FAN6921MR Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN6921MR Datasheet - Page 20
FAN6921MR
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN6921MR
Description
The highly integrated FAN6921MR combines Power Factor Correction (PFC) controller and Quasi-Resonant PWM controller
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN6921MR.pdf
(24 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
FAN6921MR
Manufacturer:
F
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
FAN6921MRMY
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
FAN6921MRMYD
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
26
© 2009 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN6921MR Rev. 1.0.2
High / Low Line Over-Power Compensation (DET Pin)
Generally, when the power switch turns off, there is a
delay time from gate signal falling edge to power switch
off. This delay is produced by an internal propagation
delay of the controller and the turn-off delay time of
PWM switch due to gate resistor and gate-source
capacitor C
voltage, this delay time produces different maximum
output power under the same PWM current limit level.
Higher input voltage generates higher maximum output
power since applied voltage on primary winding is
higher and causes higher rising slope inductor current. It
results in higher peak inductor current at the same delay
time. Furthermore, under the same output wattage, the
peak switching current at high line is lower than that at
low line. Therefore, to make the maximum output power
close at different input voltages, the controller needs to
regulate V
PWM switch current.
Referring to Figure 41, during t
switch, the input voltage is applied to primary winding
and the voltage across on auxiliary winding V
proportional to primary winding voltage. So as the input
voltage increases, the reflected voltage on auxiliary
winding V
clamps the DET pin voltage and flows out a current I
Since the current I
voltage, FAN6921MR can depend on this current I
during t
of PWM switch to perform high / low line over-power
compensation.
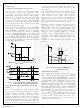
Figure 40. Measured Waveform of Valley Detection
OPWM
0V
0V
V
V
ON
AUX
DET
AUX
LIMIT
time period to regulate the current limit level
ISS
t
becomes higher as well. FAN6921MR also
OFF
Figure 39. Valley Detection
voltage of the CSPWM pin to control the
of PWM switch. At different AC input
DET
detect valley
is in accordance with V
Start to
ON
from DET pin
Idet flow out
time of the PWM
trigger Gate
Delay time
Switching
and then
signal
Valley
AUX
DET
AUX
DET
is
.
As the input voltage increases, the reflected voltage on
the auxiliary winding V
the current I
a lower level.
The R
the DET pin. Engineers can adjust this R
get proper V
characteristic curve of I
CSPWM pin is shown in Figure 42.
where V
winding; and N
Leading-Edge Blanking (LEB)
When the PFC or PWM switches are turned on, a
voltage spike is induced on the current sense resistor
due to the reciprocal effect by reverse recovery energy
of the output diode and C
prevent this spike, a leading-edge blanking time is built-
in to FAN6921MR and a small RC filter is also
recommended between the CSPWM pin and GND (e.g.
100Ω, 470pF).
I
20
DET
Figure 41. Relationship between V
DET
Figure 42. I
IN
V
resistor is connected from auxiliary winding to
is input voltage; N
IN
DET
LIMIT
P
and the controller regulates the V
N N
is turn number of primary winding.
voltage to fit power system needs. The
A
DET
Current vs. V
Characteristic Curve
P
AUX
DET
current vs. V
becomes higher as well as
OSS
R
A
DET
is turn number of auxiliary
of power MOSFET. To
LIMIT
AUX
LIMIT
Voltage
DET
www.fairchildsemi.com
and V
voltage on
resistor to
LIMIT
IN
(1)
to