SAM3S1A Atmel Corporation, SAM3S1A Datasheet - Page 801

SAM3S1A
Manufacturer Part Number
SAM3S1A
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of SAM3S1A
Flash (kbytes)
64 Kbytes
Pin Count
48
Max. Operating Frequency
64 MHz
Cpu
Cortex-M3
# Of Touch Channels
17
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
34
Ext Interrupts
34
Usb Transceiver
1
Quadrature Decoder Channels
1
Usb Speed
Full Speed
Usb Interface
Device
Spi
2
Twi (i2c)
2
Uart
3
Ssc
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
12
Adc Speed (ksps)
1000
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
16
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
Yes
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
1.8/3.3
Operating Voltage (vcc)
1.62 to 3.6
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
Yes / No
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
3
Input Capture Channels
3
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- Current page: 801 of 1118
- Download datasheet (24Mb)
35.8
35.8.1
6500C–ATARM–8-Feb-11
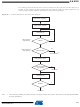
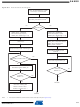
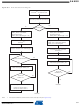
High Speed MultiMedia Card Operations
Command - Response Operation
After a power-on reset, the cards are initialized by a special message-based High Speed Multi-
Media Card bus protocol. Each message is represented by one of the following tokens:
Card addressing is implemented using a session address assigned during the initialization
phase by the bus controller to all currently connected cards. Their unique CID number identifies
individual cards.
The structure of commands, responses and data blocks is described in the High Speed MultiMe-
dia-Card System Specification. See also
High Speed MultiMediaCard bus data transfers are composed of these tokens.
There are different types of operations. Addressed operations always contain a command and a
response token. In addition, some operations have a data token; the others transfer their infor-
mation directly within the command or response structure. In this case, no data token is present
in an operation. The bits on the DAT and the CMD lines are transferred synchronous to the clock
HSMCI Clock.
Two types of data transfer commands are defined:
Both read and write operations allow either single or multiple block transmission. A multiple
block transmission is terminated when a stop command follows on the CMD line similarly to the
sequential read or when a multiple block transmission has a pre-defined block count
Transfer Operation” on page
The HSMCI provides a set of registers to perform the entire range of High Speed MultiMedia
Card operations.
After reset, the HSMCI is disabled and becomes valid after setting the MCIEN bit in the
HSMCI_CR Control Register.
The PWSEN bit saves power by dividing the HSMCI clock by 2
inactive.
The two bits, RDPROOF and WRPROOF in the HSMCI Mode Register (HSMCI_MR) allow
stopping the HSMCI Clock during read or write access if the internal FIFO is full. This will guar-
antee data integrity, not bandwidth.
All the timings for High Speed MultiMedia Card are defined in the High Speed MultiMediaCard
System Specification.
• Command: A command is a token that starts an operation. A command is sent from the host
• Response: A response is a token which is sent from an addressed card or (synchronously)
• Data: Data can be transferred from the card to the host or vice versa. Data is transferred via
• Sequential commands: These commands initiate a continuous data stream. They are
• Block-oriented commands: These commands send a data block succeeded by CRC bits.
either to a single card (addressed command) or to all connected cards (broadcast
command). A command is transferred serially on the CMD line.
from all connected cards to the host as an answer to a previously received command. A
response is transferred serially on the CMD line.
the data line.
terminated only when a stop command follows on the CMD line. This mode reduces the
command overhead to an absolute minimum.
804.).
Table 35-6 on page
802.
PWSDIV
+ 1 when the bus is
SAM3S
(See “Data
801
Related parts for SAM3S1A
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
ARM-based Flash MCU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: