turn would reset all the latches. For Am7969-175 TAXI Receivers, see Appendix C TAXI TIP #13 for single receiver cascade operation. (1) Actually, in Non Auto-Repeat Cascade Mode, the throughput is less than 100 Mbits/s due to the need to send Syncs ...
Page 79
Figure 7-1 Cascaded TAXI System Mixed Data Sources 8 4 DI0–DI7 CI0–CI7 (Note 2) SEROUT+ TAXI RX #1 SEROUT– TAXI TX #1 TLS DMS 12.5 MHz VCC SERIN+ SERIN– DMS CNB TAXI RX #1 (Note ...
Page 80
AMD 7.1 Transmit Cascaded Data with a Single TAXI Transmitter For systems that require data transfer wider than a single byte, a single TAXI Transmit- ter can be used to cascade the multiple bytes. This operation allows the data to ...
Page 81
... BYTE1 7.2 Receivers In Cascade Mode: Connections (Am7969-125 Only) Unlike transmitters, all cascaded receivers are directly connected to the media, via the two serial input data lines. All Receivers see the same serial data at the same time. The Primary Receiver always receives the first byte of serial data after a Sync. The signals used by the upstream Receiver to tell the downstream Receiver that it has captured a byte are IGM (I Got Mine) and CNB (Catch Next Byte) ...
Page 82
... Timing description for receivers in cascade mode is included in Figure 7-4. 78 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual 12.5 MHz Crystal OSC SERIN– SERIN DMS RX2 Am7969 IGM CNB CSTRB CMD DATA DSTRB VLTN D15-D8 SERIN DMS RX3 Am7969 IGM CNB N/C CSTRB CMD DATA DSTRB VLTN D7-D0 12330E-25 ...
Page 83
Figure 7-4 Receiver Timing—8-Bit Cascade Mode Internal Clock* SERIN DATA N Serial Data NRZ Data* DATA N CLK OUT 1 CNB TAXI # IGM TAXI #1 = CNB TAXI #2 Command NO CHANGE OUT CSTRB OUT TAXI #1 ...
Page 84
AMD Figure 7-5 CNB and IGM Propagating Down Cascaded Receivers Serial Data CNB1 = V CC IGM1 CNB2 IGM2 CNB3 IGM3 = N/C Note: Half of the byte is sufficient for the Receiver to decide whether the byte is a ...
Page 85
The Data Out Lines When a Receiver sees the Sync symbol it sends the data byte it just received from its Input Latch to its Decoder Latch, and then the receiver lowers its IGM. One more clock cycle is required ...
Page 86
AMD Figure 7-7 Receiver Timing in Auto-Repeat Configuration Serial Data CNB1 IGM1 CNB2 IGM2 CNB3 IGM3 = CNB1 Note: Only when a Receiver has a CNB = 1, can it accept new data. It then raises its IGM when it ...
Page 87
Figure 7-8 Receiver Timing in Auto-Repeat Configuration Serial Data CNB1 IGM1 CNB2 IGM2 CNB3 IGM3 = CNB1 Note: When IGM3 goes HIGH CNB1 goes LOW. Thus, IGM1 = CNB2 goes LOW t that. This will ripple down to IGM3. TAXIchip ...
Page 88
AMD Figure 7-9 Receiver Timing in Auto-Repeat Configuration Serial Sync Data CNB1 IGM1 CNB2 IGM2 CNB3 IGM3 = CNB1 Note: IGM3 = CNB1 so RX1 is now ready to receive new data. The cycle can now be repeated. 7.3.2 Timing ...
Page 89
... Receivers and their IGMs so the upstream (Primary) Receiver receives the next non Sync byte of data. This remains as the method of recovering from byte framing errors. 7.4 Unbalanced Configuration (Am7968/Am7969-125 Only) In reality there is no difference in connection between balanced and Unbalanced Configurations. The name only indicates that the number of Transmit bytes and the number of Receive bytes are unequal ...
Page 90
... TAXlchips will keep the line active by sending Syncs. 86 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual TTL Data Am7968 X1 X2 Clock X1 SERIN IGM CNB 8, 8, Am7969 TTL Data OUT OSC X1 X1 SERIN IGM CNB 8, Am7969 Am7969 9, 10 12330E-34 ...
Page 91
The serial link will operate in the 40 to 175 MHz range as determined by the byte rate clock, but the byte data rate will be determined by how often the user strobes the TAXI Transmitter. The transmission speed is ...
Page 92
AMD This serves to flush all extraneous data from the buffers and reset all internal state machines. Once this is completed the Transmitter may be Strobed. X1 should be left in the LOW state upon completion of the initialization. The ...
