LMV228SD National Semiconductor, LMV228SD Datasheet

LMV228SD
Specifications of LMV228SD
Related parts for LMV228SD
LMV228SD Summary of contents
Page 1
... SMD package. The LMV225 and the LMV228 are also offered in the 2 2 0.8 mm LLP package. Typical Application LMV225 © 2006 National Semiconductor Corporation Features linear in dB power detection range n Output voltage range 0 Logic low shutdown ...
Page 2
... Absolute Maximum Ratings If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications. Supply Voltage V - GND DD ESD Tolerance (Note 2) Human Body Model Machine Model Storage Temperature Range 2.7 DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V ...
Page 3
DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) Symbol Parameter Logarithmic Slope (Note 8) Logarithmic Intercept (Note 8) V Output Voltage OUT I Output Current OUT Sourcing/Sinking R Output Impedance OUT ...
Page 4
DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) Symbol Parameter Variation Due to Temperature 5.0 DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) ...
Page 5
DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) Symbol Parameter t Turn-on-Time (Note Rise Time (Note Current Into RF /E Pin ...
Page 6
DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) Symbol Parameter Logarithmic Intercept (Note 8) V Output Voltage OUT I Output Current OUT Sourcing/Sinking R Output Impedance OUT e Output Referred Noise ...
Page 7
DC and AC Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed to V (Note 4) Symbol Parameter Variation Due to Temperature Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings ...
Page 8
... LMV226UR LMV226URX LMV228TL LMV228TLX 4-Bump micro SMD LMV228UR LMV228URX LMV228SD 6-pin LLP LMV228SDX Note: TL and TLX products are offered both with leaded and lead free bumps. UR and URX products are offered with lead free bumps. www.national.com 20076002 Name V Positive Supply Voltage DD ...
Page 9
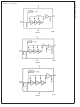
Block Diagrams 20076064 LMV225 20076049 LMV226 20076047 LMV228 9 www.national.com ...
Page 10
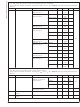
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV225 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage (LMV225) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs. RF Input Power @ 900 MHz (LMV225) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs. RF Input Power ...
Page 11
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV225 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Logarithmic Slope vs. Frequency (LMV225) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power Normalized to 25˚C @ 900 MHz (LMV225) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power Normalized to 25˚C @ ...
Page 12
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV225 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V PSRR vs. Frequency (LMV225 in microSMD) RF Input Impedance vs. Frequency Reactance (LMV225 in micro SMD) www.national.com = 25˚C. (Continued) J 20076023 @ Resistance and RF Input Impedance ...
Page 13
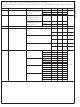
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV226 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage (LMV226) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs Input Power 900 MHz (LMV226) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs. RF Input Power ...
Page 14
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV226 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Logarithmic Slope vs. Frequency (LMV226) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power @ Normalized to 25˚C 900 MHz (LMV226) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power Normalized to 25˚C @ ...
Page 15
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV226 Unless otherwise specified 2.7V PSRR vs. Frequency (LMV226) = 25˚C. (Continued Input Impedance vs. Frequency 20076023 15 @ Resistance and Reactance (LMV226) 20076024 www.national.com ...
Page 16
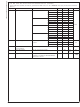
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in microSMD Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage (LMV228 in microSMD) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs. RF Input Power @ 900 MHz (LMV228 in microSMD) Output Voltage and ...
Page 17
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in microSMD Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Logarithmic Slope vs. Frequency (LMV228 in microSMD) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power Normalized to 25˚C @ 900 MHz (LMV228 in microSMD) Output Variation vs. RF ...
Page 18
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in microSMD Unless otherwise specified 2.7V PSRR vs. Frequency (LMV228 in microSMD) www.national.com = 25˚C. (Continued Input Impedance vs. Frequency Reactance (LMV228 in microSMD) 20076023 18 @ Resistance and 20076024 ...
Page 19
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in LLP Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage (LMV228 in LLP) Output Voltage and Log Conformance vs. RF Input Power @ 900 MHz (LMV228 inLLP) Output Voltage and Log ...
Page 20
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in LLP Unless otherwise specified 2.7V Logarithmic Slope vs. Frequency (LMV228 in LLP) Output Variation vs. RF Input Power Normalized to 25˚C @ 900 MHz (LMV228 in LLP) Output Variation vs. RF ...
Page 21
Typical Performance Characteristics LMV228 in LLP Unless otherwise specified 2.7V PSRR vs. Frequency (LMV228 in LLP) = 25˚C. (Continued Input Impedance vs. Frequency 20076065 21 @ Resistance and Reactance (LMV228 in LLP) 20076066 www.national.com ...
Page 22
Application Notes CONFIGURING A TYPICAL APPLICATION The LMV225/LMV226/LMV228 are power detectors in- tended for CDMA and WCDMA applications. Power applied at its input translates voltage on the output through a linear-in-dB response. The LMV225 detector is especially ...
Page 23
Application Notes (Continued) number. The goal is to have a magnitude transfer, which is sufficiently flat in the used frequency range; capacitor C should be chosen significantly larger than capacitor C assure a proper performance of the high resistive tap. ...
Page 24
Application Notes (Continued) FIGURE 5. V vs. RF Input Power P OUT The output voltage variation ∆V OUT input signals that fall within the linear range (in dB) of the detector. In other words, the output variation is independent of ...
Page 25
Application Notes (Continued) FIGURE 8. Gain Cell All gain cell outputs are AM-demodulated with a peak detec- tor and summed together. This results in a logarithmic func- tion. The logarithmic range is about: 20 · n · log (A) where, ...
Page 26
... Physical Dimensions NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED 1. EPOXY COATING 2. FOR SOLDER BUMP COMPOSITION, SEE “SOLDER INFORMATION” IN THE PACKAGE SECTION OF THE NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR WEB PAGE (www.national.com). 3. RECOMMEND NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED LANDING PAD. 4. PIN A1 IS ESTABLISHED BY LOWER LEFT CORNER WITH RESPECT TO TEXT ORIENTATION. ...
Page 27
... Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued) NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED 1. FOR SOLDER BUMP COMPOSITION, SEE “SOLDER INFORMATION” IN THE PACKAGE SECTION OF THE NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR WEB PAGE (www.national.com). 2. RECOMMEND NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED LANDING PAD. 3. PIN A1 IS ESTABLISHED BY LOWER LEFT CORNER WITH RESPECT TO TEXT ORIENTATION. ...
Page 28
... BANNED SUBSTANCE COMPLIANCE National Semiconductor follows the provisions of the Product Stewardship Guide for Customers (CSP-9-111C2) and Banned Substances and Materials of Interest Specification (CSP-9-111S2) for regulatory environmental compliance. Details may be found at: www.national.com/quality/green. ...