STK404-130S Sanyo Semiconductor Corporation, STK404-130S Datasheet - Page 4
STK404-130S
Manufacturer Part Number
STK404-130S
Description
1-Channel Class AB Audio Power Amplifier IC 100W
Manufacturer
Sanyo Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.STK404-130S.pdf
(5 pages)
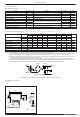
Thermal Design Example
If we define Pd, the total power dissipation on the board when this hybrid IC is in operation, the heat sink thermal
www.DataSheet4U.com
resistance, c-a, is determined as follows:
We take the power dissipation in the power transistors to be Pd evenly distributed across those N power transistors.
If we solve for c-a in equations (1) and (2), we get the following inequalities:
Values that satisfy both these inequalities at the same time are the required heat sink thermal resistance values.
Example:
For actual music signals, it is usual to use a Pd of 1/8 of P
this manner. (Note that depending on the particular safety standard used, a value somewhat different from the value of
1/8 used here may be used.)
When V
The number, N, of power transistors in the hybrid IC’s audio amplifier block is 2. Since the thermal resistance, j-c, per
transistor is 1.3°C/W, the required heat sink thermal resistance, c-a, for a guaranteed ambient temperature of 50°C will
be as follows:
Therefore, the thermal resistance that satisfies both these expressions (6,7) at the same time is 1.48°C/W.
Note that this thermal design example assumes the use of a constant-voltage power supply, and is only provided as an
example for reference purposes. Thermal designs must be tested in an actual end product.
Condition 1: The hybrid IC substrate temperature Tc must not exceed 125°C.
Condition 2: The junction temperature of each transistor must not exceed 150°C.
Pd
Ta: Guaranteed ambient temperature for the end product.
Pd
N: Number of power transistors
Pd = 47 W (when 1/8 P
From inequality (3): c-a < (125 – 50)/47=1.59 ... (6)
From inequality (4): c-a < (150 – 50)/47 – 1.3/2=1.48 ... (7)
j-c: Thermal resistance per power transistor
c-a < (125 – Ta)/Pd ... (3)
c-a < (150 – Ta)/Pd – j-c/N ... (4)
CC
= ±45V and R
c-a + Ta < 125°C ... (1)
c-a + Pd/N
L
j-c + Ta < 150°C ... (2)
= 6Ω, we get the following expression for the total power dissipation on the board, Pd:
O
max is 12.5 W) ... (5)
STK404-130S
O
max, which is the power estimated for continuous signals in
No.7730-4/5