MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR Micron Technology Inc, MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR Datasheet

MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR
Specifications of MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR
Related parts for MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR
MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C TR Summary of contents
Page 1
... MHz 5.4ns -75 100 MHz 6ns Part Number Example: MT48LC32M16A2P-75:C PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAMfront.fm - Rev. L 10/07 EN Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice. Options • Configurations – 128 Meg x 4 (32 Meg banks) – 64 Meg x 8 (16 Meg banks) – ...
Page 2
Table of Contents Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3
List of Figures Figure 1: 128 Meg x 4 SDRAM Functional Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
List of Tables Table 1: Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 5
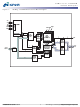
... General Description The 512Mb SDRAM is a high-speed CMOS, dynamic random-access memory containing 536,870,912 bits internally configured as a quad-bank DRAM with a synchronous interface (all signals are registered on the positive edge of the clock signal, CLK). Each of the x4’s 134,217,728-bit banks is organized as 8,192 rows by 4,096 columns by 4 bits. Each of the x8’ ...
Page 6
... A0–A12, ADDRESS 15 BA0, BA1 REGISTER PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAM.fm - Rev. L 10/ BANK0 ROW- 13 ROW- ADDRESS ADDRESS MUX MEMORY 8192 LATCH & (8,192 x 4,096 x 4) DECODER SENSE AMPLIFIERS I/O GATING 2 DQM MASK LOGIC BANK READ DATA LATCH CONTROL WRITE DRIVERS LOGIC 2 ...
Page 7
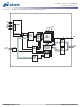
... A0–A12, ADDRESS 15 BA0, BA1 REGISTER PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAM.fm - Rev. L 10/ BANK0 ROW- 13 ROW- ADDRESS ADDRESS MUX MEMORY 8192 LATCH & (8,192 x 2,048 x 8) DECODER SENSE AMPLIFIERS I/O GATING 2 DQM MASK LOGIC BANK READ DATA LATCH CONTROL WRITE DRIVERS LOGIC 2 ...
Page 8
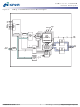
... A0–A12, ADDRESS 15 BA0, BA1 REGISTER PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAM.fm - Rev. L 10/ BANK0 ROW- 13 ROW- ADDRESS ADDRESS MUX MEMORY 8192 LATCH & (8,192 x 1,024 x 16) DECODER SENSE AMPLIFIERS I/O GATING 2 DQM MASK LOGIC BANK READ DATA LATCH CONTROL WRITE DRIVERS LOGIC 2 ...
Page 9
Figure 4: Pin Assignment (Top View) 54-Pin TSOP DQ0 - DQ1 - Note: The # symbol ...
Page 10
... A0–A12) and READ/WRITE command (column-address A0–A9, A11, A12 [x4]; A0– A9, A11 [x8]; A0–A9 [x16]; with A10 defining auto precharge) to select one location out of the memory array in the respective bank. A10 is sampled during a PRECHARGE command to determine whether all banks are to be precharged (A10 [HIGH]) or bank selected by (A10 [LOW]) ...
Page 11
Functional Description The 512Mb SDRAMs (32 Meg banks, 16 Meg banks, and 8 Meg banks) are quad-bank DRAMs that operate at 3.3V and include a synchronous interface (all ...
Page 12
Wait at least given. All banks will complete their precharge, thereby placing the device in the all banks idle state. 8. Issue an AUTO REFRESH command. 9. Wait at least are allowed. 10. Issue an AUTO REFRESH command. 11. ...
Page 13
Register Definition Mode Register The mode register is used to define the specific mode of operation of the SDRAM. This definition includes the selection of BL, a burst type, CL, an operating mode, and a write burst mode, as shown ...
Page 14
Figure 5: Mode Register Definition A12 12 Reserved Write Burst Mode M9 0 Programmed burst length 1 Single location access M8 M7 M6- Defined – – – Notes: 1. Should program M12, M11, M10 = “0, 0, 0” ...
Page 15
Table 4: Burst Definition Burst Length Full page (y) Notes: 1. For full-page accesses 4,096 (x4 2,048 (x8 1,024 (x16). 2. For A1–A9, A11, A12 (x4); A1–A9, A11 ...
Page 16
DQs will start driving after T1 and the data will be valid by T2, as shown in Figure 6. Table 5 indicates the operating frequencies at which each CL setting can be used. ...
Page 17
Commands Table 6 provides a quick reference of available commands. This is followed by a written description of each command. Three additional Truth Tables appear in the Operations section, beginning on page 35; these tables provide current state/next state information. ...
Page 18
... WRITE burst; if auto precharge is not selected, the row will remain open for subsequent accesses. Input data appearing on the DQs is written to the memory array subject to the DQM input logic level appearing coincident with the data given DQM signal is registered LOW, the corresponding data will be written to memory ...
Page 19
Auto Precharge Auto precharge is a feature that performs the same individual-bank PRECHARGE func- tion described above, without requiring an explicit command. This is accomplished by using A10 to enable auto precharge in conjunction with a specific READ or WRITE ...
Page 20
The procedure for exiting self refresh requires a sequence of commands. First, CLK must be stable (stable clock is defined as a signal cycling within timing constraints specified for the clock pin) prior to CKE going back HIGH. When CKE ...
Page 21
Figure 8: Example Meeting CLK COMMAND READs READ bursts are initiated with a READ command, as shown in Figure 9. The starting column and bank addresses are provided with the READ command, and auto precharge either is enabled or disabled ...
Page 22
Figure 10: CAS Latency COMMAND COMMAND Upon completion of a burst, assuming no other commands have been initiated, the DQs will go High-Z. A full-page burst will continue until terminated (at the end of the page, it will wrap to ...
Page 23
Figure 11: Consecutive READ Bursts COMMAND ADDRESS COMMAND ADDRESS Note: Each READ command may be to any bank. DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAM.fm - Rev. L 10/ CLK READ NOP NOP NOP BANK, ...
Page 24
Figure 12: Random READ Accesses COMMAND ADDRESS COMMAND ADDRESS Note: Each READ command may be to any bank. DQM is LOW. Data from any READ burst may be truncated with a subsequent WRITE command, and data from a fixed-length READ ...
Page 25
The DQM signal must be de-asserted prior to the WRITE command (DQM latency is zero clocks for input buffers) to ensure that the written data is not masked. Figure 13 shows the case where the clock frequency allows for bus ...
Page 26
CL; data element either the last of a burst of four or the last desired of a longer burst. Following the PRECHARGE command, a subsequent command to the same bank cannot be issued until ...
Page 27
Figure 16: Terminating a READ Burst COMMAND ADDRESS COMMAND ADDRESS Note: DQM is LOW. PDF: 09005aef809bf8f3/Source: 09005aef80818a4a 512MbSDRAM.fm - Rev. L 10/ CLK READ NOP NOP BANK, COL n D OUT ...
Page 28
WRITEs WRITE bursts are initiated with a WRITE command, as shown in Figure 17. The starting column and bank addresses are provided with the WRITE command, and auto precharge is either enabled or disabled for that access. If auto precharge ...
Page 29
Figure 18: WRITE Burst COMMAND ADDRESS Note DQM is LOW. Data for any WRITE burst may be truncated with a subsequent READ command, and data for a fixed-length WRITE burst may be immediately followed by a READ ...
Page 30
Figure 20: Random WRITE Cycles COMMAND ADDRESS Note: Each WRITE command may be to any bank. DQM is LOW. Figure 21: WRITE-to-READ COMMAND ADDRESS Note: The WRITE or READ commands may be to any bank. DQM is LOW. Data for ...
Page 31
PRECHARGE command is that it requires that the command and address buses be available at the appropriate time to issue the command; the advantage of the PRECHARGE command is that it can be used to truncate fixed-length or full-page ...
Page 32
Figure 23: Terminating a WRITE Burst COMMAND ADDRESS Note: DQMs are LOW. PRECHARGE The PRECHARGE command shown in Figure 24 is used to deactivate the open row in a particular bank or the open row in all banks. The bank(s) ...
Page 33
Power-Down Power-down occurs if CKE is registered LOW coincident with a NOP or COMMAND INHIBIT when no accesses are in progress. If power-down occurs when all banks are idle, this mode is referred to as precharge power-down; if power-down occurs ...
Page 34
Figure 26: CLOCK SUSPEND During WRITE Burst INTERNAL CLOCK COMMAND ADDRESS Note greater LOW. Figure 27: CLOCK SUSPEND During READ Burst INTERNAL CLOCK COMMAND ADDRESS Note greater. ...
Page 35
Concurrent Auto Precharge An access command to (READ or WRITE) another bank while an access command with auto precharge enabled is executing is not allowed by SDRAMs, unless the SDRAM supports concurrent auto precharge. Micron SDRAMs support concurrent auto precharge. ...
Page 36
Figure 29: READ with Auto Precharge Interrupted by a WRITE CLK COMMAND BANK n Internal States BANK m ADDRESS 1 DQM DQ Notes: 1. DQM is HIGH prevent D WRITE with Auto Precharge • Interrupted by a ...
Page 37
Figure 31: WRITE with Auto Precharge Interrupted by a WRITE CLK COMMAND BANK n Internal States BANK m ADDRESS DQ Note: DQM is LOW. Table 7: Truth Table 2 – CKE Notes 1–4 apply to entire table; notes appear below ...