Page 93
... CMD STROBE COMMAND OUT TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual = 10 bits ms. In the same way ns] = 2.015 ms. Note that 35 Normal Function DSTRB CNB SERIN+ SERIN– X1 Am7969 X2 RESET CSTRB CLK DMS VLTN IGM DMS Can Be Set For Normal 10-Bit Mode Function AMD , which is ...
Page 94
APPENDIX A Fiber Optic Data Link Manufacturer List Presented below is a partial listing of fiber optic data link suppliers that manufacture or market optical components in a data rate range compatible with the TAXIchip set. Several of these components ...
Page 95
APPENDIX B Error Detection Efficiency When a received data pattern does not represent a valid coding symbol, the TAXI Receiver asserts the VLTN pin to indicate that the current data contains an error. The Receiver cannot detect the occurrence of ...
Page 96
AMD For example, consider transmitting Hex B [1011], encoded as 10111. Error E occurs changes bits b0 & b1, resulting in encoded pattern 10100, which is Hex 2 [0010] 2 bits changed, and the run length the error = 4 ...
Page 97
Figure B Percent of Error 30 Events Figure B Percent of 30 Undetected Error Events TAXIchip Integrated Circuit Technical Manual Violation 1-Bit Error 2-Bit Error 8 Bit 9 Bit ...
Page 98
APPENDIX C TAXI Technical Information Publications The TAXI applications team has documented questions and answers that are general purpose in nature and applicable to a wide range of applications. This documentation has taken the form of TAXI Technical Information Publications ...
Page 99
TAXI TIPs TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-01 Subject: Receiver Response to Loss of Input Signal Question desired that the TAXI Receiver outputs be predictable and stable during conditions when the TAXI Transmitter may cease transmitting (power-off ...
Page 100
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-02 Subject: TAXlchip RESET Pin Function Question: How long must the RESET pin be held low in order to insure that the TAXIchip has reset? Answer: The RESET pin is level sensitive and after a ...
Page 101
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-03 Subject: Proper Use for TAXI Sync Question: What is the proper use for Sync? How often is a Sync needed? Answer: When a Transmitter has no data to send, it sends Sync. This symbol allows ...
Page 102
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-04 Subject: TAXI PLL Lock-Up During Power-On! Question: Is there a recommended power-on sequence for the TAXIchips to prevent PLL lock-up? Answer: Early versions of the -70 TAXIchips did have some sensitivities associated with hot- ...
Page 103
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-05 Subject: TAXIchip Set Crystal Specification Question: What are the design considerations for crystals used with TAXIchip set? Answer: The TAXIchip’s parallel mode oscillator uses a 4.0 MHz – 17.5 MHz crystal with a frequency tolerance ...
Page 104
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-06 Subject: TAXl for FDDI Applications? Question: Can the TAXIchip set be used for FDDI physical layer applications? Answer: The TAXIchip set is code compatible with the FDDI physical layer but there are restric- tions ...
Page 105
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-07 Subject: Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Strobe Question: When should synchronous vs. asynchronous strobing be employed? Answer: Inputs to the TAXI Transmitter can be strobed asynchronously, but with some limita- tions. In local mode, the STROBE edge ...
Page 106
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-08 Subject: TAXI Receiver Lock Time Question fully operational system in which both the Transmitter and Receiver are powered on, how long will it take for the Receiver to lock to new data ...
Page 107
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-10 Subject: TAXI Receiver CSTRB and DSTRB Pulse Width Question: What is the maximum CSTRB and DSTRB pulse width? Answer: The internal logic of the TAXI Receiver determines the pulse width of CSTRB and DSTRB based ...
Page 108
AMD Figure 11 (8-Bit Mode Example) TAXI Receiver Internal Clock Distribution Internal Bit Clock Internal Clock (Byte Rate) External Clock (CLK) Internal CSTRB & DSTRB External CSTRB & DSTRB Internal Data External Data 104 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual 9 ...
Page 109
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-11 Subject: Using Receiver CLK Output to Run a TAXI Transmitter Question possible to use the Receiver CLK output to drive the X1 input of a TAXI Transmitter? Answer: To assure accurate transmission of ...
Page 110
... GND Crystal Filter 15K 15K U1 - GND V+ LMC660C 15K 15K GND SEROUT + SERIN + SEROUT - SERIN - Am7968 Am7969 Transmitter Receiver 7 X1 CLK X1 CLK X2 X2 12330E-41 GND SEROUT + VCM2 V SEROUT – CC MC4024 Am7968 VCX2 TAXI Transmitter OUT 2 X1 CX2 CLK GND X2 12330E-42 ...
