VIPEr100ASP STMicroelectronics, VIPEr100ASP Datasheet - Page 12

VIPEr100ASP
Manufacturer Part Number
VIPEr100ASP
Description
SMPS PRIMARY I.C.
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
VIPER100ASP
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
1 450
Part Number:
VIPER100ASP
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
VIPEr100ASPTR-E
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Quantity:
1 785
Company:
Part Number:
VIPEr100ASPTRE
Manufacturer:
INF
Quantity:
4 037
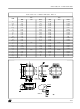
OPERATION DESCRIPTION:
CURRENT MODE TOPOLOGY:
The current mode control method, like the one
integrated in the VIPer100/100A uses two control
loops - an inner current control loop and an outer
loop for voltage control. When the Power
MOSFET output transistor is on, the inductor
current (primary side of the transformer) is
monitored with a SenseFET technique and
converted into a voltage V
current. When V
output voltage error) the power switch is switched
off. Thus, the outer voltage control loop defines
the level at which the inner loop regulates peak
current through the power switch and the primary
winding of the transformer.
Excellent open loop D.C. and dynamic line
regulation is ensured due to the inherent input
voltage feedforward characteristic of the current
mode control. This results in an improved line
regulation,
changes and better stability for the voltage
regulation loop.
Current mode topology also ensures good
limitation in the case of short circuit. During a first
phase the output current increases slowly
following the dynamic of the regulation loop. Then
it reaches
internally set and finally stops because the power
supply on V
applications the maximum peak current internally
set can be overridden by externally limiting the
voltage excursion on the COMP pin. An integrated
blanking filter inhibits the PWM comparator output
for a short time after the integrated Power
MOSFET is switched on. This function prevents
anomalous or premature termination of the
switching pulse in the case of current spikes
caused by primary side capacitance or secondary
side rectifier reverse recovery time.
STAND-BY MODE
Stand-by operation in nearly open load condition
automatically leads to a burst mode operation
allowing voltage regulation on the secondary side.
The transition from normal operation to burst
mode operation happens for a power P
by :
Where:
L
P STBY
P
is the primary inductance of the transformer.
=
1
-- - L
2
DD
instantaneous
the maximum limitation current
P
is no longer correct. For specific
I
S
2
STBY F SW
reaches V
S
COMP
correction
proportional to this
(the amplified
STBY
to
given
line
F
I
corresponding to the minimum on time that the
device is able to provide in normal operation. This
current can be computed as :
t
propagation time of the internal current sense and
comparator, and represents roughly the minimum
on time of the device. Note that P
affected by the efficiency of the converter at low
load, and must include the power drawn on the
primary auxiliary voltage.
As soon as the power goes below this limit, the
auxiliary secondary voltage starts to increase
above the 13V regulation level forcing the output
voltage of the transconductance amplifier to low
state (V
the shutdown mode where the power switch is
maintained in the off state, resulting in missing
cycles and zero duty cycle. As soon as V
back to the regulation level and the V
threshold is reached, the device operates again.
The above cycle repeats indefinitely, providing a
burst mode of which the effective duty cycle is
much lower than the minimum one when in normal
operation. The equivalent switching frequency is
also lower than the normal one, leading to a
reduced consumption on the input mains lines.
This mode of operation allows the VIPer100/100A
to meet the new German "Blue Angel" Norm with
less than 1W total power consumption for the
system when working in stand-by. The output
voltage remains regulated around the normal
level, with a low frequency ripple corresponding to
the burst mode. The amplitude of this ripple is low,
because of the output capacitors and of the low
output current drawn in such conditions.The
normal operation resumes automatically when the
power get back to higher levels than P
HIGH
SOURCE
An integrated high voltage current source provides
a bias current from the DRAIN pin during the start-
up phase. This current is partially absorbed by
internal control circuits which are placed into a
standby mode with reduced consumption and also
provided to the external capacitor connected to the
V
reaches the high voltage threshold V
UVLO logic, the device turns into active mode and
starts switching.
I STBY
STBY
b
SW
DD
+ t
is the normal switching frequency.
d
pin. As soon as the voltage on this pin
is the sum of the blanking time and of the
is the minimum controllable current,
COMP
=
VOLTAGE
--------------------------------
t
b
VIPer100/SP - VIPer100A/ASP
< V
+
L
t
d
P
COMPth
V
IN
START-UP
). This situation leads to
STBY
STBY
DDon
CURRENT
may be
DD
COMPth
.
of the
12/23
gets