SAM3S1A Atmel Corporation, SAM3S1A Datasheet - Page 798

SAM3S1A
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM3S1A
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of SAM3S1A
Flash (kbytes)
64 Kbytes
Pin Count
48
Max. Operating Frequency
64 MHz
Cpu
Cortex-M3
# Of Touch Channels
17
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
34
Ext Interrupts
34
Usb Transceiver
1
Quadrature Decoder Channels
1
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
3
Ssc
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
1000
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
16
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.62 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
Yes / No
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
3
Input Capture Channels
3
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- Current page: 798 of 1118
- Download datasheet (24Mb)
35.6
35.6.1
35.6.2
35.6.3
35.7
798
Product Dependencies
Bus Topology
SAM3S
I/O Lines
Power Management
Interrupt
The pins used for interfacing the High Speed MultiMedia Cards or SD Cards are multiplexed with
PIO lines. The programmer must first program the PIO controllers to assign the peripheral func-
tions to HSMCI pins.
Table 35-2.
The HSMCI is clocked through the Power Management Controller (PMC), so the programmer
must first configure the PMC to enable the HSMCI clock.
The HSMCI interface has an interrupt line connected to the Nested Vector Interrupt Controller
(NVIC).
Handling the HSMCI interrupt requires programming the NVIC before configuring the HSMCI.
Table 35-3.
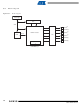
Figure 35-3. High Speed MultiMedia Memory Card Bus Topology
Instance
Instance
HSMCI
HSMCI
HSMCI
HSMCI
HSMCI
HSMCI
HSMCI
I/O Lines
Peripheral IDs
18
ID
MCCDA
MCDA0
MCDA1
MCDA2
MCDA3
Signal
MCCK
1
9 1011
2 3 4 5 6
MMC
1213 8
7
I/O Line
PA29
PA28
PA30
PA31
PA26
PA27
6500C–ATARM–8-Feb-11
Peripheral
C
C
C
C
C
C
Related parts for SAM3S1A
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
ARM-based Flash MCU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: