ML4824-2 Fairchild Semiconductor, ML4824-2 Datasheet - Page 8
ML4824-2
Manufacturer Part Number
ML4824-2
Description
The ML4824 is a controller for power factor corrected, switched mode power supplies
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.ML4824-1.pdf
(15 pages)
ML4824
3. The output of the voltage error amplifier, VEAO. The
The output of the gain modulator is a current signal, in the
form of a full wave rectified sinusoid at twice the line
frequency. This current is applied to the virtual-ground
(negative) input of the current error amplifier. In this way
the gain modulator forms the reference for the current error
loop, and ultimately controls the instantaneous current draw
of the PFC from the power line. The general form for the
output of the gain modulator is:
More exactly, the output current of the gain modulator is
given by:
where K is in units of V
Note that the output current of the gain modulator is limited
to 200µA.
Current Error Amplifier
The current error amplifier’s output controls the PFC duty
cycle to keep the average current through the boost inductor
a linear function of the line voltage. At the inverting input to
the current error amplifier, the output current of the gain
modulator is summed with a current which results from a
negative voltage being impressed upon the I
(current into I
voltage on I
in the PFC circuit, and is typically derived from a current
sense resistor in series with the negative terminal of the input
bridge rectifier. In higher power applications, two current
transformers are sometimes used, one to monitor the I
the boost MOSFET(s) and one to monitor the I
diode. As stated above, the inverting input of the current
error amplifier is a virtual ground. Given this fact, and the
arrangement of the duty cycle modulator polarities internal
to the PFC, an increase in positive current from the gain
modulator will cause the output stage to increase its duty
cycle until the voltage on I
cancel this increased current. Similarly, if the gain modula-
tor’s output decreases, the output duty cycle will decrease, to
achieve a less negative voltage on the I
Cycle-By-Cycle Current Limiter
The I
feedback loop, is a direct input to the cycle-by-cycle current
limiter for the PFC section. Should the input voltage at this
pin ever be more negative than -1V, the output of the PFC
will be disabled until the protection flip-flop is reset by the
clock pulse at the start of the next PFC power cycle.
8
I
I
GAINMOD
GAINMOD
gain modulator responds linearly to variations in this
voltage.
SENSE
SENSE
pin, as well as being a part of the current
SENSE
K
I
--------------------------------
AC
V
represents the sum of all currents flowing
RMS
VEAO 1.5V
VEAO
V
-1
2
SENSE
.
SENSE
–
1V
/3.5k ). The negative
is adequately negative to
I
AC
SENSE
SENSE
pin.
F
of the boost
pin
D
of
(1)
Overvoltage Protection
The OVP comparator serves to protect the power circuit
from being subjected to excessive voltages if the load should
suddenly change. A resistor divider from the high voltage
DC output of the PFC is fed to V
V
PWM section will continue to operate. The OVP comparator
has 125mV of hysteresis, and the PFC will not restart until
the voltage at V
set at a level where the active and passive external power
components and the ML4824 are within their safe operating
voltages, but not so low as to interfere with the boost voltage
regulation loop.
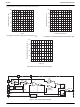
Error Amplifier Compensation
The PWM loading of the PFC can be modeled as a negative
resistor; an increase in input voltage to the PWM causes a
decrease in the input current. This response dictates the
proper compensation of the two transconductance error
amplifiers. Figure 2 shows the types of compensation
networks most commonly used for the voltage and current
error amplifiers, along with their respective return points.
The current loop compensation is returned to V
produce a soft-start characteristic on the PFC: as the
reference voltage comes up from zero volts, it creates a
differentiated voltage on IEAO which prevents the PFC
from immediately demanding a full duty cycle on its boost
converter.
There are two major concerns when compensating the
voltage loop error amplifier; stability and transient response.
Optimizing interaction between transient response and
stability requires that the error amplifier’s open-loop
crossover frequency should be 1/2 that of the line frequency,
or 23Hz for a 47Hz line (lowest anticipated international
power frequency). The gain vs. input voltage of the
OUTPUT
FB
Figure 2. Compensation Network Connections for the
PFC
exceeds 2.7V, the PFC output driver is shut down. The
15
2
4
3
Voltage and Current Error Amplifiers
I AC
V FB
V RMS
I SENSE
2.5V
FB
–
+
drops below 2.58V. The V
VEA
VEAO
MODULATOR
GAIN
16
FB
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
. When the voltage on
+
–
IEA
REV. 1.0.6 11/7/03
IEAO
FB
V REF
1
REF
should be
+
–
to