AT89C5131A-L Atmel Corporation, AT89C5131A-L Datasheet

AT89C5131A-L
Specifications of AT89C5131A-L
Related parts for AT89C5131A-L
AT89C5131A-L Summary of contents
Page 1
... MHz On-chip Oscillator with Analog PLL for 48 MHz Synthesis • Industrial Temperature Range • Low Voltage Range Supply: 2.7V to 3.6V (3.0V to 3.6V required for USB) • Packages: SO28, PLCC52, VQFP64 8-bit Flash Microcontroller with Full Speed USB Device AT89C5131A-L Rev. 4338F–USB–08/07 ...
Page 2
... RAM, a 4-level interrupt system, two 16-bit timer/counters (T0/T1), a full duplex enhanced UART (EUART) and an on-chip oscillator. In addition, AT89C5131A-L has an on-chip expanded RAM of 1024 bytes (ERAM), a dual- data pointer, a 16-bit up/down Timer (T2), a Programmable Counter Array (PCA programmable LED current sources, a programmable hardware watchdog and a power-on reset ...
Page 3
Block Diagram XTAL1 XTAL2 ALE PSEN CPU EA (2) RD (2) WR Notes: 1. Alternate function of Port 1 2. Alternate function of Port 3 3. Alternate function of Port 4 4338F–USB–08/07 (2) (2) EEPROM EUART 32Kx8 Flash 4Kx8 RAM ...
Page 4
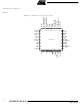
... Pinout Description Pinout AT89C5131A-L 4 Figure 1. AT89C5131A-L 52-pin PLCC Pinout P4.1/SDA 8 9 P2.3/A11 P2.4/A12 10 11 P2.5/A13 12 XTAL2 13 XTAL1 14 P2.6/A14 P2.7/A15 15 VDD 16 AVDD AVSS 19 20 P3.0/RxD P0.1/AD1 44 P0.2/AD2 43 RST 42 P0.3/AD3 41 VSS PLCC52 40 P0.4/AD4 39 P3 ...
Page 5
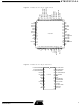
... P2.3/A11 3 P2.4/A12 4 P2.5/A13 5 XTAL2 6 XTAL1 7 P2.6/A14 8 P2.7/A15 9 VDD 10 AVDD AVSS P3.0/RxD Figure 3. AT89C5131A-L 28-pin SO Pinout P1.5/CEX2/KIN5/MISO 1 P1.6/CEX3/KIN6/SCK 2 P1.7/CEX4/KIN7/MOSI 3 P4.0/SCL 4 P4.1/SDA 5 XTAL2 6 XTAL1 7 8 VDD 9 AVSS 10 P3.0/RxD 11 PLLF VREF ...
Page 6
... Signals AT89C5131A-L 6 All the AT89C5131A-L signals are detailed by functionality on Table 1 through Table 12. Table 1. Keypad Interface Signal Description Signal Name Type Description Keypad Input Lines KIN[7:0) I Holding one of these pins high or low for 24 oscillator periods triggers a keypad interrupt if enabled. Held line is reported in the KBCON register. ...
Page 7
Table 4. Timer 0, Timer 1 and Timer 2 Signal Description (Continued) Signal Name Type Description Timer Counter 0 External Clock Input T0 I When Timer 0 operates as a counter, a falling edge on the T0 pin increments ...
Page 8
... AT89C5131A-L 8 Table 8. Ports Signal Description Signal Name Type Description Port 8-bit open-drain bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them float and can be used P0[7:0] I/O as high impedance inputs. To avoid any parasitic current consumption, Floating P0 inputs must be pulled Port 1 ...
Page 9
Table 10. USB Signal Description Signal Name Type Description USB Data + signal D+ I/O Set to high level under reset. USB Data - signal D- I/O Set to low level under reset. USB Reference Voltage VREF O Connect ...
Page 10
... AT89C5131A-L 10 Table 12. Power Signal Description Signal Name Type Description Alternate Ground AVSS GND AVSS is used to supply the on-chip PLL and the USB PAD. Alternate Supply Voltage AVDD PWR AVDD is used to supply the on-chip PLL and the USB PAD. Digital Ground VSS GND VSS is used to supply the buffer ring and the digital core ...
Page 11
... All the external components described in the figure below must be implemented as close as possible from the microcontroller package. The following figure represents the typical wiring schematic. VDD 100nF 4.7µF VSS VSS 1.5K VRef AT89C5131A-L 27R D+ 27R D- PLLF 100R 10nF VSS VSS VSS ...
Page 12
... PCB Recommandations AT89C5131A-L 12 Figure 5. USB Pads Components must be close to the microcontroller VRef possible, isolate D+ and D- signals from other signals with ground wires Figure 6. USB PLL Components must be close to the microcontroller Isolate filter components Wires must be routed in Parallel and must be as short as possible ...
Page 13
... Phase Lock Loop (PLL). All the internal clocks to the peripherals and CPU core are gen- erated by this controller. The AT89C5131A-L X1 and X2 pins are the input and the output of a single-stage on- chip inverter (see Figure 7) that can be configured with off-chip components as a Pierce oscillator (see Figure 8). Value of capacitors and crystal characteristics are detailed in the section “ ...
Page 14
... AT89C5131A-L 14 Figure 8. Crystal Connection VSS The AT89C5131A-L PLL is used to generate internal high frequency clock (the USB Clock) synchronized with an external low-frequency (the Peripheral Clock). The PLL clock is used to generate the USB interface clock. Figure 9 shows the internal structure of the PLL. The PFLD block is the Phase Frequency Comparator and Lock Detector. This block ...
Page 15
PLL Programming Divider Values 4338F–USB–08/07 The PLL is programmed using the flow shown in Figure 11. As soon as clock generation is enabled user must wait until the lock indicator is set to ensure the clock output is stable. Figure ...
Page 16
... Registers AT89C5131A-L 16 Table 14. CKCON0 (S:8Fh) Clock Control Register TWIX2 WDX2 PCAX2 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description TWI Clock This control bit is validated when the CPU clock X2 is set. When X2 is low, 7 TWIX2 this bit has no effect. Clear to select 6 clock periods per peripheral clock cycle. ...
Page 17
Table 15. CKCON1 (S:AFh) Clock Control Register Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7-1 - The value read from this bit is always 0. Do not set this bit. SPI Clock This ...
Page 18
... SFR Mapping AT89C5131A-L 18 The Special Function Registers (SFRs) of the AT89C5131A-L fall into the following categories: • C51 core registers: ACC, B, DPH, DPL, PSW, SP • I/O port registers: P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 • Timer registers: T2CON, T2MOD, TCON, TH0, TH1, TH2, TMOD, TL0, TL1, TL2, RCAP2L, RCAP2H • ...
Page 19
Table 18. SFR Descriptions Bit Addressable 0/8 1/9 CH UEPINT F8h 0000 0000 0000 0000 LEDCON B F0h 0000 0000 0000 0000 CL E8h 0000 0000 ACC E0h 0000 0000 CCON CMOD D8h 00X0 0000 00XX X000 FCON (1) PSW ...
Page 20
... AT89C5131A-L 20 The Special Function Registers (SFRs) of the AT89C5131 fall into the following categories: Table 19. C51 Core SFRs Mnemonic Add Name ACC E0h Accumulator B F0h B Register Program Status PSW D0h Word Stack Pointer SP 81h LSB of SPX Data Pointer Low byte DPL 82h ...
Page 21
Table 21. Timer SFR’s Mnemonic Add Name TH0 8Ch Timer/Counter 0 High byte TL0 8Ah Timer/Counter 0 Low byte TH1 8Dh Timer/Counter 1 High byte TL1 8Bh Timer/Counter 1 Low byte TH2 CDh Timer/Counter 2 High byte TL2 CCh Timer/Counter ...
Page 22
... Interrupt Priority Control High 0 IPL1 B2h Interrupt Priority Control Low 1 IPH1 B3h Interrupt Priority Control High 1 Table 26. PLL SFRs Mnemonic Add Name PLLCON A3h PLL Control PLLDIV A4h PLL Divider AT89C5131A CIDL WDTE ECOM0 CAPP0 CAPN0 ECOM1 CAPP1 CAPN1 ECOM2 CAPP2 ...
Page 23
Table 27. Keyboard SFRs Mnemonic Add Name Keyboard Flag KBF 9Eh Register Keyboard Input Enable KBE 9Dh Register Keyboard Level KBLS 9Ch Selector Register Table 28. TWI SFRs Mnemonic Add Name Synchronous Serial SSCON 93h Control Synchronous Serial SSCS 94h ...
Page 24
... Auxiliary Register 0 AUXR1 A2h Auxiliary Register 1 CKCON0 8Fh Clock Control 0 CKCON1 AFh Clock Control 1 LEDCON F1h LED Control FCON D1h Flash Control EECON D2h EEPROM Contol AT89C5131A EP6INTE EP5INTE EP4INTE FDAT7 FDAT6 FDAT5 FDAT4 BYCT7 BYCT6 BYCT5 BYCT4 - - ...
Page 25
Dual Data Pointer Register Figure 12. Use of Dual Pointer 7 0 DPS AUXR1(A2H) 4338F–USB–08/07 The additional data pointer can be used to speed up code execution and reduce code size. The dual DPTR structure is a way by which ...
Page 26
... AT89C5131A-L 26 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE ; Block move using dual data pointers ; Modifies DPTR0, DPTR1, A and PSW ; note: DPS exits opposite of entry state ; unless an extra INC AUXR1 is added ; 00A2 AUXR1 EQU 0A2H ; 0000 909000MOV DPTR,#SOURCE ; address of SOURCE 0003 05A2 INC AUXR1 ; switch data pointers 0005 90A000 MOV DPTR,#DEST ...
Page 27
... External Code Memory Access Memory Interface 4338F–USB–08/07 The AT89C5131A-L implement 32 Kbytes of on-chip program/code memory. Figure 13 shows the split of internal and external program/code memory spaces depending on the product. The Flash memory increases EPROM and ROM functionality by in-circuit electrical era- sure and programming. Thanks to the internal charge pump, the high voltage needed for programming or erasing Flash cells is generated on-chip using the standard V age ...
Page 28
... This signal is active low during external code fetch or external code read (MOVC instruction). This section describes the bus cycles the AT89C5131A-L executes to fetch code (see Figure 15) in the external program/code memory. External memory cycle takes 6 CPU clock periods. This is equivalent to 12 oscillator clock periods in standard mode or 6 oscillator clock periods in X2 mode ...
Page 29
Figure 16. Flash Memory Architecture Hardware Security (1 Byte) Extra Row (128 Bytes) Column Latches (128 Bytes) FM0 Memory Architecture User Space Extra Row (XRow) Hardware Security Space Column Latches Overview of FM0 Operations Mapping of the Memory Space By ...
Page 30
... Launching Programming Status of the Flash Memory Selecting FM0/FM1 AT89C5131A-L 30 The other memory spaces (user, extra row, hardware security) are made accessible in the code segment by programming bits FMOD0 and FMOD1 in FCON register in accor- dance with Table 34. A MOVC instruction is then used for reading these spaces. ...
Page 31
Loading the Column Latches Programming the Flash Spaces User 4338F–USB–08/07 Any number of data from 1 byte to 128 bytes can be loaded in the column latches. This provides the capability to program the whole memory by byte, by page ...
Page 32
... Extra Row AT89C5131A-L 32 The following procedure is used to program the Extra Row space and is summarized in Figure 18: • Load data in the column latches from address FF80h to FFFFh. • Disable the interrupts. • Launch the programming by writing the data sequence 52h followed by A2h in FCON register. ...
Page 33
Hardware Security 4338F–USB–08/07 The following procedure is used to program the Hardware Security space and is sum- marized in Figure 19: • Set FPS and map Hardware byte (FCON = 0x0C) • Disable the interrupts. • Load DPTR at address ...
Page 34
... Reading the Flash Spaces User Extra Row Hardware Security AT89C5131A-L 34 The following procedure is used to read the User space and is summarized in Figure 20: • Map the User space by writing 00h in FCON register. • Read one byte in Accumulator by executing MOVC A, @A+DPTR with & ...
Page 35
Registers 4338F–USB–08/07 Table 36. FCON (S:D1h) Flash Control Register FPL3 FPL2 FPL1 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Programming Launch Command Bits 7-4 FPL3:0 Write 5Xh followed by AXh to launch the programming according to FMOD1:0. (see Table ...
Page 36
... Flash EEPROM Memory General Description Features Flash Programming and Erasure AT89C5131A-L 36 The Flash memory increases EPROM functionality with in-circuit electrical erasure and programming. It contains 32 Kbytes of program memory organized in 256 pages of 128 bytes, respectively. This memory is both parallel and serial In-System Programmable (ISP) ...
Page 37
... Software registers are in a special page of the Flash memory which can be accessed through the API or with the parallel programming modes. This page, called “Extra Flash Memory”, is not in the internal Flash program memory addressing space. The only hardware register of the AT89C5131A-L is called Hardware Security Byte (HSB). Table 37. Hardware Security Byte (HSB) 7 ...
Page 38
... Default Values Software Registers AT89C5131A-L 38 Table 38. Program Lock bits Program Lock Bits Security level LB0 LB1 Notes unprogrammed or “one” level programmed or “zero” level don’t care 4. WARNING: Security level 2 and 3 should only be programmed after verification. ...
Page 39
... The two lock bits provide different levels of protection for the on-chip code and data, when programmed as shown to Table 41. Default value FFh – 0FFh – FFh – 58h Atmel C51 X2, Electrically D7h Erasable F7h AT89C5131A-L 32 Kbyte AT89C5131A-L 32 Kbyte, DFh revision LB1 and Table 41. 0 LB0 39 ...
Page 40
... P: programmed or “zero” level. 3. WARNING: Security level 2 and 3 should only be programmed after Flash and code verification. AT89C5131A-L parts are delivered with the ISP boot in the Flash memory. After ISP or parallel programming, the possible contents of the Flash memory are summarized in Figure 21: ...
Page 41
EEPROM Data Memory Description Write Data in the Column Latches Programming Read Data 4338F–USB–08/07 The 1-Kbyte on-chip EEPROM memory block is located at addresses 0000h to 03FFh of the ERAM memory space and is selected by setting control bits in ...
Page 42
... Registers AT89C5131A-L 42 Table 42. EECON (S:0D2h) EECON Register EEPL3 EEPL2 EEPL1 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Programming Launch command bits 7-4 EEPL3-0 Write 5Xh followed by AXh to EEPL to launch the programming. Reserved 3 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. ...
Page 43
In-System Programming (ISP) Flash Programming and Erasure 4338F–USB–08/07 With the implementation of the User Space (FM0) and the Boot Space (FM1) in Flash technology the AT89C5131 allows the system engineer the development of applications with a very high level of ...
Page 44
... Figure 23. Hardware Boot Process Algorithm ENBOOT = 0000h Application in FM0 AT89C5131A-L 44 Many algorithms can be used for the software boot process. Below are descriptions of the different flags and Bytes. Boot Loader Jump bit (BLJB): - This bit indicates if on RESET the user wants to jump to this application at address @0000h on FM0 or execute the boot loader at address @F400h on FM1 ...
