74HC14 Philips Semiconductors, 74HC14 Datasheet
74HC14
Available stocks
Related parts for 74HC14
74HC14 Summary of contents
Page 1
DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines 74HC/HCT14 Hex inverting Schmitt trigger Product specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC06 ...
Page 2
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger FEATURES Output capability: standard I category: SSI CC GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 74HC/HCT14 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL (LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC standard no. 7A. The 74HC/HCT14 provide six inverting buffers with Schmitt-trigger action. They are capable of transforming slowly changing input signals into sharply defined, jitter-free output signals ...
Page 3
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger PIN DESCRIPTION PIN NO. SYMBOL 11 10 GND Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.4 Functional diagram. September 1993 NAME AND FUNCTION data inputs data outputs ground (0 V) positive supply voltage Fig ...
Page 4
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HC For the DC characteristics see “74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications” given below. Output capability: standard I category: SSI CC Transfer characteristics for 74HC Voltages are referenced to GND (ground = 0 V) SYMBOL PARAMETER V + positive-going T threshold V negative-going T threshold ...
Page 5
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger DC CHARACTERISTICS FOR 74HCT For the DC characteristics see “74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications” given below. Output capability: standard I category: SSI CC Note to HCT types The value of additional quiescent supply current ( I To determine I per input, multiply this value by the unit load coefficient shown in the table below. ...
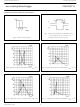
Page 6
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger TRANSFER CHARACTERISTIC WAVEFORMS Fig.6 Transfer characteristic. Fig.8 Typical HC transfer characteristics; V Fig.10 Typical HC transfer characteristics; V September 1993 Fig.7 Waveforms showing the definition and V T between limits of 20% and 70 Fig.9 Typical HC transfer characteristics ...
Page 7
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger Fig.12 Typical HCT transfer characteristics WAVEFORMS ( 50 GND HCT 1 GND Fig.13 Waveforms showing the input (nA) to output (nY) propagation delays and output transitions times. September 1993 = 5 Product specification ...
Page 8
... Philips Semiconductors Hex inverting Schmitt trigger APPLICATION INFORMATION The slow input rise and fall times cause additional power dissipation, this can be calculated using the following formula CCa f CCa CC Where additional power dissipation ( input frequency (MHz) ...