Page 111
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-12 Subject: TAXlchip Pins Internal Circuit Question: What do the TAXIchip I/O circuits look like? Answer: There are five different input circuits and two different output circuits in the TAXIchip set. Each I/O circuit has Electro ...
Page 112
AMD GND 12330E-43 ESD 300 ECL IN 300 ESD 50K GND ECL IN 108 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual TTL IN ESD DMS/CLS IN ESD 12330E- 22K 11K GND 12330E-44 TTL ...
Page 113
48K RESET ESD GND HIGH Threshold TTL OUT ESD 12330E-49 GND TTL OUT TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual X1 ESD REF. X2 ESD 12330E- 300 GND AMD 125 5.3K GND ...
Page 114
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-13 Subject: Demuxing A TAXIchip Receiver Output to Multi-Byte Words Question: How can a single TAXI Receiver be used to receive multi-byte words? Answer: INTRODUCTION For systems that require data reception wider than a single ...
Page 115
Figure 14 Logic Diagram of Cascaded Data with One TAXI Receiver /RESET DMS CNB TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual PRB CLK PRB X2 X1 VCC2 VCC1 AMD CLK PRB CLK CLK PRB PRB PRB CLK 12330E-51 111 ...
Page 116
AMD The circuitry that handles the Sync Commands or Sync Bytes generates several signals. The CMND0, CLR_CNTR, Sync and PCO are the signals that are generated by Sync Command logic. The CLR_CNTR signal is generated from the CMND0 and the ...
Page 117
High, without any additional logic. The VLTN signal is used for both Command and Data violations. Buffering of the DSTRB and VLTN signals may be necessary as illustrated in Figure 15 to meet the drive requirements of the first ...
Page 118
AMD Figure 15 Timing Diagram of 4-Demux Cascaded Receiver TAXI CLK /CLK DSTRB CSTRB RCVR DATA CLKCNTR CLK1 CLK2 CLK3 CLK4 CLKCNTR PCO Sync CLKOUT DATA OUT 114 TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual Byte 4 ...
Page 119
TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-14 Subject: 32-Bit Multiplexed Cascade with the TAXIchip Transmitter Question: How can a single TAXIchip Transmitter be used to send n-byte data words? Answer: I. INTRODUCTION Many systems have DATA/CMD paths wider than the twelve lines ...
Page 120
... On the receiver end of the link, the option is left up to the designer to either use four Am7969 TAXI Receivers or to demultiplex the data and use only one Receiver. Figure 16 has been included to give a detailed schematic of the circuit with an Am7969 TAXI Receiver on-board to complete the data path. Figures 17, 18, and 19 show typical outputs for auto-run ACK0, auto-run ACK1 and Normal run modes ...
Page 121
Figure 16 32-Bit Multiplexed Transmitter Circuit TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual AMD 12330E-53 117 ...
Page 122
AMD Figure 17 AUTORUN ACK 0 (No Sync Between Data Bytes STRB TXCLK CSTRB DSTRB Figure 18 AUTORUN ACK 1 (One Sync Between Every ...
Page 123
Figure 19 Normal Run Mode (Transmission of Syncs Depends on Host STRB TXCLK CSTRB DSTRB TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual AMD 12330E-56 119 ...
Page 124
... Bipolar IMOX–S2: 402L–1156 TiW (barrier metal): 1800 A nom. thickness AlCu: 1.0% Cu, 8000 A nom. thickness Pitch = 4 AlCu: 1.0% Cu, 15500 A nom. thickness Pitch = 8 Silox/Nitride dual layer. 7500 A nominal thickness Nitride: 6800 A nominal thickness Receiver (RX) Am7969-125 Am7969-175 4769 2 2 196 x 187 mils 4384 24 3556 ...
Page 125
Assembly/Packaging: Assembly Location: Ld. Frame Material: Bond Wire: Bonding Method: Die Attach: Molding Compound: Lead Finish Thermal Impedance RX: TX, RX socketed 2 surface mounted TAXIchip Integrated Circuits Technical Manual CerDIP (CD 028) LCC (CLT028) ...
Page 126
AMD TAXI Technical Information Publication #89-Nov ’89 Subject: TAXIchip Error Rate Example INTRODUCTION A method was devised to establish a baseline TAXIchip set error rate. A series of tests were conducted at a transmission rate of 125 MHz at room ...
Page 127
Board #4 failed on another occasion after the errors indicated above, but this failure was due to a power supply failure. Failure time was subtracted from the total run time, and errors were not indicated in the total. Also, boards ...