Page 45
... Copy of the Device ID#2: Memories size and type Copy of the Device ID#3: Name and Revision VCC VCC VCC EA ALE /RST XTAL2 Bootloader /PSEN XTAL1 1K VSS GND GND GND AT89C5131A-L Default Value Address 58h 30h D7h 31h BBh 60h FFh 61h Unconnected C2 GND Crystal GND C1 ...
Page 46
... Low Pin Count Hardware Conditions (SOIC28) AT89C5131A PSEN is an output port in normal operating mode (running user application or boot- loader code) after reset recommended to release PSEN after rising edge of reset signal. Low pin count products do not have PSEN signal, thus for these products, the boot- loader is always executed after reset thanks to the BLJB bit ...
Page 47
... Part Number ERAM Size AT89C5131A-L 1024 The AT89C5131A-L has on-chip data memory which is mapped into the following four separate segments. 1. The Lower 128 bytes of RAM (addresses 00h to 7Fh) are directly and indirectly addressable. 2. The Upper 128 bytes of RAM (addresses 80h to FFh) are indirectly addressable only ...
Page 48
... AT89C5131A-L 48 When an instruction accesses an internal location above address 7Fh, the CPU knows whether the access is to the upper 128 bytes of data RAM or to SFR space by the addressing mode used in the instruction. • Instructions that use direct addressing access SFR space. For example: MOV 0A0H, # data, accesses the SFR at location 0A0h (which is P2). • ...
Page 49
Table 45. AUXR Register AUXR - Auxiliary Register (8Eh DPU - M0 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Disable Weak Pull Up 7 DPU Cleared to enabled weak pull up on standard Ports. Set to disable weak ...
Page 50
... Auto-reload Mode AT89C5131A-L 50 The Timer 2 in the AT89C5131A-L is the standard C52 Timer 16-bit timer/counter: the count is maintained by two cascaded eight-bit timer registers, TH2 and TL2 controlled by T2CON (Table 46) and T2MOD (Table 47) registers. Timer 2 operation is similar to Timer 0 and Timer 1. C/T2 selects F external pin T2 (counter operation) as the timer clock input ...
Page 51
Figure 26. Auto-reload Mode Up/Down Counter (DCEN = 1) F CLK PERIPH Programmable Clock Output 4338F–USB–08/ T2CON (DOWN COUNTING RELOAD VALUE) FFh (8-bit) TL2 (8-bit) RCAP2L RCAP2H (8-bit) (UP COUNTING RELOAD VALUE) In the Clock-out mode, Timer ...
Page 52
... AT89C5131A possible to use Timer baud rate generator and a clock generator simulta- neously. For this configuration, the baud rates and clock frequencies are not independent since both functions use the values in the RCAP2H and RCAP2L registers. Figure 27. Clock-out Mode C/ ...
Page 53
Table 46. T2CON Register T2CON - Timer 2 Control Register (C8h TF2 EXF2 RCLK Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Timer 2 overflow Flag 7 TF2 Must be cleared by software. Set by hardware on Timer 2 ...
Page 54
... AT89C5131A-L 54 Table 47. T2MOD Register T2MOD - Timer 2 Mode Control Register (C9h Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. Reserved 6 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. Reserved ...
Page 55
Programmable Counter Array (PCA) 4338F–USB–08/07 The PCA provides more timing capabilities with less CPU intervention than the standard timer/counters. Its advantages include reduced software overhead and improved accu- racy. The PCA consists of a dedicated timer/counter which serves as the ...
Page 56
... Figure 28. PCA Timer/Counter F /6 CLK PERIPH F /2 CLK PERIPH T0 OVF P1.2 Idle AT89C5131A-L 56 CIDL WDTE CPS1 CPS0 CF CR CCF4 CCF3 CCF2 CCF1 CCF0 Table 48. CMOD Register CMOD - PCA Counter Mode Register (D9h CIDL WDTE - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Counter Idle Control ...
Page 57
The CMOD register includes three additional bits associated with the PCA (See Figure 28 and Table 48). • The CIDL bit allows the PCA to stop during idle mode. • The WDTE bit enables or disables the watchdog function ...
Page 58
... PCA Timer/Counter Module 0 Module 1 Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 CMOD.0 ECF AT89C5131A-L 58 The watchdog timer function is implemented in module 4 (See Figure 31). The PCA interrupt system is shown in Figure 29 CCF4 CCF3 CCF2 CCF1 CCF0 ECCFn CCAPMn.0 PCA Modules: each one of the five compare/capture modules has six possible func- tions. It can perform: • ...
Page 59
CAPP bit enables the positive edge. If both bits are set both edges will be enabled and a capture will occur for either transition. • The last bit in the register ECOM (CCAPMn.6) when set enables the comparator ...
Page 60
... AT89C5131A-L 60 Table 51. PCA Module Modes (CCAPMn Registers) ECOMn CAPPn CAPNn MATn There are two additional registers associated with each of the PCA modules. They are CCAPnH and CCAPnL and these are the registers that store the 16-bit count when a capture occurs or a compare should occur ...
Page 61
Table 52. CCAPnH Registers (n = 0-4) CCAP0H - PCA Module 0 Compare/Capture Control Register High (0FAh) CCAP1H - PCA Module 1 Compare/Capture Control Register High (0FBh) CCAP2H - PCA Module 2 Compare/Capture Control Register High (0FCh) CCAP3H - ...
Page 62
... PCA Capture Mode Figure 30. PCA Capture Mode CF CR Cex.n ECOMn 16-bit Software Timer/Compare Mode AT89C5131A-L 62 Table 55. CL Register CL - PCA Counter Register Low (0E9h Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description PCA Counter Value Reset Value = 0000 0000b Not bit addressable To use one of the PCA modules in the capture mode either one or both of the CCAPM bits CAPN and CAPP for that module must be set ...
Page 63
Figure 31. PCA Compare Mode and PCA Watchdog Timer Write to CCAPnL Reset Write to CCAPnH Enable 1 0 High Speed Output Mode 4338F–USB–08/07 CCF4 CF CR CCAPnH CCAPnL Match 16-bit Comparator CH CL PCA Counter/Timer ECOMn CAPPn CAPNn MATn ...
Page 64
... Figure 32. PCA High-speed Output Mode Write to Reset CCAPnL Write to CCAPnH 0 Enable 1 Pulse Width Modulator Mode AT89C5131A CCF4 CCF3 CCF2 CCF1 CCF0 CCAPnH CCAPnL Match 16-bit Comparator CH CL PCA counter/timer ECOMn CAPPn CAPNn MATn TOGn PWMn ECCFn Before enabling ECOM bit, CCAPnL and CCAPnH should be set with a non zero value, otherwise an unwanted match could happen. Once ECOM set, writing CCAPnL will clear ECOM so that an unwanted match doesn’ ...
Page 65
PCA Watchdog Timer 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 33. PCA PWM Mode Overflow Enable ECOMn CAPPn CAPNn MATn TOGn PWMn ECCFn An on-board watchdog timer is available with the PCA to improve the reliability of the system without increasing chip count. Watchdog timers ...
Page 66
... Serial I/O Port Framing Error Detection AT89C5131A-L 66 The serial I/O port in the AT89C5131A-L is compatible with the serial I/O port in the 80C52. It provides both synchronous and asynchronous communication modes. It operates as an Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART) in three full-duplex modes (modes 1, 2 and 3). Asynchronous transmission and reception can occur simul- taneously and at different baud rates ...
Page 67
Automatic Address Recognition Given Address 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 36. UART Timings in Modes 2 and 3 RXD D0 D1 Start Bit RI SMOD0 = 0 RI SMOD0 = 1 FE SMOD0 = 1 The automatic address recognition feature is enabled when ...
