DS2505 Maxim, DS2505 Datasheet - Page 18

DS2505
Manufacturer Part Number
DS2505
Description
Manufacturer
Maxim
Datasheet
1.DS2505.pdf
(24 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DS2505
Manufacturer:
ALLEGRO
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
DS2505
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DS2505P
Manufacturer:
TOS
Quantity:
1 971
Part Number:
DS2505P
Manufacturer:
DALLAS
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2505P+
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
DS2505P+T
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
DS2505P+T&R
Manufacturer:
MAXIM
Quantity:
32
Part Number:
DS2505U+
Manufacturer:
DALLAS
Quantity:
20 000
DS2505
Match ROM [55H]
The Match ROM command, followed by a 64-bit ROM sequence, allows the bus master to address a
specific DS2505 on a multidrop bus. Only the DS2505 that exactly matches the 64-bit ROM sequence
will respond to the subsequent memory function command. All slaves that do not match the 64-bit ROM
sequence will wait for a reset pulse. This command can be used with a single or multiple devices on the
bus.
Skip ROM [CCH]
This command can save time in a single-drop bus system by allowing the bus master to access the
memory functions without providing the 64-bit ROM code. If more than one slave is present on the bus
and a read command is issued following the Skip ROM command, data collision will occur on the bus as
multiple slaves transmit simultaneously (open drain pulldowns will produce a wired-AND result).
Search ROM [F0H]
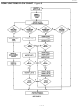
When a system is initially brought up, the bus master might not know the number of devices on the
1-Wire bus or their 64-bit ROM codes. The Search ROM command allows the bus master to use a
process of elimination to identify the 64-bit ROM codes of all slave devices on the bus. The ROM search
process is the repetition of a simple, three-step routine: read a bit, read the complement of the bit, then
write the desired value of that bit. The bus master performs this simple, three-step routine on each bit of
the ROM. After one complete pass, the bus master knows the contents of the ROM in one device. The
remaining number of devices and their ROM codes may be identified by additional passes. See Chapter 5
of the Book of DS19xx iButton Standards for a comprehensive discussion of a ROM search, including an
actual example.
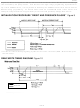
1-Wire Signaling
The DS2505 requires strict protocols to ensure data integrity. The protocol consists of five types of
signaling on one line: Reset Sequence with Reset Pulse and Presence Pulse, Write 0, Write 1, Read Data
and Program Pulse. All these signals except presence pulse are initiated by the bus master. The
initialization sequence required to begin any communication with the DS2505 is shown in Figure 9. A
reset pulse followed by a presence pulse indicates the DS2505 is ready to accept a ROM command. The
bus master transmits (TX) a reset pulse (t
, minimum 480 µs). The bus master then releases the line
RSTL
and goes into receive mode (RX). The 1-Wire bus is pulled to a high state via the pullup resistor. After
detecting the rising edge on the data pin, the DS2505 waits (t
, 15-60 µs) and then transmits the
PDH
presence pulse (t
, 60-240 µs).
PDL
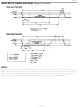
Read/Write Time Slots
The definitions of write and read time slots are illustrated in Figure 10. All time slots are initiated by the
master driving the data line low. The falling edge of the data line synchronizes the DS2505 to the master
by triggering a delay circuit in the DS2505. During write time slots, the delay circuit determines when
the DS2505 will sample the data line. For a read data time slot, if a “0” is to be transmitted, the delay
circuit determines how long the DS2505 will hold the data line low overriding the 1 generated by the
master. If the data bit is a “1”, the device will leave the read data time slot unchanged.
PROGRAM PULSE
To copy data from the 8-bit scratchpad to the EPROM Data or Status Memory, a program pulse of
12 volts is applied to the data line after the bus master has confirmed that the CRC for the current byte is
correct. During programming, the bus master controls the transition from a state where the data line is
idling high via the pullup resistor to a state where the data line is actively driven to a programming
voltage of 12 volts providing a minimum of 10 mA of current to the DS2505. This programming voltage
18 of 24