p89lpc930fdh NXP Semiconductors, p89lpc930fdh Datasheet
p89lpc930fdh
Available stocks
Related parts for p89lpc930fdh
p89lpc930fdh Summary of contents
Page 1
P89LPC930/931 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core 4 kB Flash with 256-byte data RAM Rev. 05 — 15 December 2004 1. General description The P89LPC930/931 are single-chip microcontrollers designed for applications demanding high-integration, low cost solutions over ...
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Low voltage reset (Brownout detect) allows a graceful system shutdown when power fails. May optionally be configured as an interrupt. Oscillator Fail Detect. The watchdog timer has a separate fully on-chip oscillator allowing it to perform an oscillator ...
Page 3
... Philips Semiconductors 3. Ordering information Table 1: Type number P89LPC930FDH P89LPC931FDH 3.1 Ordering options Table 2: Type number P89LPC930FDH P89LPC931FDH 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core Ordering information Package Name Description TSSOP28 plastic thin shrink small outline package; 28 leads; body width 4.4 mm TSSOP28 plastic thin shrink small outline package ...
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors 4. Block diagram CODE FLASH CONFIGURABLE I/Os CONFIGURABLE I/Os CONFIGURABLE I/Os CONFIGURABLE I/Os PROGRAMMABLE OSCILLATOR DIVIDER CRYSTAL CONFIGURABLE OR RESONATOR Fig 1. Block diagram. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core HIGH PERFORMANCE ACCELERATED ...
Page 5
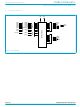
Philips Semiconductors 5. Pinning information 5.1 Pinning Fig 2. DIP28 pin configuration. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core handbook, halfpage P2 P2 KBIO/CMP2/ ...
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors 5.2 Pin description Table 3: Pin description Symbol Pin Type P0.0 - P0.7 3, 26, 25, I/O 24, 23, 22 ...
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Table 3: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin Type [1] P1.0 - P1.7 18, 17, 12, I/O, I 11 I/O I ...
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Table 3: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin Type P2 13, I/O 14, 15, 16, 27 I/O 2 I/O 13 I/O I/O 14 I/O I I/O I/O 27 I/O ...
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Table 3: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin Type P3 I [1] Input/Output for P1.0-P1.4, P1.6, P1.7. Input for P1.5. ...
Page 10
Philips Semiconductors 6. Logic symbol KBI0 CMP2 KBI1 CIN2B KBI2 CIN2A KBI3 CIN1B KBI4 CIN1A KBI5 CMPREF KBI6 CMP1 KBI7 T1 CLKOUT XTAL2 XTAL1 Fig 3. Logic symbol. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core V ...
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors 7. Special function registers Remark: Special Function Registers (SFRs) accesses are restricted in the following ways: • User must not attempt to access any SFR locations not defined. • Accesses to any defined SFR locations must be strictly ...
Page 12
Table 4: Special function registers * indicates SFRs that are bit addressable. Name Description SFR addr. Bit address ACC* Accumulator E0H AUXR1 Auxiliary function register A2H Bit address B* B register F0H ...
Page 13
Table 4: Special function registers …continued * indicates SFRs that are bit addressable. Name Description SFR addr. I2SCLH Serial clock generator/SCL DDH duty cycle register HIGH I2SCLL Serial clock generator/SCL DCH duty ...
Page 14
Table 4: Special function registers …continued * indicates SFRs that are bit addressable. Name Description SFR addr. P0M1 Port 0 output mode 1 84H P0M2 Port 0 output mode 2 85H P1M1 ...
Page 15
Table 4: Special function registers …continued * indicates SFRs that are bit addressable. Name Description SFR addr. TAMOD Timer 0 and 1 auxiliary mode 8FH Bit address TCON* Timer 0 and 1 ...
Page 16
Philips Semiconductors 8. Functional description Remark: Please refer to the P89LPC930/931 User’s Manual for a more detailed functional description. 8.1 Enhanced CPU The P89LPC930/931 uses an enhanced 80C51 CPU which runs at 6 times the speed of standard 80C51 devices. ...
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors the minimum specified operating voltage. When using an oscillator frequency above 12 MHz, in some applications, an external brownout detect circuit may be required to hold the device in reset when V specified operating voltage. 8.2.6 Clock output ...