Page 68
... Broadcast Address Reset Addresses AT89C5131A-L 68 The SADEN byte is selected so that each slave may be addressed separately. For slave A, bit 0 (the LSB don’t care bit; for slaves B and C, bit commu- nicate with slave A only, the master must send an address where bit 0 is clear (e.g. ...
Page 69
Baud Rate Selection for UART for Mode 1 and 3 Baud Rate Selection Table for UART Internal Baud Rate Generator (BRG) 4338F–USB–08/07 SADDR - Slave Address Register (A9h Reset Value = 0000 0000b Not bit addressable The ...
Page 70
... Figure 38. Internal Baud Rate Peripheral Clock BRR AT89C5131A-L 70 auto reload counter 0 /6 BRG 1 BRL SPD • The baud rate for UART is token by formula: Baud_Rate = (BRL) = 256 - overflow 0 INT_BRG 1 SMOD1 SMOD1 CLK PERIPH (1-SPD [256 - (BRL)] SMOD1 ...
Page 71
Table 56. SCON Register – SCON Serial Control Register (98h FE/SM0 SM1 SM2 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Framing Error bit (SMOD0 = 1) Clear to reset the error state, not cleared by a valid stop ...
Page 72
... UART Registers AT89C5131A-L 72 Example of computed value when SMOD1 = 1, SPD = 16.384 MHz OSC Baud Rates BRL 115200 247 57600 238 38400 229 28800 220 19200 203 9600 149 4800 43 Example of computed value when SMOD1 = 0, SPD = 16.384 MHz OSC ...
Page 73
BRL - Baud Rate Reload Register for the internal baud rate generator, UART (9Ah – – – Reset Value = 0000 0000b Table 57. T2CON Register T2CON - Timer 2 Control Register (C8h ...
Page 74
... AT89C5131A-L 74 Table 58. PCON Register PCON - Power Control Register (87h SMOD1 SMOD0 - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Serial port Mode bit 1 for UART 7 SMOD1 Set to select double baud rate in mode Serial port Mode bit 0 for UART 6 SMOD0 Cleared to select SM0 bit in SCON register. ...
Page 75
Table 59. BDRCON Register BDRCON - Baud Rate Control Register (9Bh Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit Reserved ...
Page 76
... Individual Enable AT89C5131A-L 76 The AT89C5131A-L has a total of 11 interrupt vectors: two external interrupts (INT0 and INT1), three timer interrupts (timers 0, 1 and 2), the serial port interrupt, SPI interrupt, Keyboard interrupt, USB interrupt and the PCA global interrupt. These interrupts are shown in Figure 39. ...
Page 77
Registers 4338F–USB–08/07 Each of the interrupt sources can be individually enabled or disabled by setting or clear- ing a bit in the Interrupt Enable register (Table 61). This register also contains a global disable bit, which must be cleared to ...
Page 78
... AT89C5131A-L 78 Table 61. IEN0 Register IEN0 - Interrupt Enable Register (A8h ET2 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Enable All interrupt bit 7 EA Cleared to disable all interrupts. Set to enable all interrupts. PCA interrupt enable bit Cleared to disable Set to enable. Timer 2 overflow interrupt Enable bit ...
Page 79
Table 62. IPL0 Register IPL0 - Interrupt Priority Register (B8h PPCL PT2L Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. PCA interrupt ...
Page 80
... AT89C5131A-L 80 Table 63. IPH0 Register IPH0 - Interrupt Priority High Register (B7h PPCH PT2H Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. PCA interrupt Priority high bit. PPCHPPCLPriority Level 0 0Lowest 6 PPCH ...
Page 81
Table 64. IEN1 Register IEN1 - Interrupt Enable Register (B1h EUSB - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description 7 - Reserved USB Interrupt Enable bit 6 EUSB Cleared to disable USB interrupt. Set to enable USB ...
Page 82
... AT89C5131A-L 82 Table 65. IPL1 Register IPL1 - Interrupt Priority Register (B2h PUSBL - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. USB Interrupt Priority bit 6 PUSBL Refer to PUSBH for priority level. Reserved 5 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. ...
Page 83
Table 66. IPH1 Register IPH1 - Interrupt Priority High Register (B3h PUSBH - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. USB ...
Page 84
... Interrupt Sources and Vector Addresses AT89C5131A-L 84 Table 67. Vector Table Polling Interrupt Number Priority Source 0 0 Reset 1 1 INT0 2 2 Timer INT1 4 4 Timer UART 6 7 Timer PCA 8 8 Keyboard 9 9 TWI 10 10 SPI USB ...
Page 85
... Description Interrupt 4338F–USB–08/07 The AT89C5131A-L implements a keyboard interface allowing the connection matrix keyboard based on 8 inputs with programmable interrupt capability on both high or low level. These inputs are available as an alternate function of P1 and allow to exit from idle and power down modes. ...
Page 86
... Power Reduction Mode Registers AT89C5131A inputs allow exit from idle and power down modes as detailed in section “Power- down Mode”. Table 68. KBF Register KBF - Keyboard Flag Register (9Eh KBF7 KBF6 KBF5 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Keyboard line 7 flag Set by hardware when the Port line 7 detects a programmed level ...
Page 87
Table 69. KBE Register KBE - Keyboard Input Enable Register (9Dh KBE7 KBE6 KBE5 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Keyboard line 7 Enable bit 7 KBE7 Cleared to enable standard I/O pin. Set to enable KBF.7 ...
Page 88
... AT89C5131A-L 88 Table 70. KBLS Register KBLS-Keyboard Level Selector Register (9Ch KBLS7 KBLS6 KBLS5 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Keyboard line 7 Level Selection bit 7 KBLS7 Cleared to enable a low level detection on Port line 7. Set to enable a high level detection on Port line 7. Keyboard line 6 Level Selection bit ...
Page 89
... Programmable LED 4338F–USB–08/07 AT89C5131A-L have programmable LED current sources, configured by the register LEDCON. Table 71. LEDCON Register LEDCON (S:F1h) LED Control Register LED3 LED2 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description PortLED3Configuration 0 0Standard C51 Port 7:6 LED3 current source when P3.7 is low current source when P3 ...
Page 90
... Master Input Slave Output (MISO) SPI Serial Clock (SCK) Slave Select (SS) AT89C5131A-L 90 The Serial Peripheral Interface module (SPI) allows full-duplex, synchronous, serial communication between the MCU and peripheral devices, including other MCUs. Features of the SPI module include the following: • ...
Page 91
Baud Rate 4338F–USB–08/07 pins (Figure 42). To prevent bus conflicts on the MISO line, only one slave should be selected at a time by the Master for a transmission Master configuration, the SS line can be used in ...
Page 92
... Functional Description Operating Modes AT89C5131A-L 92 Figure 43 shows a detailed structure of the SPI module. Figure 43. SPI Module Block Diagram FCLK PERIPH /4 Clock /8 /16 Divider /32 /64 /128 Clock Select SPR2 SPEN SSDIS MSTR SPI Interrupt Request The Serial Peripheral Interface can be configured as one of the two modes: Master mode or Slave mode ...
Page 93
Master Mode Slave Mode Transmission Formats 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 44. Full-duplex Master/Slave Interconnection 8-bit Shift Register SPI Clock Generator Master MCU The SPI operates in Master mode when the Master bit, MSTR is set. Only one Master SPI device can initiate ...
Page 94
... Figure 46. Data Transmission Format (CPHA = 1) SCK cycle number SPEN (internal) SCK (CPOL = 0) SCK (CPOL = 1) MOSI (from Master) MISO (from Slave) SS (to Slave) Capture point Figure 47. CPHA/SS Timing MISO/MOSI Master SS Slave SS (CPHA = 0) Slave SS (CPHA = 1) AT89C5131A MSB bit6 bit5 bit4 MSB bit6 bit5 bit4 1 2 ...
Page 95
Error Conditions Mode Fault (MODF) Write Collision (WCOL) Overrun Condition Interrupts 4338F–USB–08/07 The following flags in the SPSTA signal SPI error conditions: Mode Fault error in Master mode SPI indicates that the level on the Slave Select (SS) pin is ...
Page 96
... Registers Serial Peripheral Control Register (SPCON) AT89C5131A-L 96 Figure 48. SPI Interrupt Requests Generation SPIF SPI Transmitter CPU Interrupt Request MODF SSDIS There are three registers in the module that provide control, status and data storage functions. These registers are describes in the following paragraphs. ...
Page 97
Serial Peripheral Status Register (SPSTA) 4338F–USB–08/07 Bit Number Bit Mnemonic Description SPR2 SPR1 SPR0 Serial Peripheral Rate 2 SPR1 000Reserved 00 1F CLK PERIPH/ 010 F CLK PERIPH/ 011F CLK PERIPH/ 100F CLK PERIPH SPR0 CLK PERIPH/ ...
Page 98
... Serial Peripheral Data Register (SPDAT) AT89C5131A-L 98 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 2 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit Reserved 1 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. Reserved 0 - The value read from this bit is indeterminate. Do not set this bit. ...
Page 99
Two Wire Interface ( TWI 4338F–USB–08/07 ) This section describes the 2-wire interface. The 2-wire bus is a bi-directional 2-wire serial communication standard designed primarily for simple but efficient integrated circuit (IC) control. The system is comprised of ...
Page 100
... Figure 50. Block Diagram Input Filter SDA Output Stage Input Filter SCL Output Stage AT89C5131A-L 100 Address Register SSADR Comparator SSDAT Shift Register Arbitration & Sink Logic Timing & Control logic Serial clock generator Timer 1 overflow Control Register SSCON Status Status Decoder ...
Page 101
Description 4338F–USB–08/07 The CPU interfaces to the 2-wire logic via the following four 8-bit special function regis- ters: the Synchronous Serial Control register (SSCON; Table 86), the Synchronous Serial Data register (SSDAT; Table 87), the Synchronous Serial Control and Status ...
Page 102
... Master Transmitter Mode Master Receiver Mode AT89C5131A-L 102 A: Acknowledge bit (low level at SDA) A: Not acknowledge bit (high level at SDA) Data: 8-bit data byte P : STOP condition In Figure 52 to Figure 55, circles are used to indicate when the serial interrupt flag is set. The numbers in the circles show the status code held in SSCS. At these points, a ser- vice routine must be executed to continue or complete the serial transfer ...
Page 103
Slave Receiver Mode Slave Transmitter Mode 4338F–USB–08/07 status code in SSCS are possible. There are 40h, 48h or 38h for the master mode and also 68h, 78h or B0h if the slave mode was enabled (AA=logic 1). The appropriate action ...
Page 104
... Miscellaneous States Notes AT89C5131A-L 104 have been received, the serial interrupt flag is set and a valid status code can be read from SSCS. This status code is used to vector to an interrupt service routine. The appro- priate action to be taken for each of these status code is detailed in Table . The slave transmitter mode may also be entered if arbitration is lost while the TWI module is in the master mode ...
Page 105
Figure 52. Format and State in the Master Transmitter Mode Successfull S transmission to a slave receiver 08h Next transfer started with a repeated start condition Not acknowledge received after the slave address Not acknowledge received after a data byte ...
Page 106
... Write data byte No SSDAT action Data byte has been 30h transmitted; NOT ACK No SSDAT action has been received No SSDAT action No SSDAT action Arbitration lost in 38h SLA+W or data bytes No SSDAT action AT89C5131A-L 106 Application software response To SSCON SSSTA SSSTO SSI SSAA ...
Page 107
Figure 53. Format and State in the Master Receiver Mode Successfull transmission S SLA to a slave receiver 08h Next transfer started with a repeated start condition Not acknowledge received after the slave address Arbitration lost in slave address or ...
Page 108
... Data byte has been 50h received; ACK has been returned Read data byte Read data byte Data byte has been Read data byte 58h received; NOT ACK has been returned Read data byte AT89C5131A-L 108 Application software response To SSCON SSSTA SSSTO SSI SSAA ...
Page 109
Figure 54. Format and State in the Slave Receiver Mode Reception of the own slave address and one or more data bytes. All are acknowledged. Last data byte received is not acknowledged. Arbitration lost as master and addressed as slave ...
Page 110
... Previously addressed with own SLA+W; data has been 88h received; NOT ACK has been returned Previously addressed with general call; data has been 90h received; ACK has been returned AT89C5131A-L 110 Application Software Response To/from SSDAT To SSCON STA STO SI No SSDAT action or X ...
Page 111
Table 83. Status in Slave Receiver Mode (Continued) Status Code Status of the 2-wire bus and (SSCS) 2-wire hardware Previously addressed with general call; data has been 98h received; NOT ACK has been returned A STOP condition or repeated START ...
Page 112
... Arbitration lost in SLA+R/W as master; own SLA+R has been B0h received; ACK has been returned Data byte in SSDAT has been B8h transmitted; NOT ACK has been received AT89C5131A-L 112 A Data SLA R A8h A B0h Any number of data bytes and their associated Data ...
Page 113
Table 84. Status in Slave Transmitter Mode (Continued) Status Code Status of the 2-wire bus and (SSCS) 2-wire hardware Data byte in SSDAT has been C0h transmitted; NOT ACK has been received Last data byte in SSDAT has C8h been ...
Page 114
... Registers AT89C5131A-L 114 Table 86. SSCON Register SSCON - Synchronous Serial Control Register (93h CR2 SSIE STA Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Control Rate bit 2 7 CR2 See . Synchronous Serial Interface Enable bit 6 SSIE Clear to disable SSLC. Set to enable SSLC. Start flag ...
Page 115
Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description 1 SD1 Address bit 1 or Data bit 1. 0 SD0 Address bit 0 (R/W) or Data bit 0. Table 88. SSCS (094h) Read - Synchronous Serial Control and Status Register ...
Page 116
... Figure 56. USB Device Controller Block Diagram D+ USB D+/D- Buffer D- AT89C5131A-L 116 . The USB device controller provides the hardware that the AT89C5131 needs to inter- face a USB link to a data flow stored in a double port memory (DPRAM). The USB controller requires a 48 MHz ±0.25% reference clock, which is the output of the AT89C5131 PLL (see Section “ ...
Page 117
Serial Interface Engine (SIE) Figure 57. SIE Block Diagram End of Packet Detection Start of Packet Detection D+ D- Clk48 (48 MHz) 4338F–USB–08/07 The SIE performs the following functions: • NRZI data encoding and decoding. • Bit stuffing and un-stuffing. ...
Page 118
... IN UFI NACK C51 Endpoint FIFO write AT89C5131A-L 118 The Function Interface Unit provides the interface between the AT89C5131 and the SIE. It manages transactions at the packet level with minimal intervention from the device firmware, which reads and writes the endpoint FIFOs. Asynchronous Information ...
Page 119
Configuration General Configuration Endpoint Configuration Figure 60. Endpoint Selection UEPSTA0 Endpoint 0 UBYCTH0 UEPSTA6 Endpoint 6 UBYCTH6 4338F–USB–08/07 • USB controller enable Before any USB transaction, the 48 MHz required by the USB controller must be correctly generated (See “Clock ...
Page 120
... AT89C5131A-L 120 • Endpoint enable Before using an endpoint, this one will be enabled by setting the EPEN bit in the UEPCONX register. An endpoint which is not enabled won’t answer to any USB request. The Default Control Endpoint (Endpoint 0) will always be enabled in order to answer to USB standard requests. ...
Page 121
Read/Write Data FIFO FIFO Mapping Figure 61. Endpoint FIFO Configuration UEPSTA0 Endpoint 0 UEPSTA6 Endpoint 6 Read Data FIFO Write Data FIFO 4338F–USB–08/07 • Endpoint FIFO reset Before using an endpoint, its FIFO will be reset. This action resets the ...
Page 122
... Bulk/Interrupt Transactions Bulk/Interrupt OUT Transactions in Standard Mode AT89C5131A-L 122 Bulk and Interrupt transactions are managed in the same way. Figure 62. Bulk/Interrupt OUT transactions in Standard Mode HOST OUT DATA0 (n bytes) OUT DATA1 OUT DATA1 DATA1 OUT An endpoint will be first enabled and configured before being able to receive Bulk or Interrupt packets ...
Page 123
Bulk/Interrupt OUT Transactions in Ping-pong Mode 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 63. Bulk/Interrupt OUT Transactions in Ping-pong Mode HOST OUT DATA0 (n Bytes) ACK DATA1 (m Bytes) OUT ACK OUT DATA0 (p Bytes) ACK An endpoint will be first enabled and configured before ...
Page 124
... Bulk/Interrupt IN Transactions in Standard Mode AT89C5131A-L 124 Figure 64. Bulk/Interrupt IN Transactions in Standard Mode HOST UFI IN NAK IN DATA0 (n Bytes) ACK An endpoint will be first enabled and configured before being able to send Bulk or Inter- rupt packets. The firmware will fill the FIFO with the data to be sent and set the TXRDY bit in the UEP- STAX register to allow the USB controller to send the data stored in FIFO at the next IN request concerning this endpoint ...
Page 125
Bulk/Interrupt IN Transactions in Ping-pong Mode 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 65. Bulk/Interrupt IN Transactions in Ping-pong Mode HOST UFI IN NACK IN DATA0 (n Bytes) ACK IN DATA1 (m Bytes) ACK IN DATA0 (p Bytes) ACK An endpoint will be first enabled ...
Page 126
... Setup Stage Data Stage: Control Endpoint Direction Status Stage AT89C5131A-L 126 The DIR bit in the UEPSTAX register will Receiving Setup packets is the same as receiving Bulk Out packets, except that the RXSETUP bit in the UEPSTAX register is set by the USB controller instead of the RXOUTB0 bit to indicate that an Out packet with a Setup PID has been received on the Control endpoint ...
Page 127
Isochronous Transactions Isochronous OUT Transactions in Standard Mode Isochronous OUT Transactions in Ping-pong Mode 4338F–USB–08/07 An endpoint will be first enabled and configured before being able to receive Isochro- nous packets. When a OUT packet is received on an endpoint, ...
Page 128
... Isochronous IN Transactions in Standard Mode Isochronous IN Transactions in Ping-pong Mode AT89C5131A-L 128 If the Host sends more bytes than supported by the endpoint FIFO, the overflow data won’t be stored, but the USB controller will consider that the packet is valid if the CRC is correct. An endpoint will be first enabled and configured before being able to send Isochronous packets ...
Page 129
Miscellaneous USB Reset STALL Handshake Start of Frame Detection Frame Number Data Toggle Bit 4338F–USB–08/07 The EORINT bit in the USBINT register is set by hardware when a End Of Reset has been detected on the USB bus. This triggers ...
Page 130
... Suspend/Resume Management Suspend Resume AT89C5131A-L 130 The Suspend state can be detected by the USB controller if all the clocks are enabled and if the USB controller is enabled. The bit SPINT is set by hardware when an idle state is detected for more than 3 ms. This triggers a USB interrupt if enabled. ...
Page 131
Figure 66. Example of a Suspend/Resume Management Detection of a SUSPEND State Detection of a RESUME State USB Controller Init SPINT Clear SPINT Set SUSPCLK Disable PLL microcontroller in Power-down WUPCPU Enable PLL Clear SUSPCLK Clear WUPCPU Bit 131 ...
Page 132
... Upstream Resume Figure 67. Example of REMOTE WAKEUP Management SET_FEATURE: DEVICE_REMOTE_WAKEUP Detection of a SUSPEND State Upstream RESUME Sent AT89C5131A-L 132 A USB device can be allowed by the Host to send an upstream resume for Remote Wake Up purpose DEVICE_REMOTE_WAKEUP, the firmware will set to 1 the RMWUPE bit in the USB- CON register to enable this functionality ...
Page 133
... D+ USB Controller D- 4338F–USB–08/07 In order to be re-enumerated by the Host, the AT89C5131A-L has the possibility to sim- ulate a DETACH - ATTACH of the USB bus. The V output voltage is between 3.0V and 3.6V. This output can be connected to the REF D+ pull-up as shown in Figure 68. This output can be put in high-impedance when the DETACH bit is set the USBCON register. Maintaining this output in high imped- ance for more than 3 µ ...
Page 134
... USB Interrupt Control System AT89C5131A-L 134 Table 91. Priority Levels IPHUSB IPLUSB shown in Figure 71, many events can produce a USB interrupt: • TXCMPL: Transmitted In Data (see Table 98 on page 141). This bit is set by hardware when the Host accept a In packet. • ...
Page 135
Figure 71. USB Interrupt Control Block Diagram Endpoint 0..6) TXCMP UEPSTAX.0 RXOUTB0 UEPSTAX.1 RXOUTB1 UEPSTAX.6 RXSETUP UEPSTAX.2 STLCRC UEPSTAX.3 WUPCPU USBINT.5 EWUPCPU USBIEN.5 EORINT USBINT.4 EEORINT USBIEN.4 SOFINT USBINT.3 ESOFINT USBIEN.3 SPINT USBINT.0 ESPINT USBIEN.0 4338F–USB–08/07 EPXINT ...
Page 136
... USB Registers AT89C5131A-L 136 Table 92. USBCON Register USBCON (S:BCh) USB Global Control Register USBE SUSPCLK SDRMWUP Bit Number Bit Mnemonic Description USB Enable Set this bit to enable the USB controller. 7 USBE Clear this bit to disable and reset the USB controller, to disable the USB transceiver an to disable the USB controller clock inputs ...
Page 137
Table 93. USBINT Register USBINT (S:BDh) USB Global Interrupt Register WUPCPU Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7-6 - The value read from these bits is always 0. Do not set these bits. Wake ...
Page 138
... AT89C5131A-L 138 Table 94. USBIEN Register USBIEN (S:BEh) USB Global Interrupt Enable Register EWUPCPU Bit Number Bit Mnemonic Description Reserved 7-6 - The value read from these bits is always 0. Do not set these bits. Enable Wake Up CPU Interrupt Set this bit to enable Wake Up CPU Interrupt. (See “USBIEN Register ...
Page 139
Table 96. UEPNUM Register UEPNUM (S:C7h) USB Endpoint Number Bit Number Bit Mnemonic Description Reserved 7-4 - The value read from these bits is always 0. Do not set these bits. Endpoint Number ...
Page 140
... AT89C5131A-L 140 Table 97. UEPCONX Register UEPCONX (S:D4h) USB Endpoint X Control Register EPEN - - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Endpoint Enable Set this bit to enable the endpoint according to the device configuration. 7 EPEN Endpoint 0 will always be enabled after a hardware or USB bus reset and participate in the device configuration ...