Page 38
Table 8: Truth Table 3 – Current State Bank n, Command to Bank n Notes: 1–6 apply to entire table; notes appear below and on next page Current State CS# RAS# CAS# Any Idle ...
Page 39
The following states must not be interrupted by any executable command; COMMAND INHIBIT or NOP commands must be applied on each positive clock edge during these states. Accessing mode Precharging all: Starts with registration of a PRECHARGE ALL command ...
Page 40
Table 9: Truth Table 4 – Current State Bank n, Command to Bank m Notes 1–6 apply to entire table; notes appear below and on next page Current State CS# RAS# Any Idle X X Row ...
Page 41
A BURST TERMINATE command cannot be issued to another bank; it applies to the bank represented by the current state only. 6. All states and sequences not shown are illegal or reserved. 7. READs or WRITEs to bank m ...
Page 42
Electrical Specifications Stresses greater than those listed may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of ...
Page 43
Table 11: Temperature Limits Parameter Operating case temperature: Commercial Industrial Junction temperature: Commercial Industrial Ambient temperature: Commercial Industrial Peak reflow temperature Notes: 1. MAX operating case temperature, T side of the device, as shown on page 47. 2. Device functionality ...
Page 44
Table 13: DC Electrical Characteristics And Operating Conditions Notes 1, 5, and 6 apply to entire table; notes appear on page 47; V Parameter/Condition Supply voltage Input high voltage: Logic 1; All inputs Input low voltage: Logic 0; All inputs ...
Page 45
Table 16: Electrical Characteristics and Recommended AC Operating Conditions Notes and 11 apply to entire table; notes appear on page 47 AC Characteristics Parameter Access time from CLK (positive edge) Address hold time Address setup ...
Page 46
Table 17: AC Functional Characteristics Notes and 11 apply to entire table; notes appear below Parameter READ/WRITE command-to-READ/WRITE command CKE to clock disable or power-down entry mode CKE to clock enable or power-down exit setup ...
Page 47
Notes 1. All voltages referenced This parameter is sampled. V biased at 1.4V with minimum cycle time and the outputs open. 4. Enables on-chip refresh and address counters. 5. The minimum specifications are used ...
Page 48
V IH cannot be greater than one-third of the cycle rate pulse width ≤ 3ns for all inputs pulse width ≤ 3ns, and the pulse width cannot be greater than one-third of the cycle rate. ...
Page 49
Timing Diagrams Figure 33: Initialize and Load Mode Register CKH t CKS ( ( ) ) CKE ( ( ) ) t CMS t CMH t CMS t CMH ( ...
Page 50
Figure 34: Power-Down Mode T0 CLK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, A11, A12 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ Precharge all active ...
Page 51
Figure 35: Clock Suspend Mode CLK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND READ NOP t CMS t CMH DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, 2 COLUMN m A11, ...
Page 52
Figure 36: Auto-Refresh Mode T0 CLK t CK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE DQM / DQML, DQMH A0–A9, A11, A12 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ ...
Page 53
Figure 37: Self Refresh Mode T0 CLK t CK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, A11,A12 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ Precharge ...
Page 54
Figure 38: READ – Without Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ROW ...
Page 55
Figure 39: READ – With Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ENABLE ...
Page 56
Figure 40: Single READ – Without Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ...
Page 57
Figure 41: Single READ – With Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, A12 ROW ROW ...
Page 58
Figure 42: Alternating Bank Read Accesses CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ENABLE AUTO ...
Page 59
Figure 43: READ – Full-Page Burst CLK CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, COLUMN m 2 ...
Page 60
Figure 44: READ DQM Operation CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ...
Page 61
Figure 45: WRITE – Without Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, COLUMN m 2 ROW ...
Page 62
Figure 46: WRITE – With Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, ROW COLUMN A11, A12 ...
Page 63
Figure 47: Single WRITE – Without Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ...
Page 64
Figure 48: Single WRITE with Auto Precharge CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH NOP 4 COMMAND ACTIVE DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 t AS ...
Page 65
Figure 49: Alternating Bank WRITE Accesses CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 t AS ...
Page 66
Figure 50: WRITE – Full-Page Burst CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMH A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ROW A10 ...
Page 67
Figure 51: WRITE – DQM Operation CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM/ DQML, DQMU A0–A9, ROW A11, A12 ROW A10 ...
Page 68
Package Dimensions Figure 52: 54-Pin Plastic TSOP (400 mil) 22.22 ±0.08 0.80 TYP 0.375 ±0.075 PIN #1 ID LEAD FINISH: TIN/LEAD PLATE PLASTIC PACKAGE MATERIAL: EPOXY NOVOLAC PACKAGE WIDTH AND LENGTH DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSION. ALLOWABLE PROTRUSION IS 0.25 ...