Page 18
Philips Semiconductors Fig 4. Block diagram of oscillator control. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core XTAL1 High freq. Med. freq. XTAL2 Low freq. OSCCLK RC OSCILLATOR (7.3728 MHz) WATCHDOG OSCILLATOR (400 kHz) PCLK TIMER 0 ...
Page 19
Philips Semiconductors 8.6 CPU CLock (CCLK) wake-up delay The P89LPC930/931 has an internal wake-up timer that delays the clock until it stabilizes depending to the clock source used. If the clock source is any of the three crystal selections (low, ...
Page 20
Philips Semiconductors 8.10 Interrupts The P89LPC930/931 uses a four priority level interrupt structure. This allows great flexibility in controlling the handling of the many interrupt sources. The P89LPC930/931 supports 13 interrupt sources: external interrupts 0 and 1, timers 0 and ...
Page 21
Philips Semiconductors RTCF ERTC (RTCCON.1) WDOVF EA (IE0.7) TI & RI/RI Fig 5. Interrupt sources, interrupt enables, and power-down wake-up sources. 8.11 I/O ports The P89LPC930/931 has four I/O ports: Port 0, Port 1, Port 2, and Port 3. Ports ...
Page 22
Philips Semiconductors 8.11.1 Port configurations All but three I/O port pins on the P89LPC930/931 may be configured by software to one of four types on a bit-by-bit basis. These are: quasi-bidirectional (standard 80C51 port outputs), push-pull, open drain, and input-only. ...
Page 23
Philips Semiconductors Digital outputs are disabled by putting the port output into the Input-Only (high impedance) mode as described in Digital inputs on Port 0 may be disabled through the use of the PT0AD register, bits 1:5. On any reset, ...
Page 24
Philips Semiconductors 8.11.7 Additional port features After power-up, all pins are in Input-Only mode. Please note that this is different from the LPC76x series of devices. • After power-up, all I/O pins except P1.5, may be configured by software. • ...
Page 25
Philips Semiconductors 8.13.1 Idle mode Idle mode leaves peripherals running in order to allow them to activate the processor when an interrupt is generated. Any enabled interrupt source or reset may terminate Idle mode. 8.13.2 Power-down mode The Power-down mode ...
Page 26
Philips Semiconductors • External reset pin (during power- user configured via UCFG1. This option must be used for an oscillator frequency above 12 MHz.) • Power-on detect • Brownout detect • Watchdog Timer • Software reset • UART ...
Page 27
Philips Semiconductors 8.15.3 Mode 2 Mode 2 configures the Timer register as an 8-bit Counter with automatic reload. Mode 2 operation is the same for Timer 0 and Timer 1. 8.15.4 Mode 3 When Timer Mode 3 ...
Page 28
Philips Semiconductors 8.17.2 Mode 1 10 bits are transmitted (through TxD) or received (through RxD): a start bit (logic ‘0’), 8 data bits (LSB first), and a stop bit (logic ‘1’). When data is received, the stop bit is stored ...
Page 29
Philips Semiconductors 8.17.7 Break detect Break detect is reported in the status register (SSTAT). A break is detected when 11 consecutive bits are sensed LOW. The break detect can be used to reset the device and force the device into ...
Page 30
Philips Semiconductors 2 8.18 I C-bus serial interface 2 I C-bus uses two wires (SDA and SCL) to transfer information between devices connected to the bus, and it has the following features: • Bidirectional data transfer between masters and slaves. ...
Page 31
Philips Semiconductors P1.3/SDA P1.2/SCL Fig 8. I 8.19 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) LPC930/931 provides another high-speed serial communication interface - the SPI interface. SPI is a full-duplex, high-speed, synchronous communication bus with two operation modes: Master mode and Slave mode. ...
Page 32
Philips Semiconductors CPU clock DIVIDER BY 4, 16, 64, 128 SPI clock (master) SELECT SPI CONTROL SPI STATUS REGISTER SPI interrupt request Fig 9. SPI block diagram. The SPI interface has four pins: SPICLK, MOSI, MISO, and SS: • SPICLK, ...
Page 33
Philips Semiconductors 8.19.1 Typical SPI configurations Fig 10. SPI single master single slave configuration. Fig 11. SPI dual device configuration, where either can be a master or a slave. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core ...
Page 34
Philips Semiconductors Fig 12. SPI single master multiple slaves configuration. 9397 750 14472 Product data 8-bit microcontrollers with two-clock 80C51 core Master MISO 8-BIT SHIFT MOSI REGISTER SPICLK SPI CLOCK port GENERATOR port Rev. 05 — 15 December 2004 P89LPC930/931 ...