Page 141
Table 98. UEPSTAX (S:CEh) USB Endpoint X Status Register 7 6 DIR RXOUTB1 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Control Endpoint Direction This bit is used only if the endpoint is configured in the control type (seeSection “UEPCONX Register UEPCONX (S:D4h) ...
Page 142
... AT89C5131A-L 142 Table 99. UEPDATX Register UEPDATX (S:CFh) USB FIFO Data Endpoint EPNUM set in UEPNUM Register UEPNUM (S:C7h FDAT7 FDAT6 FDAT5 Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Endpoint X FIFO data FDAT [7:0] Data byte to be written to FIFO or data byte to be read from the FIFO, for the Endpoint X (see EPNUM) ...
Page 143
Table 101. UBYCTHX Register UBYCTHX (S:E3h) USB Byte Count High Register EPNUM set in UEPNUM Register UEPNUM Bit Number Bit Mnemonic Description Reserved 7-2 - The value read from these ...
Page 144
... AT89C5131A-L 144 Table 102. UEPRST Register UEPRST (S:D5h) USB Endpoint FIFO Reset Register EP6RST EP5RST Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is always 0. Do not set this bit. Endpoint 6 FIFO Reset Set this bit and reset the endpoint FIFO prior to any other operation, upon ...
Page 145
Table 103. UEPINT Register UEPINT (S:F8h read-only) USB Endpoint Interrupt Register EP6INT EP5INT Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is always 0. Do not set this bit. ...
Page 146
... AT89C5131A-L 146 Table 104. UEPIEN Register UEPIEN (S:C2h) USB Endpoint Interrupt Enable Register EP6INTE EP5INTE Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Reserved 7 - The value read from this bit is always 0. Do not set this bit. Endpoint 6 Interrupt Enable 6 EP6INTE Set this bit to enable the interrupts for this endpoint. ...
Page 147
Table 105. UFNUMH Register UFNUMH (S:BBh, read-only) USB Frame Number High Register CRCOK Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Frame Number CRC OK This bit is set by hardware when a new Frame Number in ...
Page 148
... The Reset input can be used to force a reset pulse longer than the internal reset con- trolled by the Power Monitor. RST input has a pull-up resistor allowing power-on reset by simply connecting an external capacitor to V and input characteristics are discussed in the Section “DC Characteristics” of the AT89C5131A-L datasheet. Figure 73. Reset Circuitry and Power-On Reset VCC RST a ...
Page 149
... RST pin. In order to properly propagate this pulse to the rest of the application in case of external capacitor or power-supply supervisor circuit kΩ resistor must be added as shown Figure 74. Figure 74. Recommended Reset Output Schematic VDD RST RST 1K VSS + VSS AT89C5131A-M To other on-board circuitry 149 ...
Page 150
... Power Monitor Description AT89C5131A-L 150 The POR/PFD function monitors the internal power-supply of the CPU core memories and the peripherals, and if needed, suspends their activity when the internal power sup- ply falls below a safety threshold. This is achieved by applying an internal reset to them. By generating the Reset the Power Monitor insures a correct start up when AT89C5131 is powered up ...
Page 151
Figure 76. Power Fail Detect Vcc Reset Vcc 4338F–USB–08/07 The Power fail detect monitor the supply generated by the voltage regulator and gener- ate a reset if this supply falls below a safety threshold as illustrated in the Figure 76 ...
Page 152
... In this case, the higher priority interrupt service routine is executed. Once the interrupt is serviced, the next instruction to be executed after RETI will be the one following the instruction that put AT89C5131A-L into power-down mode. can be lowered to save further CC ...
Page 153
Figure 77. Power-down Exit Waveform INT0 INT1 XTAL Active Phase 4338F–USB–08/07 Power-down Phase Oscillator restart Phase Exit from power-down by reset redefines all the SFRs, exit from power-down by external interrupt does no affect the SFRs. Exit from power-down by ...
Page 154
... Registers AT89C5131A-L 154 Table 108. PCON Register PCON (S:87h) Power Control Register SMOD1 SMOD0 - Bit Bit Number Mnemonic Description Serial Port Mode bit 1 7 SMOD1 Set to select double baud rate in mode Serial Port Mode bit 0 6 SMOD0 Set to select FE bit in SCON register. ...
Page 155
Hardware Watchdog Timer Using the WDT 4338F–USB–08/07 The WDT is intended as a recovery method in situations where the CPU may be sub- jected to software upset. The WDT consists of a 14-bit counter and the WatchDog Timer ReSeT (WDTRST) ...
Page 156
... WDT just before entering power-down. In the Idle mode, the oscillator continues to run. To prevent the WDT from resetting the AT89C5131A-L while in Idle mode, the user should always set up a timer that will peri- odically exit Idle, service the WDT, and re-enter Idle mode. ...
Page 157
... Pull ALE low while the device is in reset (RST high) and PSEN is high. • Hold ALE low as RST is deactivated. While the AT89C5131A ONCE mode, an emulator or test CPU can be used to drive the circuit Table 111 shows the status of the port pins during ONCE mode. Normal operation is restored when normal reset is applied. ...
Page 158
... Reduced EMI Mode AT89C5131A-L 158 The ALE signal is used to demultiplex address and data buses on port 0 when used with external program or data memory. Nevertheless, during internal code execution, ALE signal is still generated. In order to reduce EMI, ALE signal can be disabled by setting AO bit. The AO bit is located in AUXR register at bit location 0. As soon set, ALE is no longer output but remains active during MOVX and MOVC instructions and external fetches ...
Page 159
Electrical Characteristics Absolute Maximum Ratings Ambient Temperature Under Bias industrial ........................................................-40°C to 85°C Storage Temperature .................................... -65° 150°C Voltage on V from V ......................................-0. Voltage on Any Pin from V .....................-0.5V ...
Page 160
... OL Port Ports 1, 2 and Maximum total I for all output pins exceeds the test condition than the listed test conditions. AT89C5131A-L 160 Min 2.2 0.15 PFDM . I would be slightly higher if a crystal oscillator used (see Figure RST = V (see Figure 79) ...
Page 161
LED’s Table 113. LED Outputs DC Parameters Symbol Parameter I Output Low Current, P3.6 and P3.7 LED modes OL Note -20°C to +50° 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 79. I Test Condition, Idle Mode ...
Page 162
... USB DC Parameters AT89C5131A-L 162 BUS GND 3 2 USB “B” Receptacle 1.5 kΩ 27Ω pad Symbol Parameter V USB Reference Voltage REF V Input High Voltage for D+ and D- (Driven Input High Voltage for D+ and D- (Floating) IHZ V Input Low Voltage for D+ and D- ...
Page 163
AC Parameters Explanation of the AC Symbols External Program Memory Characteristics 4338F–USB–08/07 Each timing symbol has 5 characters. The first character is always a “T” (stands for time). The other characters, depending on their positions, stand for the name of ...
Page 164
... AT89C5131A-L 164 Table 115. AC Parameters for a Fix Clock ( MHz) Symbol T T LHLL T AVLL T LLAX T LLIV T LLPL T PLPH T PLIV T PXIX T PXIZ T AVIV T PLAZ Table 116. AC Parameters for a Variable Clock Symbol Type T Min LHLL T Min AVLL T Min LLAX T Max LLIV T Min LLPL ...
Page 165
External Program Memory Read Cycle ALE PSEN PORT 0 INSTR IN ADDRESS PORT 2 OR SFR-P2 External Data Memory Characteristics 4338F–USB–08/ CLCL T T LHLL LLIV T LLPL T PLPH T LLAX T PLIV T T AVLL TPLAZ ...
