FAN4800AU Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN4800AU Datasheet - Page 13
FAN4800AU
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN4800AU
Description
The highly integrated FAN4800AU/CU parts are specially designed for power supplies that consist of boost PFC and PWM
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN4800CU.pdf
(20 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FAN4800AUM
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN4800AUN
Manufacturer:
FAIRCHILD/仙童
Quantity:
20 000
© 2011 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN4800AU/CU • Rev. 1.0.0
Functional Description
Oscillator
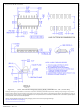
The internal oscillator frequency is determined by the
timing resistor and capacitor on the RT/CT pins as
shown in Figure 25. The frequency of the internal
oscillator is given:
Because the PWM stage generally uses a forward
converter, it is necessary to limit the maximum duty
cycle at 50%. To have a small tolerance of the
maximum duty cycle, a frequency divider with toggle
flip-flops is used, as illustrated in Figure 25. The
operation frequency of PFC and PWM stage is 1/4 of
oscillator frequency. (For FAN4800CU, the operation
frequencies for PFC and PWM stages are 1/4 and 1/2
of oscillator frequency, respectively).
The dead time for the PFC gate drive signal is
determined by:
The dead time should be smaller than 2% of the
switching period to minimize line current distortion
around the line zero crossing.
t
f
DEAD
OSC
. 0
360
56
Figure 25. Oscillator Configuration
C
T
R
Figure 26. Timing Diagram
T
C
1
T
360
C
T
(1)
(2)
13
Figure 27 shows the interleaved leading / trailing edge
modulation, where the turn-off of the PFC drive signal is
synchronized to the turn-on of the PWM drive signal.
This technique allows the PFC output diode current to
flow directly into the downstream DC/DC converter,
minimizing the current ripple of PFC output capacitor.
Gain Modulator
Gain modulator is the key block for the PFC stage
because it provides the reference to the current control
error amplifier for the input current shaping, as shown in
Figure 28. The output current of the gain modulator is a
function of V
modulator is given as a ratio between I
given V
inversely proportional to V
to implement line feed-forward. This automatically
adjusts the reference of current control error amplifier
according to the line voltage, such that the input power
of PFC converter is not changed with line voltage (as
shown in Figure 30).
V
V
G.PFC
I
G.PWM
I
DS
D
Figure 27. Interleaved Leading / Trailing
V
RMS
G.PFC
Figure 28. Gain Modulator Block
when V
EA
, I
I
D
AC,
EA
Edge Modulation
and V
is saturated to HIGH. The gain is
V
G.PWM
I
DS
RMS
RMS
2
, as shown in Figure 29,
. The gain of the gain
I
MO
G I
I
MO
AC
AC
V
and I
RMS
K V
www.fairchildsemi.com
2
(
(
V
EA
EA
AC
MAX
0.6)
with a
0.6)