ATMEGA48V_11 ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation], ATMEGA48V_11 Datasheet - Page 71

ATMEGA48V_11
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA48V_11
Description
8-bit Atmel Microcontroller with 4/8/16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash
Manufacturer
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet
1.ATMEGA48V_11.pdf
(377 pages)
- Current page: 71 of 377
- Download datasheet (9Mb)
14. I/O-ports
14.1
2545T–AVR–05/11
Overview
All AVR ports have true Read-Modify-Write functionality when used as general digital I/O ports.
This means that the direction of one port pin can be changed without unintentionally changing
the direction of any other pin with the SBI and CBI instructions. The same applies when chang-
ing drive value (if configured as output) or enabling/disabling of pull-up resistors (if configured as
input). Each output buffer has symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. The pin driver is strong enough to drive LED displays directly. All port pins have indi-
vidually selectable pull-up resistors with a supply-voltage invariant resistance. All I/O pins have
protection diodes to both V
acteristics” on page 303
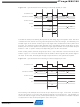
Figure 14-1. I/O pin equivalent schematic.
All registers and bit references in this section are written in general form. A lower case “x” repre-
sents the numbering letter for the port, and a lower case “n” represents the bit number. However,
when using the register or bit defines in a program, the precise form must be used. For example,
PORTB3 for bit no. 3 in Port B, here documented generally as PORTxn. The physical I/O Regis-
ters and bit locations are listed in
Three I/O memory address locations are allocated for each port, one each for the Data Register
– PORTx, Data Direction Register – DDRx, and the Port Input Pins – PINx. The Port Input Pins
I/O location is read only, while the Data Register and the Data Direction Register are read/write.
However, writing a logic one to a bit in the PINx Register, will result in a toggle in the correspond-
ing bit in the Data Register. In addition, the Pull-up Disable – PUD bit in MCUCR disables the
pull-up function for all pins in all ports when set.
Using the I/O port as General Digital I/O is described in
Most port pins are multiplexed with alternate functions for the peripheral features on the device.
How each alternate function interferes with the port pin is described in
on page
functions.
76. Refer to the individual module sections for a full description of the alternate
Pxn
for a complete list of parameters.
CC
and Ground as indicated in
C
“Register description” on page
pin
“Ports as general digital I/O” on page
"General Digital I/O" for
Figure
ATmega48/88/168
See figure
R
87.
14-1. Refer to
details
pu
Logic
“Alternate port functions”
“Electrical char-
72.
71
Related parts for ATMEGA48V_11
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Atmel CryptoMemory, 16Kbit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: