atmega103 ATMEL Corporation, atmega103 Datasheet - Page 109

atmega103
Manufacturer Part Number
atmega103
Description
Atmega103 8-bit With 128k Bytes Of In-system Programmable Flash
Manufacturer
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet
1.ATMEGA103.pdf
(141 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
atmega103-6AC
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
1
Company:
Part Number:
atmega103-6AI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
586
- Current page: 109 of 141
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
Programming the EEPROM
0945I–AVR–02/07
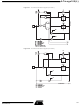
Figure 74. Programming the Flash Waveforms (Continued)
The programming algorithm for the EEPROM data memory is as follows (refer to “Pro-
gramming the Flash” on page 107 for details on command, address and data loading):
1. A: Load Command “0001 0001”.
2. H: Load Address High Byte ($00 - $0F).
3. B: Load Address Low Byte ($00 - $FF).
4. E: Load Data Low Byte ($00 - $FF).
L: Write Data Low Byte.
1. Set BS to “0”. This selects low data.
2. Give WR a negative pulse. This starts programming of the data byte. RDY/BSY
3. Wait until RDY/BSY goes high to program the next byte.
(See Figure 75 for signal waveforms.)
The loaded command and address are retained in the device during programming. For
efficient programming, the following should be considered:
•
•
•
These considerations also apply to Flash, EEPROM and signature bytes reading.
goes low.
The command needs only be loaded once when writing or reading multiple memory
locations.
Address High Byte needs only be loaded before programming a new 256-word page
in the EEPROM.
Skip writing the data value $FF that is the contents of the entire EEPROM after a
chip erase.
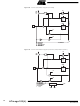
RDY/BSY
RESET
PAGEL
XTAL1
DATA
XA1
XA0
BS1
BS2
WR
OE
+12V
DATA HIGH
ATmega103(L)
109
Related parts for atmega103
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
U6046BREAR WINDOW HEATING TIMER / LONG-TERM TIMER
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: