ATmega1284RZAP Atmel Corporation, ATmega1284RZAP Datasheet - Page 310

ATmega1284RZAP
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega1284RZAP
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega1284RZAP
Flash (kbytes)
128 Kbytes
Max. Operating Frequency
20 MHz
Max I/o Pins
32
Spi
3
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
16
Eeprom (bytes)
4096
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.8 to 3.6
Timers
3
Frequency Band
2.4 GHz
Max Data Rate (mb/s)
0.25
Antenna Diversity
No
External Pa Control
No
Power Output (dbm)
3
Receiver Sensitivity (dbm)
-101
Receive Current Consumption (ma)
16.0
Transmit Current Consumption (ma)
17.0
Link Budget (dbm)
104
- Current page: 310 of 380
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
25.9.1
25.10 Programming via the JTAG Interface
25.10.1
8059D–AVR–11/09
Serial Programming Characteristics
Programming Specific JTAG Instructions
For characteristics of the Serial Programming module see “SPI Timing Characteristics” on page
328.
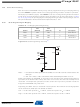
Figure 25-12. Serial Programming Waveforms
Programming through the JTAG interface requires control of the four JTAG specific pins: TCK,
TMS, TDI, and TDO. Control of the reset and clock pins is not required.
To be able to use the JTAG interface, the JTAGEN Fuse must be programmed. The device is
default shipped with the fuse programmed. In addition, the JTD bit in MCUCSR must be cleared.
Alternatively, if the JTD bit is set, the external reset can be forced low. Then, the JTD bit will be
cleared after two chip clocks, and the JTAG pins are available for programming. This provides a
means of using the JTAG pins as normal port pins in Running mode while still allowing In-Sys-
tem Programming via the JTAG interface. Note that this technique can not be used when using
the JTAG pins for Boundary-scan or On-chip Debug. In these cases the JTAG pins must be ded-
icated for this purpose.
During programming the clock frequency of the TCK Input must be less than the maximum fre-
quency of the chip. The System Clock Prescaler can not be used to divide the TCK Clock Input
into a sufficiently low frequency.
As a definition in this datasheet, the LSB is shifted in and out first of all Shift Registers.
The Instruction Register is 4-bit wide, supporting up to 16 instructions. The JTAG instructions
useful for programming are listed below.
The OPCODE for each instruction is shown behind the instruction name in hex format. The text
describes which Data Register is selected as path between TDI and TDO for each instruction.
The Run-Test/Idle state of the TAP controller is used to generate internal clocks. It can also be
used as an idle state between JTAG sequences. The state machine sequence for changing the
instruction word is shown in
SERIAL DATA OUTPUT
SERIAL CLOCK INPUT
SERIAL DATA INPUT
SAMPLE
(MOSI)
(MISO)
(SCK)
Figure 25-13 on page
MSB
MSB
311.
ATmega1284P
LSB
LSB
310
Related parts for ATmega1284RZAP
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller with 128K bytes In-system programmable flash, 8 MHz, power supply =2.7 - 5.5V
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Microcontroller with 128K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 2.4GHZ XCEIVER 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU ATMEGA644/AT86RF230 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BUNDLE ATMEGA644P/AT86RF230 QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BUNDLE ATMEGA644P/AT86RF230 TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU ATMEGA1281/AT86RF230 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU, 8BIT, AVR, 16K FLASH, 28PDIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller Modules MCU CARD BIGAVR6 100P W/ ATMEGA2560
Manufacturer:
mikroElektronika