Page 166
... AT89C5131A-L 166 Table 118. AC Parameters for a Variable Clock ( MHz) Symbol T RLRH T WLWH T RLDV T RHDX T RHDZ T LLDV T AVDV T LLWL T AVWL T QVWX T QVWH T WHQX T RLAZ T WHLH Min Max 130 130 100 0 30 160 165 50 100 75 10 160 Units ...
Page 167
External Data Memory Write Cycle ALE PSEN WR PORT 0 ADDRESS PORT 2 OR SFR-P2 4338F–USB–08/07 Table 119. AC Parameters for a Variable Clock Symbol Type T Min RLRH T Min WLWH T Max RLDV T Min RHDX T Max ...
Page 168
... External Data Memory Read Cycle ALE PSEN RD PORT 0 ADDRESS PORT 2 OR SFR-P2 Serial Port Timing - Shift Register Mode AT89C5131A-L 168 T LLDV T LLWL T AVDV T LLAX A0-A7 T RLAZ T AVWL ADDRESS A8-A15 OR SFR P2 Table 120. Symbol Description ( MHz) Symbol T XLXL T QVHX T XHQX T XHDX T XHDV Table 121 ...
Page 169
Shift Register Timing Waveform INSTRUCTION ALE CLOCK T QVXH OUTPUT DATA WRITE to SBUF INPUT DATA CLEAR RI External Clock Drive Characteristics (XTAL1) External Clock Drive Waveforms AC Testing Input/Output Waveforms Float Waveforms 4338F–USB–08/ ...
Page 170
... AT89C5131A-L 170 For timing purposes as port pin is no longer floating when a 100 mV change from load voltage occurs and begins to float when a 100 mV change from the loaded V occurs ≥ ±20 mA level OH OL 4338F–USB–08/07 ...
Page 171
Clock Waveforms STATE4 INTERNAL CLOCK P1 P2 XTAL2 ALE EXTERNAL PROGRAM MEMORY FETCH PSEN P0 DATA SAMPLED FLOAT P2 (EXT) READ CYCLE WRITE CYCLE PORT OPERATION MOV PORT SRC MOV DEST P0 MOV DEST ...
Page 172
... Flash EEPROM Memory and Data EEPROM Memory AT89C5131A-L 172 Table 124. Timing Symbol Definitions Signals S (Hardware PSEN, EA Condition) R RST B FBUSY Flag Table 125. Memory AC Timing VDD = 3.3V ± 10 -40 to +85°C A Symbol Parameter T Input PSEN Valid to RST Edge SVRL T Input PSEN Hold after RST Edge ...
Page 173
USB AC Parameters V CRS Differential Data Lines SPI Interface AC Parameters Definition of Symbols 4338F–USB–08/07 Rise Time 90% 90% 10 Table 126. USB AC Parameters Symbol Parameter t Rise Time R t Fall Time F t Full-speed ...
Page 174
... OHOL T CHCH T CHCX T CLCX T IVCL T CLIX T CLOV, T CLOX AT89C5131A-L 174 Test conditions: capacitive load on all pins= 50 pF. Table 128. SPI Interface Master AC Timing V = 2 -40 to +85° Symbol Parameter Clock Period Clock High Time Clock Low Time , T SS Low to Clock edge ...
Page 175
Waveforms (input) (CPOL= 0) (input) (CPOL= 1) (input) MISO (output) MOSI (input) (input) SCK (CPOL= 0) (input) SCK (CPOL= 1) (input) MISO (output) MOSI (input) 4338F–USB–08/07 Figure 84. SPI Slave Waveforms (CPHA SLCH T T SLCL CHCH ...
Page 176
... SCK (CPOL= 1) (output) MOSI (input) MISO (output) SS (output) SCK (CPOL= 0) (output) SCK (CPOL= 1) (output) MOSI (input) MISO (output) AT89C5131A-L 176 Figure 86. SPI Master Waveforms (SSCPHA CHCH T T CHCX CLCX T T IVCH CHIX T T IVCL CLIX MSB IN BIT 6 T CLOV ...
Page 177
... Ordering Information Table 129. Possible Order Entries Part Number Memory Size (Kbytes) AT89C5131A-RDTIL AT89C5131A-S3SIL AT89C5131A-TISIL AT89C5131A-RDTUL AT89C5131A-S3SUL AT89C5131A-TISUL Note: 1. Optional Packing and Package options (please consult Atmel sales representative): -Tape and Reel -Dry Pack -Known good dice 4338F–USB–08/07 Supply Voltage 32 3 ...
Page 178
... Packaging Information 64-lead VQFP AT89C5131A-L 178 4338F–USB–08/07 ...
Page 179
PLCC STANDARD NOTES FOR PLCC: 1/ CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS : INCHES 2/ DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI Y 14.5M - 1982. 3/ "D" AND "E1" DIMENSIONS DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH OR PROTUSIONS. MOLD FLASH OR PROTUSIONS SHALL NOT EXCEED ...
Page 180
... SO AT89C5131A-L 180 4338F–USB–08/07 ...
Page 181
Document Revision History Changes from 4338D - 09/05 to 4338E - 06/06 Changes from 4338E - 06/06 to 4338F - 08/07 4338F–USB–08/07 1. Correction to Figure 4 on page 11. 1. Hardware Conditions section Page 45 changed to recommend the ...
Page 182
... AT89C5131A-L 182 Features................................................................................................. 1 Description ............................................................................................ 2 Block Diagram....................................................................................... 3 Pinout Description ................................................................................ 4 Pinout.................................................................................................................... 4 Signals .................................................................................................................. 6 Typical Application ............................................................................. 11 Recommended External components................................................................. 11 PCB Recommandations ..................................................................................... 12 Clock Controller.................................................................................. 13 Introduction ......................................................................................................... 13 Oscillator............................................................................................................. 13 PLL ..................................................................................................................... 14 Registers............................................................................................................. 16 SFR Mapping ....................................................................................... 18 Dual Data Pointer Register ................................................................ 25 Program/Code Memory ...................................................................... 27 External Code Memory Access .......................................................................... 27 Flash Memory Architecture................................................................................. 28 Overview of FM0 Operations .............................................................................. 29 Registers ...
Page 183
Flash Programming and Erasure........................................................................ 43 Boot Process ...................................................................................................... 44 Application-Programming-Interface .................................................................... 45 XROW Bytes....................................................................................................... 45 Hardware Conditions .......................................................................................... 45 On-chip Expanded RAM (ERAM)....................................................... 47 Timer 2 ................................................................................................. 50 Auto-reload Mode ............................................................................................... 50 Programmable Clock Output .............................................................................. 51 Programmable Counter ...
Page 184
... AT89C5131A-L 184 USB Controller .................................................................................. 116 Description........................................................................................................ 116 Configuration .................................................................................................... 119 Read/Write Data FIFO ...................................................................................... 121 Bulk/Interrupt Transactions............................................................................... 122 Control Transactions......................................................................................... 126 Isochronous Transactions................................................................................. 127 Miscellaneous ................................................................................................... 129 Suspend/Resume Management ....................................................................... 130 Detach Simulation............................................................................................. 133 USB Interrupt System ....................................................................................... 133 USB Registers .................................................................................................. 136 Reset .................................................................................................. 148 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 148 Reset Input ...
Page 185
SO........................................................................................................ 180 Document Revision History ............................................................. 181 Changes from 4338D - 09/05 to 4338E - 06/06................................................ 181 Changes from 4338E - 06/06 to 4338F - 08/07 ................................................ 181 185 ...
Page 186
... Atmel products are not suitable for, and shall not be used in, automotive applications. Atmel’sAtmel’s products are not intended, authorized, or warranted for use as components in applications intended to support or sustain life. © Atmel Corporation 2007. All rights reserved. Atmel are the trademarks of Atmel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other terms and product names may be trademarks of others. Atmel Operations Memory ...