Page 35
Philips Semiconductors 8.20 Analog comparators Two analog comparators are provided on the P89LPC930/931. Input and output options allow use of the comparators in a number of different configurations. Comparator operation is such that the output is a logic 1 (which ...
Page 36
Philips Semiconductors 8.20.2 Comparator interrupt Each comparator has an interrupt flag contained in its configuration register. This flag is set whenever the comparator output changes state. The flag may be polled by software or may be used to generate an ...
Page 37
Philips Semiconductors 8.22 Watchdog timer The watchdog timer causes a system reset when it underflows as a result of a failure to feed the timer prior to the timer reaching its terminal count. It consists of a programmable 12-bit prescaler, ...
Page 38
Philips Semiconductors 8.24 Flash program memory 8.24.1 General description The P89LPC930/931 Flash memory provides in-circuit electrical erasure and programming. The Flash can be read, erased, or written as bytes. The Sector and Page Erase functions can erase any Flash sector ...
Page 39
Philips Semiconductors addition, erasing and reprogramming of user-programmable bytes including UCFG1, the Boot Status Bit, and the Boot Vector is supported. As shipped from the factory, the upper 512 bytes of user code space contains a serial In-System Programming (ISP) ...
Page 40
Philips Semiconductors the Boot Vector and Boot Status Bit. After programming the Flash, the status byte should be programmed to zero in order to allow execution of the user’s application code beginning at address 0000H. In-System Programming (ISP): removing the ...
Page 41
Philips Semiconductors 9. Limiting values [1] Table 6: Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter T operating bias ambient temperature amb(bias) T storage temperature range stg V voltage on XTAL1, XTAL2 pin to ...
Page 42
Philips Semiconductors 10. Static characteristics Table 7: DC electrical characteristics 3.6 V unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter I power supply current, ...
Page 43
Philips Semiconductors Table 7: DC electrical characteristics 3.6 V unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter V brownout trip voltage with BO BOV ...
Page 44
Philips Semiconductors 11. Dynamic characteristics Table 8: AC characteristics 3.6 V unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter f internal RC oscillator frequency ...
Page 45
Philips Semiconductors Table 8: AC characteristics …continued 3.6 V unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter t Enable lag time (Slave) SPILAG 2.0 ...
Page 46
Philips Semiconductors Table 9: AC characteristics 3.6 V, unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter f internal RC oscillator frequency RCOSC f internal ...
Page 47
Philips Semiconductors Table 9: AC characteristics …continued 3.6 V, unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter t Enable lead time (Slave) SPILEAD 3.0 ...
Page 48
Philips Semiconductors Table 9: AC characteristics …continued 3.6 V, unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter t Fall time SPIF SPI outputs (SPICLK, ...
Page 49
Philips Semiconductors SS SPICLK (CPOL = 0) (output) SPICLK (CPOL = 1) (output) MISO (input) t SPIF MOSI (output) Fig 16. SPI master timing (CPHA = 1 SPIR t SPILEAD SPICLK (CPOL = 0) (input) t SPIF SPICLK ...
Page 50
Philips Semiconductors SS t SPIR t SPILEAD SPICLK (CPOL = 0) (input) t SPIF SPICLK (CPOL = 1) (input) t SPIOH t SPIDV t SPIA MISO Not defined (output) MOSI (input) Fig 18. SPI slave timing (CPHA = 1). t ...
Page 51
Philips Semiconductors Table 10: AC characteristics, ISP entry mode 3.6 V, unless otherwise specified +85 C for industrial, unless otherwise specified. amb Symbol Parameter t RST delay from V ...
Page 52
Philips Semiconductors 13. Package outline TSSOP28: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 28 leads; body width 4 pin 1 index 1 e DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT ...
Page 53
Philips Semiconductors 14. Revision history Table 12: Revision history Rev Date CPCN Description 05 20041215 - Product data (9397 750 14472) Modification: • Added 18 MHz information. 04 20040106 - Product data (9397 750 12284); ECN 853-2406 01-A15015 dated 16 ...
Page 54
Philips Semiconductors 15. Data sheet status [1] Level Data sheet status Product status I Objective data Development II Preliminary data Qualification III Product data Production [1] Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design. ...
Page 55
Philips Semiconductors Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . ...